Abstract
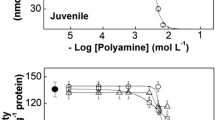
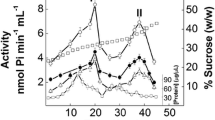
Aiming to clarify the mechanism of inhibition of (Na+, K+)-ATPase activity by polyamines, we examined the effects of exogenous putrescine, spermidine, and spermine on the kinetic behavior of phosphoenzyme-linked partial reactions using a microsomal gill (Na+, K+)-ATPase from juvenile and adult M. amazonicum, a freshwater palaemonid shrimp. The time course of phosphointermediate formation is greater (0.089 ± 0.006 s−1) in adults than in juveniles (0.053 ± 0.003 s−1) for spermidine, but similar to juveniles (0.059 ± 0.004 s−1) for putrescine. Maximum phosphointermediate formation for the (Na+, K+)-ATPase from juveniles decreased by 46% and 32% with spermidine and putrescine, respectively. In adults, maximum phosphointermediate levels decreased by 50% and 8%, respectively. For both spermidine and putrescine, dephosphorylation rates were higher for adults than for juveniles, and were higher than in controls without polyamines. Spermine had a negligible effect (<10%) on phosphorylation/dephosphorylation rates of both juvenile and adult enzymes. This is the first report on the effects of polyamines on phosphoenzyme-linked partial reactions in juvenile and adult M. amazonicum gill (Na+, K+)-ATPases. Our findings suggest that the phosphorylation/dephosphorylation steps of this gill enzyme may be regulated by polyamines during ontogenetic development.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albers RW (1967) Biochemical aspects of active transport. Annu Rev Biochem 6:727–756
Post RL, Hegyvary C, Kume S (1972) Activation by adenosine triphosphate in the phosphorylation kinetics of sodium and potassium ion transport adenosine triphosphatase. J Biol Chem 247:6530–6540
Lingrel LB, Williams MT, Vorhees CV, Moseley AE (2007) Na, K-ATPase and the role of α isoforms in behavior. J Bioenerg Biomembr 39:385–389
Morth JP, Pedersen BP, Toustrup-Jensen MS, Sorensen TLM, Petersen J, Eersen JP, Vilsen B, Nissen P (2007) Crystal structure of the sodium–potassium pump. Nature 450:1043–1050
Geering K (2008) Functional roles of Na, K-ATPase subunits. Curr Opinion Nephrol Hypert 17: 526–532
Poulsen H, Khandelia H, Morth P, Bublitz M, Mouritsen OG, Egebjerg J, Nissen P (2010) Neurological disease mutations compromise a C-terminal ion pathway in the Na1/K1-ATPase. Nature 467:99–102
Kaplan JH (2002) Biochemistry of Na, K-ATPase. Annu Rev Biochem 71:511–535
McDonough AA, Geering K, Farley RA (1990) The sodium pump needs its beta subunit. FASEB J 4:1598–1605
Geering K (2001) The functional role of beta subunits in oligomeric P-type ATPases. J Bioenerg Biomemb 33:425–438
Therien AG, Blostein R (2000) Mechanisms of sodium pump regulation. Am J Physiol 279:C541–C566
Cortes VF, Veiga-Lopes FE, Barrabin H, Alves-Ferreira M, Fontes CFL (2006) The gamma subunit of Na+ ,K+-ATPase: role on ATPase activity and regulatory phosphorylation by PKA. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 38:1901–1913
