Abstract
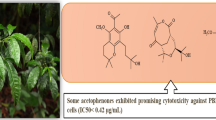
Celangulin V is a natural β-dihydroagarofuran derivative isolated from Celastrus angulatus which shows insecticidal activity in many agricultural pests. Using celangulin V as a molecular probe, we find out a new pesticide target: subunit H of V-ATPase. To explore the potential application of this novel target, lead sulfonamides have been found through virtual screening. Combined with the previous work, 46 sulfonamide derivatives are designed and synthesized. All target compounds are first screened for their insecticidal activities against Mythimna separata. The results of bioassay reveal that most of the designed compounds exhibit significant insecticidal activities against third-instar larvae of M. separata under the concentration of 10 mg/mL, and compound 8.4 shows the highest activity with LC50 value of 1.72 mg/mL, 15-fold smaller than that of celangulin V (25.89 mg/mL). Molecular docking results further indicated that compound 8.4 might serve as a potential inhibitor of the subunit H of V-ATPase. This study provides a potential sulfonamide candidate compound for the M. separata control.
Graphical abstract





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Verger PJP, Boobis AR (2013) Reevaluate pesticides for food security and safety. Science 341:717–718. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1241572
Fritsche J (2018) Recent developments and digital perspectives in food safety and authenticity. J Agric Food Chem 66:7562–7567. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.8b00843
Tilman D, Balzer C, Hill J, Befort BL (2011) Global food demand and the sustainable intensification of agriculture. Proc Natl Acad Sci 108:20260–20264. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1116437108
Tudi M, Daniel Ruan H, Wang L et al (2021) Agriculture development, pesticide application and its impact on the environment. Int J Environ Res Public Health 18:1112. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18031112
Urech PA, Staub T, Voss G (1997) Review: Resistance as a concomitant of modern crop protection. Pestic Sci 51:227–234. https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1096-9063(199711)51:3%3c227::AID-PS646%3e3.0.CO;2-X
Shaw DR, Asmus AB, Schroeder J, Ervin DE (2023) Changing the paradigm for pesticide resistance management. Pest Manag Sci 79:4726–4730
Bretschneider T, Benet-Buchholz J, Fischer R, Nauen R (2003) Spirodiclofen and spiromesifen—novel acaricidal and insecticidal tetronic acid derivatives with a new mode of action. Chimia 57:697. https://doi.org/10.2533/000942903777678588
Li S, Lv M, Li T et al (2021) Spirodiclofen ether derivatives: semisynthesis, structural elucidation, and pesticidal activities against Tetranychus cinnabarinus Boisduval, Aphis citricola Van der Goot and Mythimna separata Walker. Pest Manag Sci 77:2395–2402. https://doi.org/10.1002/ps.6267
Lahm GP, Cordova D, Barry JD (2009) New and selective ryanodine receptor activators for insect control. Bioorg Med Chem 17:4127–4133. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmc.2009.01.018
Zhao Y, Xu L, Tong J et al (2012) Synthesis, crystal structure and biological activity of novel anthranilic diamide insecticide containing alkyl ether group. Mol Divers 16:711–725. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11030-012-9406-x
Hayashi N, Sasama Y, Takahashi N, Ikemi N (2013) Cyflumetofen, a novel acaricide—its mode of action and selectivity. Pest Manag Sci 69:1080–1084. https://doi.org/10.1002/ps.3470
Morita M, Ueda T, Yoneda T et al (2007) Flonicamid, a novel insecticide with a rapid inhibitory effect on aphid feeding. Pest Manag Sci 63:969–973. https://doi.org/10.1002/ps.1423
Jeanmart S, Edmunds AJF, Lamberth C, Pouliot M (2016) Synthetic approaches to the 2010–2014 new agrochemicals. Bioorg Med Chem 24:317–341
Chio EH, Li QX (2022) Pesticide research and development: general discussion and spinosad case. J Agric Food Chem 70:8913–8919. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.2c03821
Yang C, Li X, Wei J et al (2018) Synthesis and insecticidal activity in vitro and vivo of novel benzenesulfonyl derivatives based on potent target subunit H of V-ATPase. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 28:3164–3167. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmcl.2018.08.030
Gang F, Li X, Yang C et al (2020) Synthesis and insecticidal activity evaluation of virtually screened phenylsulfonamides. J Agric Food Chem 68:11665–11671. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.0c02153
Liguori A, Sindona G, Romeo G, Uccella N (1987) Direct conversion of hydroxamic acids into nitriles. Synthesis 1987:168–168. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-1987-27874
Zhao W-Y, Yang C-F, Han L-J et al (2022) Design, synthesis, and insecticidal activities of propargyloxy-naphthalene-sulfonamide derivatives. J Asian Nat Prod Res 24:361–370. https://doi.org/10.1080/10286020.2021.1925254
Qi Z, Xue X, Wu W et al (2006) Preparation of monoclonal antibody against celangulin V and immunolocalization of receptor in the oriental armyworm, Mythimna separata Walker (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). J Agric Food Chem 54:7600–7605. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf060890n
Lu L, Qi Z, Zhang J, Wu W (2015) Separation of binding protein of celangulin V from the midgut of mythimna separata Walker by affinity chromatography. Toxins 7:1738–1748. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins7051738
Wang Y, Zhang J, Feng M et al (2017) Insight into the mode of action of celangulin V on the transmembrane potential of midgut cells in lepidopteran larvae. Toxins 9:393. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins9120393
Jumper J, Evans R, Pritzel A et al (2021) Highly accurate protein structure prediction with AlphaFold. Nature 596:583–589. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-021-03819-2
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China [Grant No. 21977083].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
HQ,·TG, JZ, and YH planned and performed the experiments with advice from ·WW, JZ, and KY. HQ wrote the manuscript with the help from CW.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Qian, H., Guo, T., Zhang, J. et al. Diversifying the benzenesulfonamide scaffold for potential V-ATPase inhibitors: synthesis and insecticidal activity evaluation. Mol Divers (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11030-023-10800-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11030-023-10800-w