Abstract
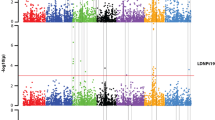
Blackleg disease caused by the fungus Leptosphaeria maculans is one of the most devastating diseases of Brassica napus. Association mapping was used to evaluate the response of 139 B. napus accessions originated from 16 countries with 4 growth habit types to inoculation with L. maculans isolates from pathogenicity group 4. All accessions were inoculated at the seedling stage and 37,346 single nucleotide polymorphism markers based upon genotyping-by-sequencing were used for analysis. One major QTL associated with the blackleg disease was identified on chromosome A01 at 9.66 Mbp and explains about 14.7 % of phenotypic variation (p value <2.2E−05). Orthologs of Arabidopsis thaliana hydroxyproline-rich glycoprotein family protein, acyl-CoA oxidase 1 and cysteine-/histidine-rich C1 domain family protein that are involved in plant defense mechanism were identified in this QTL region. At a lower significance (p value <0.00139), thirty-five additional markers were identified which are located on 13 other chromosomes. Stepwise regression identified that these markers belong to ten QTL regions and together explain 51.04 % of phenotypic variations. Additional twenty orthologs of A. thaliana disease resistance genes, transcription factors, genes in phytohormone pathway and signaling in plant defense pathway have been identified to be associated with the blackleg disease. Based on the haplotype at the most significant QTL, a total of 22 genotypes were evaluated in the greenhouse. As expected with the haplotype, we had 100 % success in predicting the phenotype. These markers could further be used for identification of phenotype that can be used in the breeding program.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andreasson E, Jenkins T, Brodersen P, Thorgrimsen S, Petersen NHT et al (2005) The MAP kinase substrate MKS1 is a regulator of plant defense responses. EMBO J 24:2579–2589
Arruda MP, Brown P, Brown-Guedira G, Krill AM, Thurber C et al (2016) Genome-wide association mapping of Fusarium head blight resistance in wheat using genotyping-by-sequencing. Plant Genome 9:1–14
Bansal VK, Kharbanda PD, Stringam GR, Thiagarajah MR, Tewari JP (1994) A comparison of greenhouse and field screening methods for blackleg resistance in double haploid lines of Brassica napus. Plant Dis 78:276–281
Bradbury PJ, Zhang Z, Kroon DE, Casstevens TM, Ramdoss Y, Buckler ES (2007) TASSEL: software for association mapping of complex traits in diverse samples. Bioinformatics 23:2633–2635
Bradley CA (2005) First report of pathogenicity groups 3 and 4 of Leptosphaeria maculans on Canola in North Dakota. Plant Dis 89:776
Brosche M, Blomster T, Salojarvi J, Cui F, Sipari N et al (2014) Transcriptomics and functional genomics of ROS-induced cell death regulation by RADICAL-INDUCED CELL DEATH1. Plos Genet 10(2):e1004112
Brun H, Levivier S, Somda I, Ruer D, Renard M, Chevre AM (2000) A field method for evaluating the potential durability of new resistance sources: application to the Leptosphaeria maculans Brassica napus pathosystem. Phytopathology 90:961–966
Cargeeg LA, Thurling N (1980) Contribution of host-pathogen interactions to the expression of the blackleg disease of spring rape (Brassica napus L.) caused by Leptosphaeria-maculans (DESM) Ces Et De Not. Euphytica 29:465–476
Chalhoub B, Denoeud F, Liu S, Parkin IAP, Tang H et al (2014) Early allopolyploid evolution in the post-Neolithic Brassica napus oilseed genome. Science 345:950–953
Chen Y, Fernando WGD (2005) First report of canola blackleg caused by pathogenicity group 4 of Leptosphaeria maculans in Manitoba. Plant Dis 89:339
Corbin DR, Sauer N, Lamb CJ (1987) Differential regulation of a hydroxyproline-rich glycoprotein gene family in wounded and infected plants. Mol Cell Biol 7:4337–4344
de Torres-Zabala M, Truman W, Bennett MH, Lafforgue G, Mansfield JW et al (2007) Pseudomonas syringae pv. tomato hijacks the Arabidopsis abscisic acid signalling pathway to cause disease. EMBO J 26:1434–1443
del Rio Mendoza LE, Nepal A, Markell S (2012) Outbreak of blackleg in canola in North Dakota is caused by new pathogenicity groups. Plant Health Prog. doi:10.1094/PHP-2012-0410-01-RS
