Abstract
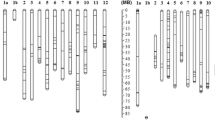
Trichomes are differentiated epidermal cells and can be found on above ground organs of nearly all land plants. Results from previous studies show that trichomes play important roles against a wide range of both biotic and abiotic stresses. By examining differences between parental genotypes of available populations, we identified a population of recombinant inbred lines showing clear segregation for trichome density and length. Assessing the F8 lines of the population growing in the field detected a major locus on chromosome arm 4BL. This locus was detected based the assessments of either fully expanded third leaves or flag leaves after anthesis. Based on the position of the QTL, an SSR marker was used to identify heterozygous plants at this locus from F5 lines derived from the same cross for the F8 population. Three pairs of near isogenic lines targeting this locus were obtained from these heterozygous plants. Difference in trichome length between the two lines with opposite alleles for each of these NIL pairs were similar to that between the two parental genotypes for the mapping populations, confirming that this single locus is mainly responsible for the trichome characteristics measured in this study. The allele with long and dense trichome is dominant as this characteristic was shown by the heterozygous individuals at this marker locus. Apart from the targeted locus, NIL pairs have highly homogeneous genetic backgrounds. Thus, the NILs could be invaluable in understanding the relationship between trichome density and resistance or tolerance to various biotic and abiotic stresses.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Atwell S, Huang YS, Vilhjalmsson BJ, Willems G, Horton M, Li Y, Meng DZ, Platt A, Tarone AM, Hu TT, Jiang R, Muliyati NW, Zhang X, Amer MA, Baxter I, Brachi B, Chory J, Dean C, Debieu M, de Meaux J, Ecker JR, Faure N, Kniskern JM, Jones JDG, Michael T, Nemri A, Roux F, Salt DE, Tang C, Todesco M, et al. (2010) Genome-wide association study of 107 phenotypes in Arabidopsis thaliana inbred lines. Nature. 465: 627–631. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature08800
Bickford CP (2016) Ecophysiology of leaf trichomes. Funct Plant Biol 43:807–814. https://doi.org/10.1071/FP16095
Blanco A, Bellomo MP, Cenci A, De Giovanni C, D’Ovidio R, Iacono E, Laddomada B, Pagnotta MA, Porceddu E, Sciancalepore A, Simeone R, Tanzarella OA (1998) A genetic linkage map of durum wheat. Theor Appl Genet 97:721–728. https://doi.org/10.1007/s001220050948
Dobrovolskaya O, Pshenichnikova TA, Arbuzova VS, Lohwasser U, Ro¨der MS, Bo¨rner A (2007) Molecular mapping of genes determining hairy leaf character in common wheat with respect to other species of the Triticeae. Euphytica 155:285–293. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-006-9329-7
Doroshkov AV, Konstantinov DK, Afonnikov DA, Gunbin KV (2019) The evolution of gene regulatory networks controlling Arabidopsis thaliana L. trichome development. BMC Plant Biol 19:53. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-019-1640-2
Ehleringer J (1982) The influence of water stress and temperature on leaf pubescence development in Encelia farinose. Am J Bot 69:670–675. https://doi.org/10.1002/j.1537-2197.1982.tb13306.x
Galdon-Armero J et al (2018) The ratio of trichomes to stomata is associated with water use efficiency in Solanum lycopersicum (tomato). Plant J 96(3):607–619. https://doi.org/10.1111/tpj.14055
Gao S, Zheng Z, Hu H, Jiang Y, Liu M, Stiller J, Zhou M, Liu C (2020) Delineating a locus conferring Fusarium crown rot resistance on chromosome arm 1HL in barley by developing and analysing a large population derived from near isogenic lines. Crop J. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cj.2020.03.008
Ghorashy SR, Pendleton JW, Bernard RL, Bauer ME (1971) Effect of leaf pubescence on transpiration, photosynthetic rate and seed yield of three near-isogenic lines of soybeans. Crop Sci 11:426–427. https://doi.org/10.2135/cropsci1971.0011183X001100030035x
Handley R, Ekbom B, Ågren J (2005) Variation in trichome density and resistance against a specialist insect herbivore in natural populations of Arabidopsis thaliana. Ecol Entomol 30:284–292. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.0307-6946.2005.00699.x
Hauser MT (2014) Molecular basis of natural variation and environmental control of trichome patterning. Front Plant Sci 5:320. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2014.00320
Hoxie RP, Wellso SG, Webster JA (1975) Cereal leaf beetle response to wheat Trichome length and density. Environ Entomol 4:365–370. https://doi.org/10.1093/ee/4.3.365
Imboden L et al (2018) Surface interactions of Fusarium graminearum on barley. Mol Plant Pathol 19:1332–1342. https://doi.org/10.1111/mpp.12616