Silva ECC, Masui DC, Furriel RP, McNamara JC, Barrabin H, Scofano HM, Perales J, Teixeira-Ferreira A, Leone FA, Fontes CFL (2012) Identification of a crab gill FXYD2 protein and regulation of crab microsomal Na, K-ATPase activity by mammalian FXYD2 peptide. Biochim Biophys Acta 1818:2588–2597
Horisberger JD (2004) Recent insights into the structure e mechanism of the sodium pump. Physiology 19:377–388
Jorgensen PL, Nielsen JM, Rasmussen JH, Pedersen PA (1998) Structure-function relationships based on E1–E2 transitions and cation binding in NaK-pump protein. Biochim Biophys Acta 1365:65–70
Morth JP, Poulsen P, Toustrup-Jensen MS, Schack VR, Egebjerg J, Andersen JP, Vilsen B, Nissen P (2009) The structure of the Na+,K+-ATPase and mapping of isoform differences and disease-related mutations. Philos Trans R Soc Lond Biol Sci 364:217–227
Glynn IM (1985) The (Na+K+)-transporting adenosine triphosphatase. In: Martonosi AN (ed) The enzymes of biological membranes, 3. Plenum Press, New York, pp 35–114
Fedosova NU, Champeil P, Esmann M (2003) Rapid filtration analysis of nucleotide binding to Na, K-ATPase. BioChemistry 42:3536–3543
Petrushanko IY, Mitkevich VA, Anashkina AA, Klimanova EA, Dergousova EA, Lopina OD, Makarov AA (2014) Critical role of γ-phosphate in structural transition of Na, K-ATPase upon ATP binding. Sci Report 4:5165
Stekhoven FMAHS, Swarts HGP, Depont JJHHM, Bonting SL (1981) Studies on (Na+,K+)-activated ATPase: mangnesium induces low-affinity non-phosphorylating nucleotide binding-sites per molecule. Biochim Biophys Acta 649:533–540
Beaugé L (2001) Breakdown of Na+/K+-exchanging ATPase phosphoenzymes formed from ATP and from inorganic phosphate during Na+-ATPase activity. Eur J Biochem 268:5627–5632
Glynn IM, Karlish SJ (1975) The sodium pump. Annu Rev Physiol 37:13–55
Hobbs AS, Albers RW, Froehlich JP (1983) Effects of oligomycin on the partial reactions of the sodium plus potassium-stimulated adenosine-triphosphate. J Biol Chem 258:8163–8168
Sen AK, Tobin T, Post RL (1969) A cycle for ouabain inhibition of sodium-dependent and potassium-dependent adenosine triphosphatase. J Biol Chem 244:6596–6604
Yoda Y, Yoda S (1983) Characteristics of the electric-eel Na, K-ATPase phosphoprotein. Curr Top Membr Transp 19:343–347
Yoda S, Yoda A (1986) ADP- and K+-sensitive phosphorylated intermediate of Na, K-ATPase. J Biol Chem 261:1147–1152
Yoda S, Yoda A (1987) Two different phosphorylation-dephosphorylation cycles of Na, K-ATPase proteoliposomes accompanying Na+ transport in the absence of K+. J Biol Chem 262:110–115
Klodos I, Nørby JG (1986) (Na++ K+)-ATPase: confirmation of the three-pool model for the phosphointermediates of Na+-ATPase activity. Estimation of the enzyme-ATP dissociation rate constant. Biochim Biophys Acta 897:302–314
Poulsen H, Morth P, Egebjerg J, Nissen P (2010) Phosphorylation of the Na+ ,K+-ATPase and the H+ ,K+-ATPase. FEBS Lett 584:2589–2595
Péqueux A (1995) Osmotic regulation in crustaceans. J Crust Biol 15:1–60
Freire CA, Onken H, McNamara JC (2008) A structure–function analysis of ion transport in crustacean gills and excretory organs. Comp Biochem Physiol 151A:272–304
Henry RP, Lucu C, Onken H, Weihrauch D (2012) Multiple functions of the crustacean gill: osmotic/ionic regulation, acid-base balance, ammonia excretion, and bioaccumulation of toxic metals. Front Physiol 3:431