Delourme R, Pilet-Nayel ML, Archipiano M, Horvais R, Tanguy X et al (2004) A cluster of major specific resistance genes to Leptosphaeria maculans in Brassica napus. Phytopathology 94:578–583
Delourme R, Chevre AM, Brun H, Rouxel T, Balesdent MH et al (2006a) Major gene and polygenic resistance to Leptosphaeria maculans in oilseed rape (Brassica napus). Eur J Plant Pathol 114:41–52
Delourme R, Falentin C, Huteau V, Clouet V, Horvais R et al (2006b) Genetic control of oil content in oilseed rape (Brassica napus L.). Theor Appl Genet 113:1331–1345
Delourme R, Piel N, Horvais R, Pouilly N, Domin C et al (2008) Molecular and phenotypic characterization of near isogenic lines at QTL for quantitative resistance to Leptosphaeria maculans in oilseed rape (Brassica napus L.). Theor Appl Genet 117:1055–1067
Despres C, Chubak C, Rochon A, Clark R, Bethune T et al (2003) The Arabidopsis NPR1 disease resistance protein is a novel cofactor that confers redox regulation of DNA binding activity to the basic domain/leucine zipper transcription factor TGA1. Plant Cell 15:2181–2191
Elshire RJ, Glaubitz JC, Sun Q, Poland JA, Kawamoto K et al (2011) A robust, simple genotyping-by-sequencing (GBS) approach for high diversity species. Plos One 6:e19379
Eulgem T, Somssich IE (2007) Networks of WRKY transcription factors in defense signaling. Curr Opin Plant Biol 10:366–371
Ferreira ME, Rimmer SR, Williams PH, Osborn TC (1995) Mapping loci controlling Brassica napus resistance to Leptosphaeria-maculans under different screening conditions. Phytopathology 85:213–217
Fitt BDL, Brun H, Barbetti MJ, Rimmer SR (2006) World-wide importance of phoma stem canker (Leptosphaeria maculans and L. biglobosa) on oilseed rape (Brassica napus). Eur J Plant Pathol 114:3–15
Flor H (1971) The current status of the gene-for-gene concept. Annu Rev Phytopathol 9:275–296
Franceschi J, del Rio L (2014) Characterization of virulence of different pathogenicity groups of Leptosphaeria maculans on Brassica napus L. Phytopathology 104:42
Gajardo HA, Wittkop B, Soto-Cerda B, Higgins EE, Parkin IAP et al (2015) Association mapping of seed quality traits in Brassica napus L. using GWAS and candidate QTL approaches. Mol Breed 35:143
Goff KE, Ramonell KM (2007) The role and regulation of receptor-like kinases in plant defense. Gene Regul Syst Biol 1:167–175
Gurung S, Mamidi S, Bonman JM, Xiong M, Brown-Guedira G, Adhikari TB (2014) Genome-wide association study reveals novel quantitative trait loci associated with resistance to multiple leaf spot diseases of spring wheat. Plos One 9(9):e108179
Hansen M, Kraft T, Ganestam S, Sall T, Nilsson NO (2001) Linkage disequilibrium mapping of the bolting gene in sea beet using AFLP markers. Genet Res 77:61–66
Henderson MP (1918) The black-leg disease of cabbage caused by Phoma lingam (Tode) Desmaz. Phytopathology 8:379–431
Hind SR, Pulliam SE, Veronese P, Shantharaj D, Nazir A et al (2011) The COP9 signalosome controls jasmonic acid synthesis and plant responses to herbivory and pathogens. Plant J 65:480–491
Hong EP, Park JW (2012) Sample size and statistical power calculation in genetic association studies. Genom Inform 10:117–122
Honsdorf N, Becker HC, Ecke W (2010) Association mapping for phenological, morphological, and quality traits in canola quality winter rapeseed (Brassica napus L.). Genome 53:899–907
Howlett BJ (2004) Current knowledge of the interaction between Brassica napus and Leptosphaeria maculans. Can J Plant Pathol Revue Canadienne De Phytopathologie 26:245–252
Hwang IS, Choi DS, Kim NH, Kim DS, Hwang BK (2014) The pepper cysteine/histidine-rich DC1 domain protein CaDC1 binds both RNA and DNA and is required for plant cell death and defense response. New Phytol 201:518–530
Ishiga Y, Ishiga T, Uppalapati SR, Mysore KS (2013) Jasmonate ZIM-domain (JAZ) protein regulates host and nonhost pathogen-induced cell death in tomato and Nicotiana benthamiana. Plos One 8(9):e75728
Jestin C, Lode M, Vallee P, Domin C, Falentin C et al (2011) Association mapping of quantitative resistance for Leptosphaeria maculans in oilseed rape (Brassica napus L.). Mol Breeding 27:271–287
Jia L, Yan W, Zhu C, Agrama HA, Jackson A et al (2012) Allelic analysis of sheath blight resistance with association mapping in rice. Plos One 7(3):e32703
