Abstract
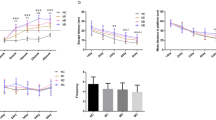
Vitamin D3 deficiency is associated with an increased risk of dementia. An association between vitamin D3 deficiency and subjective cognitive complaints in geriatric patients has been previously reported. This study aimed to evaluate the effects of two doses of vitamin D3 on spatial memory (using the Radial Maze) and cytokine levels [tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), interleukin-1β (IL-1β), interleukin-6 (IL-6), and interleukin-10 (IL-10)] on 2-, 6-, 13-, 22-, and 31-month-old male Wistar rats. Animals were supplemented with vitamin D3 at doses of 42 IU/kg and 420 IU/kg for 21 days. A radial maze test was performed to evaluate spatial memory. After the behavioral test, the frontal cortex and hippocampus were dissected for enzyme immunoassay analyses to measure the cytokine levels (TNFα, IL-1β, IL-6, and IL-10). Our results showed that vitamin D3 supplementation reversed spatial memory impairment at the supplemented doses (42 and 420 IU/kg) in 6-, 13-, and 22-month-old animals and at a dose of 420 IU/kg in 31-month-old animals. The lower dose (42 IU/kg) regulates both pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokines mainly in the frontal cortex. Our results suggest that vitamin D3 has a modulatory action on pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokines, since older animals showed increased cytokine levels compared to 2-month-old animals, and that vitamin D3 may exert an immunomodulatory effect on aging.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable.
Code availability
Not applicable.
References
Al-Harbi AN, Khan KM, Rahman A (2017) Developmental vitamin D deficiency affects spatial learning in wistar rats. J Nutr 147(9):1795–1805
Annweiler C, Allali G, Allain P, Bridenbaugh S, Schott AM, Kressig RW, Beauchet O (2009) Vitamin D and cognitive performance in adults: a systematic review. Eur J Neurol 16(10):1083–1089
Annweiler C, Montero-Odasso M, Llewellyn DJ, Richard-Devantoy S, Duque G, Beauchet O (2013) Meta-analysis of memory and executive dysfunctions in relation to vitamin D. Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease : JAD 37(1):147–171
Barter J, Kumar A, Bean L, Ciesla M, Foster TC (2021) Adulthood systemic inflammation accelerates the trajectory of age-related cognitive decline. Aging (Albany NY) 13(18):22092–22108
Briones TL, Darwish H (2012) Vitamin D mitigates age-related cognitive decline through the modulation of pro-inflammatory state and decrease in amyloid burden. J Neuroinflammation 9:244
Camara ML, Corrigan F, Jaehne EJ, Jawahar MC, Anscomb H, Koerner H, Baune BT (2013) TNF-α and its receptors modulate complex behaviours and neurotrophins in transgenic mice. Psychoneuroendocrinology 38(12):3102–3114
Casaccia-Bonnefil P, Pandozy G, Mastronardi F (2008) Evaluating epigenetic landmarks in the brain of multiple sclerosis patients: a contribution to the current debate on disease pathogenesis. Prog Neurobiol 86(4):368–378
Cheng J, Rui Y, Qin L, Xu J, Han S, Yuan L, Yin X, Wan Z (2017) Vitamin D combined with resveratrol prevents cognitive decline in SAMP8 mice. Curr Alzheimer Res 14(8):820–833
Collin C, Assmann KE, Deschasaux M, Andreeva VA, Lemogne C, Charnaux N, Sutton A, Hercberg S, Galan P, Touvier M, Kesse-Guyot E (2016) Plasma vitamin D status and recurrent depressive symptoms in the French SU.VI.MAX cohort. Europ J Nutri
Davinelli S, Maes M, Corbi G, Zarrelli A, Willcox DC, Scapagnini G (2016) Dietary phytochemicals and neuro-inflammaging: from mechanistic insights to translational challenges. Immunity Ageing 13:16
del Rey A, Balschun D, Wetzel W, Randolf A, Besedovsky HO (2013) A cytokine network involving brain-borne IL-1β, IL-1ra, IL-18, IL-6, and TNFα operates during long-term potentiation and learning. Brain Behav Immun 33:15–23
