Abstract
Purpose
Hepatic encephalopathy (HE) or hepatic coma is a demanding, not utterly understood complication of acute and chronic liver dysfunction and portosystemic shunting. In HE, hyperammonemia and inflammatory responses are believed to act in synergism. Probiotics, Lactobacillus plantarum UBLP40 and Bacillus clausii UBBC07 reduce small intestinal bacterial overgrowth and hyperammonemia, thereby preventing HE development.
Methods
The effect of probiotics-Lactobacillus plantarum UBLP40 (107 CFU/day, 14 days) and Bacillus clausii UBBC07 (107 CFU/day, 14 days) combination and standard drug-lactulose (2.5 ml/kg in 3 divided doses, 14 days) was studied in thioacetamide (250 mg/kg for three days) induced acute HE in rats by measuring behavioural parameters, biochemical parameters (serum AST, ALT, ALP and ammonia level), neurochemical parameters and histopathology study in brain and liver.
Results
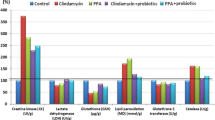
In contrast to only thioacetamide treated rats, probiotics treatment substantially (p < 0.001) reduced liver function parameters, i.e. serum AST, ALT, ALP, and ammonia, improved behaviour parameters, i.e. decreased motor disruption, improved memory impairment. Probiotics treated rats have also shown a substantial improvement in oxidative stress parameters i.e. reduced lipid peroxidation and increased glutathione level in brain tissue and ameliorated the histopathological changes induced by thioacetamide in the brain and liver.
Conclusions
It can be concluded based on the findings that the combination therapy of Lactobacillus plantarum UBLP40 and Bacillus clausiiUBBC07 proves to be effective in acute hepatic encephalopathy in the preclinical stage, and further studies are required to assess this therapy potential in the clinical setting.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article [and its supplementary information files].
References
Afifi N, Ramadan A, El-Eraky W et al (2016) Quercetin protects against thioacetamide-induced hepatotoxicity in rats through decreased oxidative stress biomarkers, the inflammatory cytokines; (TNF-α), (NF-κ B) and DNA fragmentation. Der Pharma Chem 8:48–55
Agarwal AN, Mais DD (2019) Sensitivity and Specificity of Alzheimer Type II Astrocytes in Hepatic Encephalopathy. Arch Pathol Lab Med 143:1256–1258. https://doi.org/10.5858/arpa.2018-0455-OA
Aldridge DR, Tranah EJ, Shawcross DL (2015) Pathogenesis of hepatic encephalopathy: role of ammonia and systemic inflammation. J Clin Exp Hepatol 5:S7–S20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jceh.2014.06.004
Auron A, Brophy PD (2012) Hyperammonemia in review: pathophysiology, diagnosis, and treatment. Pediatr Nephrol 27:207–222. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-011-1838-5
Azhari H, Swain MG (2018) Role of Peripheral Inflammation in Hepatic Encephalopathy. J Clin Exp Hepatol 8:281–285. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jceh.2018.06.008
Ballan R, Battistini C, Xavier-Santos D, Saad SMI (2020) Interactions of probiotics and prebiotics with the gut microbiota. Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci 171:265–300. https://doi.org/10.1016/bs.pmbts.2020.03.008
Chen WC, Quigley EMM (2014) Probiotics, prebiotics & synbiotics in small intestinal bacterial overgrowth: opening up a new therapeutic horizon! Indian J Med Res 140:582–584
Chen T-M, Subeq Y-M, Lee R-P et al (2008) Single-dose intravenous thioacetamide administration as a model of acute liver damage in rats. Int J Exp Pathol 89:223–231. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2613.2008.00576.x
Cooper AJ (2001) Role of glutamine in cerebral nitrogen metabolism and ammonia neurotoxicity. Ment Retard Dev Disabil Res Rev 7:280–286. https://doi.org/10.1002/mrdd.1039
