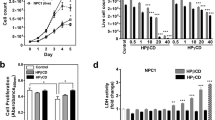
Abstract
Niemann-Pick C disease (NPC) is an autosomal recessive genetic disorder resulting from mutation in one of two cholesterol transport genes: NPC1 or NPC2, causing accumulation of unesterified cholesterol, together with glycosphingolipids, within the endosomal/lysosomal compartment of cells. The result is a severe disease in both multiple peripheral organs and the central nervous system, causing neurodegeneration and early death. However, the pathophysiological mechanisms of NPC1 remain poorly understood. Recent studies have shown that the primary lysosomal defect found in fibroblasts from NPC1 patients is accompanied by a deregulation of mitochondrial organization and function. There is currently no cure for NPC1, but recently the potential of β-cyclodextrin (β-CD) for the treatment of the disease was discovered, which resulted in the redistribution of cholesterol from subcellular compartments to the circulation and increased longevity in an animal model of NPC1. Considering the above, the present work evaluated the in vitro therapeutic potential of β-CD to reduce cholesterol in fibroblasts from NPC1 patients. β-CD was used in its free and nanoparticulate form. We also evaluated the β-CD potential to restore mitochondrial functions, as well as the beneficial combined effects of treatment with antioxidants N-Acetylcysteine (NAC) and Coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10). Besides, we evaluated oxidative and nitrative stress parameters in NPC1 patients. We showed that oxidative and nitrative stress could contribute to the pathophysiology of NPC1, as the levels of lipoperoxidation and the nitrite and nitrate levels were increased in these patients when compared to healthy individuals, as well as DNA damage. The nanoparticles containing β-CD reduced the cholesterol accumulated in the NPC1 fibroblasts. This result was potentiated by the concomitant use of the nanoparticles with the antioxidants NAC and CoQ10 compared to those presented by healthy individuals cells ́. In addition, treatments combining β-CD nanoparticles and antioxidants could reduce mitochondrial oxidative stress, demonstrating advantages compared to free β-CD. The results obtained are promising regarding the combined use of β-CD loaded nanoparticles and antioxidants in the treatment of NPC1 disease.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable.
References
Abi-Mosleh L, Infante RE, Radhakrishnan A, Goldstein JL, Brown MS (2009) Cyclodextrin overcomes deficient lysosome-to-endoplasmic reticulum transport of cholesterol in Niemann-Pick type C cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106(46). https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0910916106
Aqul A, Liu B, Ramirez CM, Pieper AA, Estill SJ, Burns DK, Liu B, Repa JJ, Turley SD, Dietschy JM (2011) Unesterified cholesterol accumulation in late endosomes/lysosomes causes neurodegeneration and is prevented by driving cholesterol export from this compartment. J Neurosci 31(25):9404–9413. http://www.jneurosci.org/content/31/25/9404.abstract
Balboa E, Castro J., Pinochet MJ, Cancino GI, Matías N, José Sáez P, Martínez A, Álvarez AR, Garcia-Ruiz C, Fernandez-Checa JC, Zanlungo S (2017) MLN64 induces mitochondrial dysfunction associated with increased mitochondrial cholesterol content. Redox Biol 12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.redox.2017.02.024
Biancini GB, Moura DJ, Manini PR, Faverzani JL, Netto CBO, Deon M, Giugliani R, Saffi J, Vargas CR (2015) DNA damage in Fabry patients: An investigation of oxidative damage and repair. Mutat Res Genet Toxicol Environ Mutagen 784–785:31–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mrgentox.2015.04.012
Coelho JC, Giugliani R (2000) Fibroblasts of skin fragments as a tool for the investigation of genetic diseases: Technical recommendations. Genet Mol Biol 23(2). https://doi.org/10.1590/S1415-47572000000200004
Cologna SM, Cluzeau CVMM, Yanjanin NM, Blank PS, Dail MK, Siebel S, Toth CL, Wassif CA, Lieberman AP, Porter FD (2014) Human and mouse neuroinflammation markers in Niemann-Pick disease, type C1. J Inherit Metab Dis 37(1):83–92. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10545-013-9610-6
Crumling MA, King KA, Duncan RK (2017) Cyclodextrins and iatrogenic hearing loss: New drugs with significant risk. In: Frontiers in Cellular Neuroscience (Vol. 11). https://doi.org/10.3389/fncel.2017.00355