Kaur S, Cogan NOI, Ye G, Baillie RC, Hand ML et al (2009) Genetic map construction and QTL mapping of resistance to blackleg (Leptosphaeria maculans) disease in Australian canola (Brassica napus L.) cultivars. Theor Appl Genet 120:71–83
Kraakman ATW, Niks RE, Van den Berg P, Stam P, Van Eeuwijk FA (2004) Linkage disequilibrium mapping of yield and yield stability in modern spring barley cultivars. Genetics 168:435–446
Langer SM, Longin CFH, Würschum T (2014) Flowering time control in European winter wheat. Front Plant Sci 5:537
Lee SJ, Lee MY, Yi SY, Sang KH, Choi SH et al (2002) PPI1: a novel pathogen-induced basic region-leucine zipper (bZIP) transcription factor from pepper. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 15:540–548
Li H, Sivasithamparam K, Barbetti MJ (2003) Breakdown of a Brassica rapa subsp sylvestris single dominant blackleg resistance gene in B. napus rapeseed by Leptosphaeria maculans field isolates in Australia. Plant Dis 87:752
Li H, Smyth F, Barbetti MJ, Sivasithamparam K (2006) Relationship between Brassica napus seedling and adult plant responses to Leptosphaeria maculans is determined by plant growth stage at inoculation and temperature regime. Field Crops Res 96:428–437
Li X, Yan W, Agrama H, Jia L, Shen X et al (2011) Mapping QTLs for improving grain yield using the USDA rice mini-core collection. Planta 234:347–361
Liu J, Wang W, Mei D, Wang H, Fu L et al (2016) Characterizing variation of branch angle and genome-wide association mapping in rapeseed (Brassica napus L.). Front Plant Sci 7:21
Mamidi S, Chikara S, Goos RJ, Hyten DL, Annam D et al (2011) Genome-wide association analysis identifies candidate genes associated with iron deficiency chlorosis in soybean. Plant Genome 4:154–164
Mamidi S, Lee RK, Goos JR, McClean PE (2014) Genome-wide association studies identifies seven major regions responsible for iron deficiency chlorosis in soybean (Glycine max). Plos One 9(9):e107469
Marino DA, del Rio LE (2010) Screening of plant introduction materials from Brassica species for resistance against PG3 and PG4 isolates of blackleg. Phytopathology 100:S77–S78
Marone D, Russo MA, Laido G, De Leonardis AM, Mastrangelo AM (2013) Plant nucleotide binding site-leucine-rich repeat (NBS-LRR) genes: active guardians in host defense responses. Int J Mol Sci 14:7302–7326
McHale L, Tan XP, Koehl P, Michelmore RW (2006) Plant NBS-LRR proteins: adaptable guards. Genome Biol 7:212. doi:10.1186/gb-2006-7-4-212
Mengistu A, Rimmer SR, Koch E, Williams PH (1991) Pathogenicity grouping of isolates of Leptosphaeria-maculans on Brassica napus cultivars and their disease reaction profiles on rapid-cycling Brassicas. Plant Dis 75:1279–1282
Nepal A, Markell S, Knodel J, Bradley CA, Mendoza LEdR (2014) Prevalence of blackleg and pathogenicity groups of Leptosphaeria maculans in North Dakota. Plant Dis 98:328–335
Petre B, Major I, Rouhier N, Duplessis S (2011) Genome-wide analysis of eukaryote thaumatin-like proteins (TLPs) with an emphasis on poplar. BMC Plant Biol 11:33. doi:10.1186/1471-2229-11-33
Pilet ML, Delourme R, Foisset N, Renard M (1998) Identification of loci contributing to quantitative field resistance to blackleg disease, causal agent Leptosphaeria maculans (Desm.) Ces. et de Not., in Winter rapeseed (Brassica napus L.). Theor Appl Genet 96:23–30
Poland JA, Endelman J, Dawson J, Rutkoski J, Wu S et al (2012) Genomic selection in wheat breeding using genotyping-by-sequencing. Plant Genomes 5:103–113
Price AL, Zaitlen NA, Reich D, Patterson N (2010) New approaches to population stratification in genome-wide association studies. Nat Rev Genet 11:459–463
Quirino BF, Normanly J, Amasino RM (1999) Diverse range of gene activity during Arabidopsis thaliana leaf senescence includes pathogen-independent induction of defense-related genes. Plant Mol Biol 40:267–278
Raman H, Raman R, Taylor B, Lindbeck K, Coombes N et al (2011) Blackleg resistance in rapeseed: phenotypic screen, molecular markers and genome wide linkage and association mapping. 17th Australian Research Assembly on Brassicas (ARAB), Wagga Wagga, NSW, Australia
Raman R, Taylor B, Marcroft S, Stiller J, Eckermann P et al (2012) Molecular mapping of qualitative and quantitative loci for resistance to Leptosphaeria maculans causing blackleg disease in canola (Brassica napus L.). Theor Appl Genet 125:405–418