da Silva SS, Vitolo M, González JMD, de OliveiraS, RP (2014) Overview of Lactobacillus plantarum as a promising bacteriocin producer among lactic acid bacteria. Food Res Int 64:527–536. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2014.07.041
Dalal R, McGee RG, Riordan SM, Webster AC (2017) Probiotics for people with hepatic encephalopathy. Cochrane database Syst Rev 2:CD008716. https://doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD008716.pub3
Danduga RCSR, Dondapati SR, Kola PK et al (2018) Neuroprotective activity of tetramethylpyrazine against 3-nitropropionic acid induced Huntington’s disease-like symptoms in rats. Biomed Pharmacother 105:1254–1268. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2018.06.079
Diether NE, Willing BP (2019) Microbial Fermentation of Dietary Protein: An Important Factor in Diet−Microbe−Host Interaction. Microorganisms 7(1):19. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms7010019
Duc LH, Hong HA, Barbosa TM et al (2004) Characterization of Bacillus probiotics available for human use. Appl Environ Microbiol 70:2161–2171. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.70.4.2161-2171.2004
El-Baz FK, Salama A, Salama RAA (2019) Therapeutic Effect of Dunaliella salina Microalgae on Thioacetamide- (TAA-) Induced Hepatic Liver Fibrosis in Rats: Role of TGF-β and MMP9. Biomed Res Int 2019:7028314. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/7028314
El-Baz FK, Salama AAA, Hussein RA (2020) Dunaliella salina microalgae oppose thioacetamide-induced hepatic fibrosis in rats. Toxicol Reports 7:36–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxrep.2019.10.017
El-Baz FK, Elgohary R, Salama A (2021) Amelioration of Hepatic Encephalopathy Using Dunaliella salina Microalgae in Rats: Modulation of Hyperammonemia/TLR4. Biomed Res Int 2021:8843218. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/8843218
El-Marasy SA, El Awdan SA, Abd-Elsalam RM (2019) Protective role of chrysin on thioacetamide-induced hepatic encephalopathy in rats. Chem Biol Interact 299:111–119. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbi.2018.11.021
Ennaceur A, Delacour J (1988) A new one-trial test for neurobiological studies of memory in rats. 1: Behavioral data. Behav Brain Res 31:47–59. https://doi.org/10.1016/0166-4328(88)90157-x
Farjam M, Dehdab P, Abbassnia F et al (2012) Thioacetamide-induced acute hepatic encephalopathy in rat: behavioral, biochemical and histological changes. Iran Red Crescent Med J 14(3):164–170
Giannini EG, Testa R, Savarino V (2005) Liver enzyme alteration: a guide for clinicians. CMAJ 172(3):367–379. https://doi.org/10.1503/cmaj.1040752
Hadjihambi A, Arias N, Sheikh M, Jalan R (2018) Hepatic encephalopathy: a critical current review. Hepatol Int 12:135–147. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12072-017-9812-3
Hernández-Gómez JG, López-Bonilla A, Trejo-Tapia G et al (2021) In vitro bile salt hydrolase (Bsh) activity screening of different probiotic microorganisms. Foods 10:1–10. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10030674
Jaeger V, DeMorrow S, McMillin M (2019) The Direct Contribution of Astrocytes and Microglia to the Pathogenesis of Hepatic Encephalopathy. J Clin Transl Hepatol 7:352–361. https://doi.org/10.14218/JCTH.2019.00025
Kornerup LS, Gluud LL, Vilstrup H, Dam G (2018) Update on the Therapeutic Management of Hepatic Encephalopathy. Curr Gastroenterol Rep 20:21. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11894-018-0627-8
Li S, Tan H-Y, Wang N et al (2015) The Role of Oxidative Stress and Antioxidants in Liver Diseases. Int J Mol Sci 16:26087–26124. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms161125942
Liu Y, Tran DQ, Rhoads JM (2018) Probiotics in Disease Prevention and Treatment. J Clin Pharmacol 58(Suppl 1):S164–S179. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcph.1121