Davidson CD, Ali NF, Micsenyi MC, Stephney G, Renault S, Dobrenis K, Ory DS, Vanier MT, Walkley SU (2009) Chronic cyclodextrin treatment of murine Niemann-Pick C disease ameliorates neuronal cholesterol and glycosphingolipid storage and disease progression. PLoS ONE 4(9). https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0006951
Dean O, Giorlando F, Berk M (2011) N-acetylcysteine in psychiatry: Current therapeutic evidence and potential mechanisms of action. J Psychiatry Neurosci. https://doi.org/10.1503/jpn.100057
Diaz Jacques CE, de Souza HM, Sperotto NDM, Veríssimo RM, da Rosa HT, Moura DJ, Saffi J, Giugliani R, Vargas CR (2018) Hunter syndrome: Long-term idursulfase treatment does not protect patients against DNA oxidation and cytogenetic damage. Mutat Res Genet Toxicol Environ Mutagen 835:21–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mrgentox.2018.08.013
Dizdaroglu M (2012) Oxidatively induced DNA damage: Mechanisms, repair and disease. Cancer Lett 327(1–2):26–47. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2012.01.016
Donida B, Raabe M, Tauffner B, Farias MA, Machado AZ, Timm F, Kessler RG, Hammerschmidt TG, Reinhardt LS, Brito VB, Portugal RV, Bernardi A, Frozza R, Moura DJ, Giugliani R, Poletto F, Vargas CR (2020) Nanoparticles containing β-cyclodextrin potentially useful for the treatment of Niemann-Pick C. J Inherit Metab Dis 43(3):586–601. https://doi.org/10.1002/jimd.12210
Duberley KE, Heales SJR, Abramov AY, Chalasani A, Land JM, Rahman S, Hargreaves IP (2014) Effect of Coenzyme Q10 supplementation on mitochondrial electron transport chain activity and mitochondrial oxidative stress in Coenzyme Q 10 deficient human neuronal cells. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 50(1):60–63. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biocel.2014.02.003
Fujimoto C, Yamasoba T (2019) Mitochondria-targeted antioxidants for treatment of hearing loss: A systematic review. In: Antioxidants (Vol. 8, Issue 4). https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox8040109
Griffin LD, Gong W, Verot L, Mellon SH (2004) Niemann-Pick type C disease involves disrupted neurosteroidogenesis and responds to allopregnanolone. Nat Med 10(7). https://doi.org/10.1038/nm1073
Hammerschmidt TG, Donida B, Faverzani JL, Moura AP, dos Reis BG, Machado AZ, Kessler RG, Sebastião FM, Reinhardt LS, Moura DJ, Vargas CR (2022) Cytokine profile and cholesterol levels in patients with Niemann-Pick type C disease presenting neurological symptoms: in vivo effect of miglustat and in vitro effect of N-acetylcysteine and coenzyme Q10. Exp Cell Res 416(2):113175. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yexcr.2022.113175
Hargreaves IP (2003) Ubiquinone: cholesterol’s reclusive cousin. Ann Clin Biochem 40:2017–2218
Hovakimyan M, Maass F, Petersen J, Holzmann C, Witt M, Lukas J, Frech MJ, Hübner R, Rolfs A, Wree A (2013) Combined therapy with cyclodextrin/allopregnanolone and miglustat improves motor but not cognitive functions in Niemann-Pick Type C1 mice. Neuroscience 252. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2013.08.001
Ito F, Sono Y, Ito T (2019) Measurement and clinical significance of lipid peroxidation as a biomarker of oxidative stress: Oxidative stress in diabetes, atherosclerosis, and chronic inflammation. Antioxidants 8(3). https://doi.org/10.3390/ANTIOX8030072
Jürs AV, Völkner C, Liedtke M, Huth K, Lukas J, Hermann A, Frech MJ (2020) Oxidative stress and alterations in the antioxidative defense system in neuronal cells derived from NPC1 patient-specific induced pluripotent stem cells. Int J Mol Sci 21(20):1–13. https://doi.org/10.3390/IJMS21207667
Kennedy BE, Madreiter CT, Vishnu N, Malli R, Graier WF, Karten B (2014) Adaptations of energy metabolism associated with increased levels of mitochondrial cholesterol in Niemann-Pick type C1-deficient cells. J Biol Chem 289(23). https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M114.559914
Kim SJ, Lim MS, Kang SK, Lee YS, Kang KS (2008) Impaired functions of neural stem cells by abnormal nitric oxide-mediated signaling in an in vitro model of Niemann-Pick type C disease. Cell Res 18(6):686–694. https://doi.org/10.1038/CR.2008.48
Li H, Turley SD, Liu B, Repa JJ, Dietschy JM (2008) GM2/GD2 and GM3 gangliosides have no effect on cellular cholesterol pools or turnover in normal or NPC1 mice. J Lipid Res 49(8). https://doi.org/10.1194/jlr.M800180-JLR200
Liu Y, Wu YP, Wada R, Neufeld EB, Mullin KA, Howard AC, Pentchev PG, Vanier MT, Suzuki K, Proia RL (2000) Alleviation of neuronal ganglioside storage does not improve the clinical course of the Niemann-Pick C disease mouse. Hum Mol Genet 9(7). https://doi.org/10.1093/hmg/9.7.1087