Raman H, Raman R, Larkan N (2013) Genetic dissection of blackleg resistance loci in rapeseed (Brassica napus L.). In: Andersen SB (ed) Plant breeding from laboratories to fields. InTech, Rijeka, pp 85–120
Rezaeizad A, Wittkop B, Snowdon R, Hasan M, Mohammadi V et al (2011) Identification of QTLs for phenolic compounds in oilseed rape (Brassica napus L.) by association mapping using SSR markers. Euphytica 177:335–342
Robles LM, Wampole JS, Christians MJ, Larsen PB (2007) Arabidopsis enhanced ethylene response 4 encodes an EIN3-interacting TFIID transcription factor required for proper ethylene response, including ERF1 induction. J Exp Bot 58:2627–2639
Roux M, Schwessinger B, Albrecht C, Chinchilla D, Jones A et al (2011) The Arabidopsis leucine-rich repeat receptor-like kinases BAK1/SERK3 and BKK1/SERK4 are required for innate immunity to hemibiotrophic and biotrophic pathogens. Plant Cell 23:2440–2455
Rouxel T, Penaud A, Pinochet X, Brun H, Gout L et al (2003) A 10-year survey of populations of Leptosphaeria maculans in France indicates a rapid adaptation towards the Rlm1 resistance gene of oilseed rape. Eur J Plant Pathol 109:871–881
Saal B, Struss D (2005) RGA- and RAPD-derived SCAR markers for a Brassica B-genome introgression conferring resistance to blackleg in oilseed rape. Theor Appl Genet 111:281–290
Schilmiller AL, Koo AJK, Howe GA (2007) Functional diversification of acyl-coenzyme A oxidases in jasmonic acid biosynthesis and action. Plant Physiol 143:812–824
Sosnowski MR, Scott ES, Ramsey MD (2004) Infection of Australian canola cultivars (Brassica napus) by Leptosphaeria maculans is influenced by cultivar and environmental conditions. Australas Plant Pathol 33:401–411
Stephan S, Mamidi S, Lee R, McKain MR, McClean PE et al (2016) Optimization of genotyping by sequencing (GBS) data in common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.). Mol Breeding 36:1–9
ten Hove CA, de Jong M, Lapin D, Andel A, Sanchez-Perez GF et al (2011) Trans-repression of gene activity upstream of T-DNA tagged RLK902 links Arabidopsis root growth inhibition and downy mildew resistance. Plos One 6(4):e19028
van Damme M, Huibers RP, Elberse J, Van den Ackerveken G (2008) Arabidopsis DMR6 encodes a putative 2OG-Fe(II) oxygenase that is defense-associated but required for susceptibility to downy mildew. Plant J 54:785–793
van den Burg HA, Takken FLW (2010) SUMO-, MAPK-, and resistance protein-signaling converge at transcription complexes that regulate plant innate immunity. Plant Signal Behav 5:1597–1601
West JS, Kharbanda PD, Barbetti MJ, Fitt BDL (2001) Epidemiology and management of Leptosphaeria maculans (phoma stem canker) on oilseed rape in Australia, Canada and Europe. Plant Pathol 50:10–27
Williams P (1985) The crucifer genetics cooperative. Plant Mol Biol Rep 3:129–144
Wu Y (2008) Association mapping of complex diseases with ancestral recombination graphs: models and efficient algorithms. J Comput Biol 15:667–684
Yang KY, Liu YD, Zhang SQ (2001) Activation of a mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway is involved in disease resistance in tobacco. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:741–746
Yu JM, Pressoir G, Briggs WH, Bi IV, Yamasaki M et al (2006) A unified mixed-model method for association mapping that accounts for multiple levels of relatedness. Nat Genet 38:203–208
Zeng LR, Vega-Sanchez ME, Zhu T, Wang GL (2006) Ubiquitination-mediated protein degradation and modification: an emerging theme in plant-microbe interactions. Cell Res 16:413–426
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge the financial support for this project from the National Institute of Food and Agriculture (under North Central Region Canola Research Grants), Northern Canola Growers’ Association and Centre of Excellence for Agro-biotechnology for Oilseed Development, State of North Dakota, USA.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rahman, M., Mamidi, S., del Rio, L. et al. Association mapping in Brassica napus (L.) accessions identifies a major QTL for blackleg disease resistance on chromosome A01. Mol Breeding 36, 90 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-016-0513-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-016-0513-8