Evans DH, Piermarini PM, Choe KP (2005) The multifunctional fish gill: dominant site of gas exchange, osmoregulation, acid-base regulation, and excretion of nitrogenous waste. Physiol Rev 85:97–177
McNamara JC, Faria SC (2012) Evolution of osmoregulatory patterns and gill ion transport mechanisms in the decapod Crustacea: a review. J Comp Physiol 182B:997–1014
Sáez AG, Lozano E, Zaldívar-Riverón A (2009) Evolutionary history of Na, K-ATPases and their osmoregulatory role. Genetica 136:479–490
Lee CE, Kiergaard M, Gelembiuk GW, Eads BD, Posavi M (2011) Pumping ions: rapid parallel evolution of ionic regulation following habitat invasions. Evol Int J Org Evol 65:2229–2244
Towle DW, Kays WT (1986) Basolateral localization of Na+ ,K+-ATPase in gill epithelium of two osmoregulating crabs, Callinectes sapidus and Carcinus maenas. J Exp Zool 239:311–318
Taylor HH, Taylor EW (1992) Microscopic anatomy of invertebrates. In: Harrison FW, Humas AG (eds) Decapod crustacea, vol 10. Wiley-Liss, New York, pp 203–293
McNamara JC, Torres AH (1999) Ultracytochemical location of Na+/K+-ATPase activity and effects of high salinity acclimation in gill and renal epithelia of the freshwater shrimp Macrobrachium olfersii (Crustacea, Decapoda). J Exp Biol 284:617–628
Holthuis LB (1952) A general revision of the Palaemonidae (Crustacea Decapoda Natantia) of the Americas. II. The subfamily Palaemonidae. Occasional Paper 12. Allan Hancock Foundations Publications, 396 pp
Odinetz-Collart O, Rabelo H (1996) Variation in egg size of the fresh-water prawn Macrobrachium amazonicum (Decapoda: Palaemonidae). J Crustacean Biol 16:684–688
Magalhães C, Bueno SLS, Bond-Buckup G, Valenti WC, Silva HLM., Kiyohara F, Mossolin EC, Rocha SS (2005) Exotic species of freshwater decapod crustaceans in the state of São Paulo, Brazil: records and possible causes of their introduction. Biodivers Conserv 14:1929–1945
Charmantier G, Anger K (2001) Ontogeny of osmoregulatory patterns in the South American shrimp Macrobrachium amazonicum: Loss of hypo-regulation in a land-locked population indicates phylogenetic separation from estuarine ancestors. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 396:89–98
Anger K (2013) Neotropical Macrobrachium (Caridea: Palaemonidae): on the biology, origin, and radiation of freshwater-invading shrimp. J Crust Biol 33:151–183
Santos A, Hayd L, Anger K (2013) A new species of Macrobrachium Spence Bate, 1868 (Decapoda, Palaemonidae), M. pantanalense, from the Pantanal, Brazil. Zootaxa 3700:534–546
Pileggi LA, Mantelatto FL (2012) Taxonomic revision of doubtful Brazilian freshwater shrimp species of the genus Macrobrachium (Decapoda, Palaemonidae). Iheringia, Série Zoologia 102:426–437
Pantaleão JAF, Hirose GL, Costa RC (2014) Occurrence of male morphotypes of Macrobrachium amazonicum (Caridea, Palaemonidea) in a population with an entirely freshwater life cycle. Braz J Biol 74:S223–S232
Moreira GS, McNamara JC, Moreira PS (1986) The effect of salinity on the upper thermal limits of survival and metamorphosis during larval development in Macrobrachium amazonicum (Heller) (Decapoda, Palaemonidae). Crustaceana 50:231–238