Mostafa RE, Salama AAA, Abdel-Rahman RF, Ogaly HA (2017) Hepato- and neuro-protective influences of biopropolis on thioacetamide-induced acute hepatic encephalopathy in rats. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 95:539–547. https://doi.org/10.1139/cjpp-2016-0433
Muramatsu K (1967) Direct Colorimetric Method for the Determination of Free Ammonia in Blood. Agric Biol Chem 31:301–308. https://doi.org/10.1080/00021369.1967.10858803
Parekh PJ, Balart LA (2015) Ammonia and Its Role in the Pathogenesis of Hepatic Encephalopathy. Clin Liver Dis 19:529–537. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cld.2015.05.002
Patel C, Patel P, Acharya S (2020) Therapeutic Prospective of a Spore-Forming Probiotic-Bacillus clausii UBBC07 Against Acetaminophen-Induced Uremia in Rats. Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins 12:253–258. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12602-019-09540-x
Prakash R, Mullen KD (2010) Mechanisms, diagnosis and management of hepatic encephalopathy. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 7:515–525. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrgastro.2010.116
Ruiz-Larrea MB, Leal AM, Liza M et al (1994) Antioxidant effects of estradiol and 2-hydroxyestradiol on iron-induced lipid peroxidation of rat liver microsomes. Steroids 59:383–388. https://doi.org/10.1016/0039-128x(94)90006-x
Savy N, Brossier D, Brunel-Guitton C et al (2018) Acute pediatric hyperammonemia: current diagnosis and management strategies. Hepat Med 10:105–115. https://doi.org/10.2147/HMER.S140711
Suárez I, Bodega G, Fernández B (2002) Glutamine synthetase in brain: effect of ammonia. Neurochem Int 41:123–142. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0197-0186(02)00033-5
Swaminathan M, Ellul MA, Cross TJ (2018) Hepatic encephalopathy: current challenges and future prospects. Hepat Med 10:1–11. https://doi.org/10.2147/HMER.S118964
Vijitruth R, Liu M, Choi D-Y et al (2006) Cyclooxygenase-2 mediates microglial activation and secondary dopaminergic cell death in the mouse MPTP model of Parkinson’s disease. J Neuroinflammation 3:6. https://doi.org/10.1186/1742-2094-3-6
Vorhees CV, Williams MT (2014) Assessing spatial learning and memory in rodents. ILAR J 55:310–332. https://doi.org/10.1093/ilar/ilu013
Yoon H, Lee JG, Yoo JH et al (2013) Effects of metabolic syndrome on fibrosis in chronic viral hepatitis. Gut Liver 7:469–474. https://doi.org/10.5009/gnl.2013.7.4.469
You DD, Choi GS, Kim JM et al (2017) Long-term Outcomes for Liver Transplant Recipients in Terms of Hepatic Encephalopathy. Transplant Proc 49:1425–1429. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.transproceed.2017.02.054
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The authors declare that all data were generated in-house and that no paper mill was used.
Conceptualization: [Chirag Patel, Lalita Shahgond, Sanjeev Acharya, Priyanshi Patel]; Methodology: [Lalita Shahgond, Khushboo Thakur, Dipta Sarkar]; Formal analysis and investigation: [Chirag Patel, Lalita Shahgond, Khushboo Thakur, Dipta Sarkar]; Writing—original draft preparation: [Chirag Patel, Lalita Shahgond, Priyanshi Patel]; Writing—review and editing: [Chirag Patel, Lalita Shahgond, Sanjeev Acharya]; Supervision: [Sanjeev Acharya].
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
Ethics approval
IAEC (Institutional Animal Ethics Committee) approved the experimental protocol SSR/IAEC/2019/05.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Authors give consent for information to be published in the journal- Metabolic Brain Disease.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shahgond, L., Patel, C., Thakur, K. et al. Therapeutic potential of probiotics – Lactobacillus plantarum UBLP40 and Bacillus clausii UBBC07 on thioacetamide-induced acute hepatic encephalopathy in rats. Metab Brain Dis 37, 185–195 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-021-00862-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-021-00862-w