Liu B, Ramirez CM, Miller AM, Repa JJ, Turley SD, Dietschy JM (2010). Cyclodextrin overcomes the transport defect in nearly every organ of NPC1 mice leading to excretion of sequestered cholesterol as bile acid. J Lipid Res 51(5). https://doi.org/10.1194/jlr.M000257
Matthews RT, Yang L, Browne S, Baik M, Beal MF (1998) Coenzyme Q10 administration increases brain mitochondrial concentrations and exerts neuroprotective effects. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95(15). https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.95.15.8892
Montero R, Yubero D, Salgado MC, González MJ, Campistol J, del Mar O’Callaghan M, Pineda M, Delgadillo V, Maynou J, Fernandez G, Montoya J, Ruiz-Pesini E, Meavilla S, Neergheen V, García-Cazorla A, Navas P, Hargreaves I, Artuch R (2019) Plasma coenzyme Q10 status is impaired in selected genetic conditions. Sci Rep. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-37542-2
Parasassi T, Brunelli R, Costa G, de Spirito M, Krasnowska EK, Lundeberg T, Pittaluga E, Ursini F (2010) Thiol redox transitions in cell signaling: A lesson from N-acetylcysteine. TheScientificWorldJournal. https://doi.org/10.1100/tsw.2010.104
Patterson MC, Hendriksz CJ, Walterfang M, Sedel F, Vanier MT, Wijburg F (2012) Recommendations for the diagnosis and management of Niemann-Pick disease type C: An update. Mol Genet Metab 106(3):330–344. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymgme.2012.03.012
Paulina Ordonez M, Roberts EA, Kidwell CU, Yuan SH, Plaisted WC, Goldstein LSB (2012) Disruption and therapeutic rescue of autophagy in a human neuronal model of Niemann Pick type C1. Hum Mol Genet 21(12):2651. https://doi.org/10.1093/HMG/DDS090
Perry SW, Norman JP, Barbieri J, Brown EB, Gelbard HA (2011) Mitochondrial membrane potential probes and the proton gradient: A practical usage guide. In: BioTechniques (Vol. 50, Issue 2). https://doi.org/10.2144/000113610
Pontikis CC, Davidson CD, Walkley SU, Platt FM, Begley DJ (2013) Cyclodextrin alleviates neuronal storage of cholesterol in Niemann-Pick C disease without evidence of detectable blood-brain barrier permeability. J Inherit Metab Dis 36(3). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10545-012-9583-x
Reddy JV, Ganley IG, Pfeffer SR (2006) Clues to neuro-degeneration in Niemann-Pick type C disease from global gene expression profiling. PLoS ONE 1(1). https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0000019
Repetto G, del Peso A, Zurita JL (2008) Neutral red uptake assay for the estimation of cell viability/cytotoxicity. Nat Protoc 3(7):1125–1131. https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2008.75
Ribas GS, Pires R, Coelho JC, Rodrigues D, Mescka CP, Vanzin CS, Biancini GB, Negretto G, Wayhs CAY, Wajner M, Vargas CR (2012) Oxidative stress in Niemann-Pick type C patients: A protective role of N-butyl-deoxynojirimycin therapy. Int J Dev Neurosci 30(6):439–444. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijdevneu.2012.07.002
Sandhir R, Sood A, Mehrotra A, Kamboj SS (2012) N-acetylcysteine reverses mitochondrial dysfunctions and behavioral abnormalities in 3-nitropropionic acid-induced Huntington’s disease. Neurodegener Dis 9(3):145–157. https://doi.org/10.1159/000334273
Singh NP, McCoy MT, Tice RR, Schneider EL (1988) A simple technique for quantitation of low levels of DNA damage in individual cells. Exp Cell Res. https://doi.org/10.1016/0014-4827(88)90265-0
Tang X, Li Z, Zhang W, Yao Z (2019) Nitric oxide might be an inducing factor in cognitive impairment in Alzheimer’s disease via downregulating the monocarboxylate transporter 1. Nitric Oxide Biol Chem 91:35–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.NIOX.2019.07.006
Trares K, Gào X, Perna L, Rujescu D, Stocker H, Möllers T, Beyreuther K, Brenner H, Schöttker B (2020) Associations of urinary 8-iso-prostaglandin F2α levels with all-cause dementia, Alzheimer’s disease, and vascular dementia incidence: results from a prospective cohort study. Alzheimers Dement 16(5):804–813. https://doi.org/10.1002/ALZ.12081
Vanier MT, Latour P (2015) Laboratory diagnosis of Niemann-Pick disease type C: The filipin staining test. In: Methods in Cell Biology (Vol. 126). Elsevier Ltd. https://doi.org/10.1016/bs.mcb.2014.10.028
Vanier MT (2013) Niemann–Pick diseases. In: Handbook of Clinical Neurology (pp. 1717–1721). https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-444-59565-2.00041-1