Augusto A, Greene LJ, Laure HJ, McNamara JC (2007) The ontogeny of isosmotic intracellular regulation in the diadromous, freshwater palaemonid shrimps, Macrobrachium amazonicum and M. olfersi (Crustacea, Decapoda). J Crust Biol 27:626–634
Santos LCF, Belli NM, Augusto A, Masui DC, Leone FA, McNamara JC, Furriel RPM (2007) Gill (Na+, K+)-ATPase in diadromous, freshwater palaemonid shrimps: species-specific kinetic characteristics and α-subunit expression. Comp Biochem Physiol 148A:178–188
Belli NM, Faleiros RO, Firmino KCS, Masui DC, Leone FA, McNamara JC, Furriel RPM (2009) Na, K-ATPase activity and epithelial interfaces in gills of the freshwater shrimp Macrobrachium amazonicum (Decapoda, Palaemonidae). Comp Biochem Physiol 152A:431–439
Leone FA, Masui DC, Bezerra TMS, Garçon DP, Valenti WC, Augusto AS, McNamara JC (2012) Kinetic analysis of gill (Na+ ,K+)-ATPase activity in selected ontogenetic stages of the Amazon river shrimp, Macrobrachium amazonicum (Decapoda, Palaemonidae): interactions at ATP- and cation-binding sites. J Memb Biol 245:201–215
Kalac P (2009) Recent advances in the research on biological roles of dietary polyamines in man. J Appl Biomed 7:65–74
Igarashi K, Kashiwagi K: Modulation of cellular function by polyamines. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 42: 39–51
Pegg AE (2009) Mammalian polyamine metabolism e function. IUBMB Life 61:880–894
Tabor CW, Tabor H (1984) Polyamines. Ann Rev Biochem 53:749–790
Pottosin I, Velarde-Buendia AM, Bose J, Fugisang AT, Shabala S (2014) Polyamines cause plasma membrane depolarization, activate Ca 2+-, and modulate H+-ATPase pump activity in roots. J Exp Botany 65:2463–2472
Koenig H, Goldstone A, Lu CY (1983) Polyamines regulate calcium fluxes in a rapid plasma membrane response. Nature 305:530–534
Seiler N, Dezeure F (1990) Polyamine transport in mammalian cells. Int J Biochem 22:211–218
Aziz SM, Olson JW, Gillespie MN (1994) Multiple polyamine transport pathways in cultured pulmonary artery smooth muscle cells: regulation by hypoxia. Am J Resp Cell Mol Biol 10:160–166
Kobayashi M, Fujisaki H, Sugawara M, Iseki K, Miyazaki K (1999) The presence of an Na+/spermine antiporter in the rat renal brush-border membrane. J Pharm Pharmacol 51:279–284
Lin X, Fenn E, Veenstra RD (2006) An amino-terminal lysine residue of rat connexin 40 that is required for spermine block. J Physiol 570:251–269
Tassoni A, Antognoni F, Bagni N (1996) Polyamines binding to plasma membrane vesicles isolated from zucchini hypocotyls. Plant Physiol 110:817–824
Fukushima Y (1990) Membrane destruction by polyamines. Biomed Res 11:345–352
Meksuriyen D, Fukuchi-Shigimori T, Kashiwagi K, Toida T, Imanari T, Kawai G, Igarashi K (1998) Complex formation of ATP, Mg 2+, and spermine: structural evidence and biological significance. J Biol Chem 273:30939–30944
Ha HC, Sirisoma NS, Kuppusamy P, Zweier JL, Woster Pm, Casero RA Jr (1998) The natural spermine functions directly as a free radical scavenger. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:11140–11145.
