Abstract
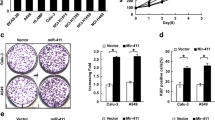
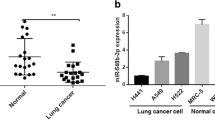
microRNAs have been reported to play vital role in lung cancer proliferation and metastasis; the role of miR-4326 in tumor progression has not been studied. Here, we studied the effect of miR-4326 on lung cancer cell proliferation; we found that miR-4326 was significantly upregulated in lung cancer tissues determined using TCGA dataset and clinical specimens, meanwhile it was also upregulated in lung cancer cells. Overexpression of miR-4326 promoted lung cancer cell proliferation analyzed by MTT, soft agar growth, and BrdU incorporation assay, while miR-4326 knockdown suppressed lung cancer cell proliferation. We found miR-4326 targets tumor suppressor adenomatous polyposis coli 2 (APC2), which is a negative regulator of Wnt pathway, by binding to the 3′UTR of APC2. Wnt pathway could increase Cyclin D1 and c-MYC expression, we also found that miR-4326 could increase their expression, suggesting that APC2 was the target of miR-4326. Moreover, double knockdown of APC2 and miR-4326 promoted lung cancer cell proliferation, confirming that miR-4326 promoted lung cancer cell proliferation by inhibiting APC2.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mahapatra A (2010) Lung cancer—genomics and personalized medicine. ACS Chem Biol 5(6):529–531. https://doi.org/10.1021/cb1001476
Kim ES, Hirsh V, Mok T, Socinski MA, Gervais R, Wu YL et al (2008) Gefitinib versus docetaxel in previously treated non-small-cell lung cancer (INTEREST): a randomised phase III trial. Lancet 372(9652):1809–1818. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(08)61758-4
Shaw AT, Yasothan U, Kirkpatrick P (2011) Crizotinib. Nat Rev Drug Discovery 10(12):897–898. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrd3600
Tsao MS, Sakurada A, Cutz JC, Zhu CQ, Kamel-Reid S, Squire J et al (2005) Erlotinib in lung cancer—molecular and clinical predictors of outcome. N Engl J Med 353(2):133–144. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa050736
John B, Enright AJ, Aravin A, Tuschl T, Sander C, Marks DS (2004) Human microRNA targets. PLoS Biol 2(11):e363. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pbio.0020363
Yang D, Zhan M, Chen T, Chen W, Zhang Y, Xu S et al (2017) miR-125b-5p enhances chemotherapy sensitivity to cisplatin by down-regulating Bcl2 in gallbladder cancer. Sci Rep 7:43109. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep43109
McCormick RI, Blick C, Ragoussis J, Schoedel J, Mole DR, Young AC et al (2013) miR-210 is a target of hypoxia-inducible factors 1 and 2 in renal cancer, regulates ISCU and correlates with good prognosis. Br J Cancer 108(5):1133–1142. https://doi.org/10.1038/bjc.2013.56
Faversani A, Amatori S, Augello C, Colombo F, Porretti L, Fanelli M et al (2017) miR-494-3p is a novel tumor driver of lung carcinogenesis. Oncotarget. 8(5):7231–7247. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.13933
Sun CC, Li SJ, Zhang F, Zhang YD, Zuo ZY, Xi YY et al (2016) The novel miR-9600 suppresses tumor progression and promotes paclitaxel sensitivity in non-small-cell lung cancer through altering STAT3 expression. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids 5:e387. https://doi.org/10.1038/mtna.2016.96
Hao GJ, Hao HJ, Ding YH, Wen H, Li XF, Wang QR et al (2017) Suppression of EIF4G2 by miR-379 potentiates the cisplatin chemosensitivity in nonsmall cell lung cancer cells. FEBS Lett. https://doi.org/10.1002/1873-3468.12566
Zhang L, Zeng D, Chen Y, Li N, Lv Y, Li Y et al (2016) miR-937 contributes to the lung cancer cell proliferation by targeting INPP4B. Life Sci 155:110–115. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2016.05.014
Yang Y, Ahn YH, Chen Y, Tan X, Guo L, Gibbons DL et al (2014) ZEB1 sensitizes lung adenocarcinoma to metastasis suppression by PI3K antagonism. J Clin Investig 124(6):2696–2708. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI72171
Chen Y, Min L, Ren C, Xu X, Yang J, Sun X et al (2017) miRNA-148a serves as a prognostic factor and suppresses migration and invasion through Wnt1 in non-small cell lung cancer. PLoS ONE 12(2):e0171751. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0171751
Shieh JM, Tang YA, Hu FH, Huang WJ, Wang YJ, Jen J et al (2017) A histone deacetylase inhibitor enhances expression of genes inhibiting Wnt pathway and augments activity of DNA demethylation reagent against non-small cell lung cancer. Int J Cancer. https://doi.org/10.1002/ijc.30664
Stamos JL, Weis WI (2013) The beta-catenin destruction complex. Cold Spring Harbor Perspect Biol 5(1):a007898. https://doi.org/10.1101/cshperspect.a007898
Croy HE, Fuller CN, Giannotti J, Robinson P, Foley AV, Yamulla RJ et al (2016) The poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase enzyme tankyrase antagonizes activity of the beta-catenin destruction complex through ADP-ribosylation of axin and APC2. J Biol Chem 291(24):12747–12760. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M115.705442
Kunttas-Tatli E, Roberts DM, McCartney BM (2014) Self-association of the APC tumor suppressor is required for the assembly, stability, and activity of the Wnt signaling destruction complex. Mol Biol Cell 25(21):3424–3436. https://doi.org/10.1091/mbc.E14-04-0885
McCartney BM, Price MH, Webb RL, Hayden MA, Holot LM, Zhou M et al (2006) Testing hypotheses for the functions of APC family proteins using null and truncation alleles in Drosophila. Development 133(12):2407–2418. https://doi.org/10.1242/dev.02398
Ge YX, Wang CH, Hu FY, Pan LX, Min J, Niu KY et al (2017) New advances of TMEM88 in cancer initiation and progression, with special emphasis on Wnt signaling pathway. J Cell Physiol. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.25853
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declared that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Guopeng Xu and Zhongwei Zhang have contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, G., Zhang, Z., Zhang, L. et al. miR-4326 promotes lung cancer cell proliferation through targeting tumor suppressor APC2. Mol Cell Biochem 443, 151–157 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-017-3219-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-017-3219-2