Vanier MT (2015) Complex lipid trafficking in Niemann-Pick disease type C. J Inherit Metab Dis 38(1). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10545-014-9794-4
Vázquez MC, Balboa E, Alvarez AR, Zanlungo S (2012) Oxidative stress: A pathogenic mechanism for Niemann-Pick type C disease. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2012. https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/205713
Vejux A, Lizard G (2009) Cytotoxic effects of oxysterols associated with human diseases: Induction of cell death (apoptosis and/or oncosis), oxidative and inflammatory activities, and phospholipidosis. Mol Aspects Med 30(3):153–170. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mam.2009.02.006
Wassif CA, Cross JL, Iben J, Sanchez-Pulido L, Cougnoux A, Platt FM, Ory DS, Ponting CP, Bailey-Wilson JE, Biesecker LG, Porter FD (2016) High incidence of unrecognized visceral/neurological late-onset Niemann-Pick disease, type C1, predicted by analysis of massively parallel sequencing data sets. Genet Med 18(1):41–48. https://doi.org/10.1038/gim.2015.25
Weber C, Bysted A, Hølmer G (1997) Coenzyme q10 in the diet–daily intake and relative bioavailability. Mol Aspects Med. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0098-2997(97)00003-4
Wehrmann ZT, Hulett TW, Huegel KL, Vaughan KT, Wiest O, Helquist P, Goodson H (2012) Quantitative comparison of the efficacy of various compounds in lowering intracellular cholesterol levels in Niemann-Pick Type C fibroblasts. PLoS ONE 7(10). https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0048561
Woś M, Szczepanowska J, Pikuła S, Tylki-Szymańska A, Zabłocki K, Bandorowicz-Pikuła J (2016) Mitochondrial dysfunction in fibroblasts derived from patients with Niemann-Pick type C disease. Arch Biochem Biophys 593:50–59. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ABB.2016.02.012
Yang X, Yang Y, Li G, Wang J, Yang ES (2008) Coenzyme Q10 attenuates β-amyloid pathology in the aged transgenic mice with Alzheimer presenilin 1 mutation. J Mol Neurosci 34(2). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-007-9033-7
Yu W, Gong JS, Ko M, Garver WS, Yanagisawa K, Michikawa M (2005) Altered cholesterol metabolism in Niemann-Pick type C1 mouse brains affects mitochondrial function. J Biol Chem 280(12):11731–11739. https://doi.org/10.1074/JBC.M412898200
Zampieri S, Mellon SH, Butters TD, Nevyjel M, Covey DF, Bembi B, Dardis A (2009) Oxidative stress in NPC1 deficient cells: Protective effect of allopregnanolone. J Cell Mol Med 13(9 B):3786–3796. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1582-4934.2008.00493.x
Zhang YH, Wang DW, Xu SF, Zhang S, Fan YG, Yang YY, Guo S Q, Wang S, Guo T, Wang ZY, Guo C (2018) α-Lipoic acid improves abnormal behavior by mitigation of oxidative stress, inflammation, ferroptosis, and tauopathy in P301S Tau transgenic mice. Redox Biol 14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.redox.2017.11.001
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank the patients and their families, as well as the medical staff of the for logistic and technical support in the developmental of this study.
Funding
This work was supported by: Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior (CAPES/MEC-Brasil); Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPq/MCTI-Brasil number 430443/2018–8); Fundo de Incentivo à Pesquisa e Eventos (FIPE/HCPA – number 2018–0648).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection and analysis were performed by Tatiane G Hammerschmidt, Bruna Donida, Marco Raabe, Jéssica L Faverzani, Andryele Z Machado, Rejane G Kessler, Luiza S Reinhardt, Fernanda Poletto and Dinara J Moura. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Tatiane G Hammerschmidt and Bruna Donida, as well as revised by Carmen R Vargas. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Consent to participate and publish
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants, or from legal guardians, included in the study.
Declarations of interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Hammerschmidt, T.G., Donida, B., Raabe, M. et al. Evidence of redox imbalance and mitochondrial dysfunction in Niemann-Pick type C 1 patients: the in vitro effect of combined therapy with antioxidants and β‐cyclodextrin nanoparticles. Metab Brain Dis 38, 507–518 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-022-01128-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-022-01128-9