Toner M, Vaio G, McLaughlin A, McLaughlin S (1988) Adsorption of cations to phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate. BioChemistry 27:7435–7443
Heinrich-Hirsch B, Ahlers J, Peter HW (1977) Inhibition of Na+ ,K+-ATPase from chick brain by polyamines. Enzyme 22:235–241
Robinson JD, Leach CA, Robinson LJ (1986) Cation sites, spermine, and the reaction sequence of the (Na+K+)-dependent ATPase. Biochim Biophys Acta 856:536–544
Kuntzweiler TA, Wallick ET, Johnson CL, Lingrel JB (1995) Glutamic-acid-327 in the sheep alpha-1 isoform of Na+ ,K+-ATPase stabilizes a K+-induced conformational change. J Biol Chem 270:2993–3000
Quarfoth G, Ahmed K, Foster D (1978) Effects of polyamines on partial reactions of membrane (Na+K+)-ATPase. Biochim Biophys Acta 526:580–590
Tashima Y, Hasegawa M, Mizunuma H (1978) Activation of (Na+K+)-adenosine triphosphatase by spermine. Biochem Biophys Res Comm 82:13–18
Lovett DL, Watts SA (1995) Changes in polyamine levels in response to acclimation salinity in gills of the blue-crab Callinectes-sapidus rathbun. Comp Biochem Physiol 110B:115–119
Péqueux A, Labras P, Cann-Moisan C, Coroff J, Sebert P (2002) Polyamines, indolamines, and catecholamines in gills and haemolymph of the euryhaline crab, Eriocheir sinensis. Effects of high pressure and salinity. Crustaceana 75:567–578
Silva ECC, Masui DC, Furriel RPM, Mantelatto FLM, McNamara JC, Barrabin H, Leone FA, Scofano HM, Fontes CFL (2008) Regulation by the exogenous polyamine spermidine of Na, K-ATPase activity from the gills of the euryhaline swimming crab Callinectes danae (Brachyura, Portunidae). Comp Biochem Physiol 149B:622–629
Garçon DP, Lucena MN, França JL, McNamara JC, Fontes CFL, Leone FA (2011) Na+, K+-ATPase activity in the posterior gills of the blue crab, Callinectes ornatus (Decapoda, Brachyura): modulation of ATP hydrolysis by the biogenic amines spermidine and spermine. J Memb Biol 244:9–20
Lucena MN, McNamara JC, Leone FA (2016) Gill (Na+, K+)-ATPase from the Amazon River shrimp, Macrobrachium amazonicum (Decapoda, Palaemonidae): effect of exogenous biogenic amines on enzyme activity in juveniles and adults. Hydrobiologia. doi:10.1007/s10750-016-2753-3
Jantaro S, Maenpaa P, Mulo P, Incharoensakdi A (2003) Content and biosynthesis of polyamines in salt and osmotically stressed cells of Synechocystis sp PCC 6803. FEMS Microbiol Lett 228:129–135
Araujo MC, Valenti WC (2007) Feeding habit of the Amazon River prawn Macrobrachium amazonicum larvae. Aquaculture 265:187–193
Hayd LA, Anger K, Valenti WC (2008) The moulting cycle of larval amazon river prawn Macrobrachium amazonicum reared in the laboratory. Nauplius 16:55–63
Leone FA, Bezerra TMS, Garçon DP, Lucena MN, Pinto MR, Fontes CFL, McNamara JC (2014) Modulation by K+ and NH4 + of microsomal (Na+, K+)-ATPase activity in selected ontogenetic stages of the diadromous river shrimp Macrobrachium amazonicum (Decapoda, Palaemonidae). PLOS ONE 9(2):e8925. doi:10.1371/journalpone008925
Leone FA, Baranauskas JA, Furriel RPM, Borin IA: SigrafW (2005) An easy-to-use program for fitting enzyme kinetic data. Biochem Mol Biol Ed 33:399–403
Walseth TF, Johnson RA (1979) The enzymatic preparation of alpha-32P.ATP, alpha-32P.GTP, 32P.cAMP, and 32P.cGMP, and their use in the assay of adenylate and guanylate cyclases and cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterases. Adv Cyclic Nucleotide Res 10:135–167
Maia JCC, Gomes SL, Juliani MA (1983) A laboratory manual proceedings. In: CM Morel (ed) Genes and antigens of parasites-FIOCRUZ, Brasil, RJ, pp 144–157
Barrabin H, Fontes CFL, Scofano HM, Nørby JG (1990) Phosphorylation of (Na+, K+)-ATPase by ATP in the presence of K+ and dimethyl sulfoxide but in the absence of Na+. Biochim Biophys Acta 1023:266–273
Fontes CFL, Barrabin H, Scofano HM, Nørby JG (1992) The role of Mg2+ and K+ in the phosphorylation of Na+,K(+)-ATPase by ATP in the presence of dimethyl sulfoxide but in the absence of Na+. Biochim Biophys Acta 1104:215–225