Jiang Y, Habib A, Zheng Z, etc LC (2019) Development of tightly linked markers and identification of candidate genes for Fusarium crown rot resistance in barley by exploiting a near-isogenic line-derived population. Theor Appl Genet 132:217–225. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-018-3209-0
Khlestkina EK, Pestsova EG, Salina E, Röder MS, Arbuzova VS, Koval SF, Börner A (2002) Genetic mapping and tagging of wheat genes using RAPD, STS and SSR markers. Cell Mol Biol Lett 7:795–802
Kivimaki M, Karkkainen K, Gaudeul M, Loe G, Agren J (2007) Gene, phenotype and function: GLABROUS1 and resistance to herbivory in natural populations of Arabidopsis lyrata. Mol Ecol 16:453–462. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-294X.2007.03109.x
Konrad W, Burkhardt J, Ebner M, Roth-Nebelsick A (2014) Leaf pubescence as a possibility to increase water use efficiency by promoting condensation. Ecohydrology 8:480–492. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-294X.2007.03109.x
Larkin JC, Young N, Prigge M, Marks MD (1996) The control of trichome spacing and number in Arabidopsis. Development 122:997–1005
Levin DA (1973) The role of Trichomes in plant defense. Q Rev Biol 48:3–15
Li HB, Zhou MX, Liu CJ (2009) A major QTL conferring crown rot resistance in barley and its association with plant height. Theor Appl Genet 118:903–910. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-008-0948-3
Li WL, Challa GS, Zhu HL, Wei WJ (2016) Recurrence of chromosome rearrangements and reuse of DNA breakpoints in the evolution of the triticeae genomes. G3 Genes|Genomes|Genetics 6(12):3837–3847
Liu CJ, Atkinson MD, Chinoy CN, Devos KM, Gale MD (1992) Non-homoeologous translocations between group 4, 5 and 7 chromosomes within wheat and rye. Theor Appl Genet 83:305–312. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00224276
Liu YX, Yang XM, Ma J, Wei YM, Zheng YL, Ma HX, Yao JB, Manners JM, Liu CJ (2010) Plant height affects crown rot severity in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Phytopathology 100:1276–1281. https://doi.org/10.1094/PHYTO-05-10-0142
Luo W, Ma J, Zhou X-H et al (2016) Genetic analysis of glume hairiness (hg) gene in bread wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Genet Resour Crop Ev 63:763–769. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10722-016-0393-0
Luo W, Liu J, Liu C, Lan X, Ma J et al. (2020) Transcriptome analysis of near-isogenic lines for glume hairiness of wheat. Gene 739: 144517. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gene.2020.144517
Ma J, Yan GJ, Liu CJ (2012) Development of near-isogenic lines for a major QTL on 3BL conferring Fusarium crown rot resistance in hexaploid wheat. Euphytica 183:147–152. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-011-0414-1
Ma J, Stiller J et al (2013) Sequence-based analysis of translocations and inversions in bread wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). PLoS One 8(11):e79329. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0079329
Ma J, Stiller J, Zheng Z et al (2015) A high-throughput pipeline for detecting locus-specific polymorphism in hexaploid wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Plant Methods 11(1)
Marks M.D (1997) Molecular genetic analysis of trichome development in Arabidopsis. Ann Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mole Biology, 48:137–163. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.arplant.48.1.137
Mauricio R (2005) Ontogenetics of QTL: the genetic architecture of trichome density over time in Arabidopsis thaliana. Genetica 123:75–85. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10709-002-2714-9
Maystrenko OI (1976) Identification and location of genes controlling leaf hairing in young plants of common wheat. Genetika 12:5–15
Murray M, Thompson WF (1980) Rapid isolation of high molecular weight plant DNA. Nucleic Acids Res 8(19):4321–4326. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/8.19.4321
Paterson AH, Lander ES, Hewitt JD, Peterson S, Linoln SE, Tanksley SD (1988) Resolution of quantitative traits into Mendelian factors by using a complete linkage map of restriction fragment length polymorphisms. Nature 335:721–736. https://doi.org/10.1038/335721a0
Richards RA (1996) Defining selection criteria to improve yield under drought. Plant Growth Regul 20:57–166. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00024012
Roberts JJ, Gallun RL, Patterson FL, Foster JE (1979) Effects of wheat leaf pubescence on the hessian fly. J Econ Entomol 72:211–214. https://doi.org/10.1093/jee/72.2.211
Schillinger JA, Gallun RL (1968) Leaf pubescence of wheat as a deterrent to the cereal leaf beetle, Oulema melanopus. Ann Entomol Soc Am 61(4):900–903. https://doi.org/10.1093/aesa/61.4.900