Dellu F, Fauchey V, Le Moal M, Simon H (1997) Extension of a new two-trial memory task in the rat: influence of environmental context on recognition processes. Neurobiol Learn Mem 67(2):112–120
Dougherty KA, Dilisio MF, Agrawal DK (2016) Vitamin D and the immunomodulation of rotator cuff injury. J Inflamm Res 9:123–131
Esiri MM (2007) Ageing and the brain. J Pathol 211(2):181–187
Foyet HS, Hritcu L, Ciobica A, Stefan M, Kamtchouing P, Cojocaru D (2011) Methanolic extract of Hibiscus asper leaves improves spatial memory deficits in the 6-hydroxydopamine-lesion rodent model of Parkinson’s disease. J Ethnopharmacol 133(2):773–779
Franceschi C, Campisi J (2014) Chronic inflammation (inflammaging) and its potential contribution to age-associated diseases. J Gerontol Ser A, Biol Sci Med Sci 69(Suppl 1):S4-9
Franceschi C, Bonafe M, Valensin S, Olivieri F, De Luca M, Ottaviani E, De Benedictis G (2000) Inflamm-aging. An evolutionary perspective on immunosenescence. Ann N Y Acad Sci 908:244–254
Goshen I, Kreisel T, Ounallah-Saad H, Renbaum P, Zalzstein Y, Ben-Hur T, Levy-Lahad E, Yirmiya R (2007) A dual role for interleukin-1 in hippocampal-dependent memory processes. Psychoneuroendocrinology 32(8–10):1106–1115
Gruver AL, Hudson LL, Sempowski GD (2007) Immunosenescence of ageing. J Pathol 211(2):144–156
Heidary M, Rakhshi N, Pahlevan Kakhki M, Behmanesh M, Sanati MH, Sanadgol N, Kamaladini H, Nikravesh A (2014) The analysis of correlation between IL-1B gene expression and genotyping in multiple sclerosis patients. J Neurol Sci 343(1–2):41–45
Hritcu L, Cioanca O, Hancianu M (2012) Effects of lavender oil inhalation on improving scopolamine-induced spatial memory impairment in laboratory rats. Phytomedicine 19(6):529–534
Hubackova S, Krejcikova K, Bartek J, Hodny Z (2012) Interleukin 6 signaling regulates promyelocytic leukemia protein gene expression in human normal and cancer cells. J Biol Chem 287(32):26702–26714
Khairova RA, Machado-Vieira R, Du J, Manji HK (2009) A potential role for pro-inflammatory cytokines in regulating synaptic plasticity in major depressive disorder. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 12(4):561–578
Latimer CS, Brewer LD, Searcy JL, Chen KC, Popovic J, Kraner SD, Thibault O, Blalock EM, Landfield PW, Porter NM (2014) Vitamin D prevents cognitive decline and enhances hippocampal synaptic function in aging rats. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 111(41):E4359-4366
Lee JY, Kho S, Yoo HB, Park S, Choi JS, Kwon JS, Cha KR, Jung HY (2014) Spatial memory impairments in amnestic mild cognitive impairment in a virtual radial arm maze. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat 10:653–660
Li AJ, Katafuchi T, Oda S, Hori T, Oomura Y (1997) Interleukin-6 inhibits long-term potentiation in rat hippocampal slices. Brain Res 748(1–2):30–38
Littlejohns TJ, Henley WE, Lang IA, Annweiler C, Beauchet O, Chaves PH, Fried L, Kestenbaum BR, Kuller LH, Langa KM, Lopez OL, Kos K, Soni M, Llewellyn DJ (2014) Vitamin D and the risk of dementia and Alzheimer disease. Neurology 83(10):920–928
Llewellyn DJ, Langa KM, Lang IA (2009) Serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D concentration and cognitive impairment. J Geriatr Psychiatry Neurol 22(3):188–195
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ (1951) Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193(1):265–275
Minciullo PL, Catalano A, Mandraffino G, Casciaro M, Crucitti A, Maltese G, Morabito N, Lasco A, Gangemi S, Basile G (2016) Inflammaging and anti-inflammaging: The role of cytokines in extreme longevity. Arch Immunol Ther Exp 64(2):111–126