Fontes CFL, Scofano HM, Barrabin H, Nørby JG (1995) The effect of dimethyl sulfoxide on the substrate site of Na+/K(+)-ATPase studied through phosphorylation by inorganic phosphate and ouabain binding. Biochim Biophys Acta 1235:43–51
Read SM, Northcote DH (1981) Minimization of variation in the response to different proteins of the Coomassie blue-G dye-binding assay for protein. Anal Biochem 116:53–64
Cornelius F, Fedosova NU, Klodos I (1991) Interaction between substrate site and cation binding sites in Pi phosphorylation of Na, K-ATPase. Ann NY Acad Sci 834:390–393, 1997
Janne J, Alhone L, Leinonen P (1991) Polyamines: from molecular biology to clinical application. Ann Med 23:241–259
Watts SA, Lee KJ, Cline GB (1994) Elevated ornithine decarboxylase activity e polyamine levels during early development in the brine shrimp Artemia franciscana. J Exp Zool 270:426–431
Nielsen JM, Pedersen PA, Karlish SJD, Jorgensen PL (1998) Importance of intramembrane carboxylic acids for occlusion of K+ ions at equilibrium in renal Na, K-ATPase. BioChemistry 37:1961–1968
Mandal AK, Mikhailova L, Arguelo JM (2003) The Na, K-ATPase S5-H5 helix. Structural link between phosphorylation and cation-binding sites. Ann NY Acad Sci 986:224–225
Féraille E, Carranza ML, Gonin S, Béguin P, Pedemonte C, Rousselot M, Caverzasio J, Geering K, Martin PY, Favre H (1999) Insulin-induced stimulation of Na1,K1-ATPase activity in kidney proximal tubule cells depends on phosphorylation of the a-subunit at Tyr-10. Mol Biol Cell 10:2847–2859
Féraille E, Doucet A (2001) Sodium-potassium-adenosinetriphosphatase-dependent sodium transport in the kidney: hormonal control. Physiol Rev 81:345–418
Bibert S, Roy S, Schaer D, Horisberger JD, Geering K (2008) Phosphorylation of phospholemman (FXYD1) by protein kinases A and C modulates distinct Na, K-ATPase isozymes. J Biol Chem 283:476–486
Teriete P, Thai K, Choi J, Marassi FM (2009) Effects of PKA phosphorylation on the conformation of the Na, K-ATPase regulatory protein FXYD1. Biochim Biophys Acta 1788:2462–2470
Arystarkhova E, Wetzel RK, Asinovski NK, Sweadner K (1999) The gamma subunit modulates Na+ and K+ affinity of the renal Na, K-ATPase. J Biol Chem 247:33183–33185
Cortes VF, Ribeiro IM, Barrabin H, Alves-Ferreira M, Fontes CFL (2011) Regulatory phosphorylation of FXYD2 by PKC and cross interactions between FXYD2, plasmalemmal Ca-ATPase and Na, K-ATPase. Arch Biochem Biophys 505:75–82
Elgavish A, Wallace RW, Pillion DJ, Meezan E (1984) Polyamines stimulate D-glucose transport in isolated renal brush-border membrane vesicles. Biochim Biophys Acta 777:1–8
Acknowledgements
This investigation was supported by research grants from the Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de São Paulo (FAPESP 2010/17534-0 and 2013/22625-1), Conselho de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPq 470177/2008-0), and Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado do Amazonas (FAPEAM 573976/2008-2). DPG (2010/06395-9) and MNL (2013/24252-9) received post-doctoral scholarships from FAPESP. FAL (302776/2011-7), JCM (300662/2009-2), and CFLF (308847/2014-8) received research scholarships from CNPq. This laboratory (FAL) is integrated with the Amazon Shrimp Network (Rede de Camarão da Amazônia) and with INCT-ADAPTA (Centro de Estudos de Adaptações da Biota Aquática da Amazônia). FAL is a Senior Professor at the Departamento de Química, FFCLRP/USP.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lucena, M.N., Garçon, D.P., Fontes, C.F.L. et al. Polyamines regulate phosphorylation–dephosphorylation kinetics in a crustacean gill (Na+, K+)-ATPase. Mol Cell Biochem 429, 187–198 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-017-2946-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-017-2946-8