Somers DJ, Isaac P, Edwards KA (2004) High-density microsatellite consensus map for bread wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Theor Appl Genet 109:1105–1114. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-004-1740-7
Symonds VV, Godoy AV, Alconada T, Botto JF, Juenger TE, Casal JJ, Lloyd AM (2005) Mapping quantitative trait loci in multiple populations of Arabidopsis thaliana identifies natural allelic variation for trichome density. Genetics 169:1649–1658. https://doi.org/10.1534/genetics.104.031948
Szymanski DB (2005) Breaking the WAVE complex: the point of Arabidopsis trichomes. Curr Opin Plant Biol 8:103–112
Taketa S, Chang CL, Ishii M, Takeda K (2002) Chromosome arm location of the gene controlling leaf pubescence of a Chinese local wheat cultivar ‘Hong-Mang-mai’. Euphytica 125:141–147. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1015812907111
Traw MB, Bergelson J (2003) Interactive effects of jasmonic acid, salicylic acid, and gibberellin on induction of trichomes in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 133:1367–1375. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.103.027086
Tuinstra MR, Ejeta G, Goldsbrough PB (1997) Heterogeneous inbred family (HIF) analysis: a method for developing near-isogenic lines that differ at quantitative trait loci. Theor Appl Genet 95:1005–1011. https://doi.org/10.1007/s001220050654
Van Ooijen JW (2004) MapQTLH 5. Software for the mapping of quantitative trait loci in experimental populations Kyazma BV. Wageningen
Van Ooijen JW (2006) JointMap 4. Software for the calculation of genetic linkage maps in experimental populations Kyazma BV. Wageningen, The Netherlands
Voorrips RE (2002) MapChart: software for the graphical presentation of linkage maps and QTLs. J Hered 93:77–78. https://doi.org/10.1093/jhered/93.1.77
Wan H, Yang Y, Li J, Zhang Z, Yang W (2015) Mapping a major QTL for hairy leaf sheath introgressed from Aegilops tauschii and its association with enhanced grain yield in bread wheat. Euphytica 205:275–285. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-015-1457-5
Wellso SG, Hoxie RP (1982) The influence of environment on the expression of Trichomes in wheat. Crop Sci 22:879–886. https://doi.org/10.2135/cropsci1982.0011183X002200040043x
Yan W, Li HB, Cai SB, Ma HX, Rebetzke GJ, Liu CJ (2011) Effects of plant height vary with type I and type II resistance of Fusarium head blight in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Plant Pathol 60:506–512. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-3059.2011.02426.x
Zhang H, Wu K, Wang YF et al. (2012) A WUSCHEL-like homeobox gene, OsWOX3B responses to NUDA/GL locus in rice. Rice 5:30. https://doi.org/10.1186/1939-84333-5-30
Zheng Z, Kilian A, Yan G, Liu C (2014) QTL conferring Fusarium crown rot resistance in the elite bread wheat variety EGA Wylie. PLoS ONE 9(4):e96011. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0096011
Zheng Z, Ma J, Stiller J et al (2015) Fine mapping of a large-effect QTL conferring Fusarium crown rot resistance on the long arm of chromosome 3B in hexaploid wheat. BMC Genomics 16(1):850
Acknowledgements
Work reported here was supported by the Innovation Research Team Building Project of Agricultural Ecology from Fujian Academy of Agricultural Sciences (Project code: STIT2017-1-9) and the Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Organization (CSIRO), Australia (Project code: R-04818). ZTC is grateful to the Young Talent Program of Fujian Academy of Agricultural Sciences (YC2016-7) for funding his visit to CSIRO Agriculture & Food in Australia. WL and HZ are grateful to the Sichuan Agricultural University and the China Scholarship Council for supports during the tenures of their PhD candidature. The authors are also grateful to Caritta Eliasson for her invaluable technical assistance and the two anonymous reviewers for their help in improving the manuscript.
Funding
This study was funded by the Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Organization (CSIRO), Australia (Project code: R-10191-01), the Young Talent Program of Fujian Academy of Agricultural Sciences (YC2016–7).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
ZTC, ZYY and CJL conceived the study; ZTC, ZZ, WL and HZ conducted experiments and analysed data; ZTC and CJL prepared the manuscript with contributions from all other authors.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
ESM 1
(DOCX 188 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, Z., Zheng, Z., Luo, W. et al. Detection of a major QTL conditioning trichome length and density on chromosome arm 4BL and development of near isogenic lines targeting this locus in bread wheat. Mol Breeding 41, 10 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-021-01201-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-021-01201-8