Mora-Gallegos A, Rojas-Carvajal M, Salas S, Saborio-Arce A, Fornaguera-Trias J, Brenes JC (2015) Age-dependent effects of environmental enrichment on spatial memory and neurochemistry. Neurobiol Learn Mem 118:96–104
Nossov S, Dines JS, Murrell GA, Rodeo SA, Bedi A (2014) Biologic augmentation of tendon-to-bone healing: scaffolds, mechanical load, vitamin D, and diabetes. Instr Course Lect 63:451–462
Pang Q, Qi X, Jiang Y, Wang O, Li M, Xing X, Dong J, Xia W (2016) Clinical and genetic findings in a Chinese family with VDR-associated hereditary vitamin D-resistant rickets. Bone Research 4:16018
Paxinos G, Watson C (1998) The rat brain in stereotaxic coordinates. Academic Press, San Diego
Phillips PM, Jarema KA, Kurtz DM, MacPhail RC (2010) An observational assessment method for aging laboratory rats. J Am Assoc Lab Anim Sci 49(6):792–799
Prattichizzo F, De Nigris V, La Sala L, Procopio AD, Olivieri F, Ceriello A (2016) “Inflammaging” as a druggable target: A senescence-associated secretory phenotype-centered view of type 2 diabetes. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2016:1810327
Simpson RJ, Hammacher A, Smith DK, Matthews JM, Ward LD (1997) Interleukin-6: structure-function relationships. Protein Sci 6(5):929–955
Soni M, Kos K, Lang IA, Jones K, Melzer D, Llewellyn DJ (2012) Vitamin D and cognitive function. Scand J Clin Lab Investig Suppl 243:79–82
Tonelli LH, Postolache TT (2005) Tumor necrosis factor alpha, interleukin-1 beta, interleukin-6 and major histocompatibility complex molecules in the normal brain and after peripheral immune challenge. Neurol Res 27(7):679–684
Tot Babberich Ede N, Gourdeau C, Pointel S, Lemarchant B, Beauchet O, Annweiler C (2015) Biology of subjective cognitive complaint amongst geriatric patients: vitamin D involvement. Curr Alzheimer Res 12(2):173–178
Vilela TC, Muller AP, Damiani AP, Macan TP, da Silva S, Canteiro PB, de Sena Casagrande A, Pedroso GDS, Nesi RT, de Andrade VM, de Pinho RA (2017) Strength and aerobic exercises improve spatial memory in aging rats through stimulating distinct neuroplasticity mechanisms. Mol Neurobiol 54(10):7928–7937
Watson N, Ding B, Zhu X, Frisina RD (2017) Chronic inflammation - inflammaging - in the ageing cochlea: A novel target for future presbycusis therapy. Ageing Res Rev 40:142–148
Acknowledgements
We thank all funding agencies and authors for their contributions to this research.
Funding
The Laboratory of Experimental Neurology at the University of Southern Santa Catarina (UNESC) supported this study. Laboratory of Experimental Neurology (Brazil) is funded by grants from the National Council for Scientific and Technological Development (CNPq), Coordination for the Improvement of Higher Education Personnel (CAPES), Foundation for the Support of Research and Innovation of the State of Santa Catarina (FAPESC) (JB – FAPESC N° 06/2017 – APOIO A GRUPOS DE PESQUISA DAS INSTITUIÇÕES DO SISTEMA ACAFE – TERMO DE OUTORGA N° 2018TR1551), UNESC and "For Women in Science" 2019, a program by L'oreal Brazil in partnership with UNESCO in Brazil and the Brazilian Academy of Sciences (ABC). JB, AGD, and TEAF were recipients of CNPq (Brazil) Productivity Fellowships.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All the authors contributed equally to the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Attached in the supplementary material.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Conflict of interest
No competing financial interests exist.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Bellettini-Santos, T., Garcez, M.L., Mina, F. et al. Vitamin D3 improves spatial memory and modulates cytokine levels in aged rats. Metab Brain Dis 38, 1155–1166 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-022-01152-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-022-01152-9