Abstract
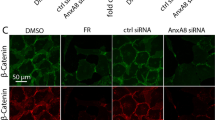
PIWI subfamily of proteins is shown to be primarily expressed in germline cells. They maintain the genomic integrity by silencing the transposable elements. Although the role of PIWI proteins in germ cells has been documented, their presence and function in somatic cells remains unclear. Intriguingly, we detected all four members of PIWI-like proteins in human ocular tissues and somatic cell lines. When HIWI2 was knocked down in retinal pigment epithelial cells, the typical honeycomb morphology was affected. Further analysis showed that the expression of tight junction (TJ) proteins, CLDN1, and TJP1 were altered in HIWI2 knockdown. Moreover, confocal imaging revealed disrupted TJP1 assembly at the TJ. Previous studies report the role of GSK3β in regulating TJ proteins. Accordingly, phospho-kinase proteome profiler array indicated increased phosphorylation of Akt and GSK3α/β in HIWI2 knockdown, suggesting that HIWI2 might affect TJ proteins through Akt-GSK3α/β signaling axis. Moreover, treating the HIWI2 knockdown cells with wortmannin increased the levels of TJP1 and CLDN1. Taken together, our study demonstrates the presence of PIWI-like proteins in somatic cells and the possible role of HIWI2 in preserving the functional integrity of epithelial cells probably by modulating the phosphorylation status of Akt.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cox DN, Chao A, Baker J et al (1998) A novel class of evolutionarily conserved genes defined by piwi are essential for stem cell self-renewal. Genes Dev 12:3715–3727. doi:10.1101/gad.12.23.3715
Kuramochi-Miyagawa S, Kimura T, Yomogida K et al (2001) Two mouse piwi-related genes: miwi and mili. Mech Dev 108:121–133. doi:10.1016/S0925-4773(01)00499-3
Juliano CE, Reich A, Liu N et al (2013) PIWI proteins and PIWI-interacting RNAs function in hydra somatic stem cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci 111:337–342. doi:10.1073/pnas.1320965111
Reddien PW, Oviedo NJ, Jennings JR et al (2005) SMEDWI-2 is a PIWI-like protein that regulates planarian stem cells. Science 310:1327–1330. doi:10.1126/science.1116110
Kawaoka S, Hayashi N, Suzuki Y et al (2009) The Bombyx ovary-derived cell line endogenously expresses PIWI/PIWI-interacting RNA complexes. RNA 15:1258–1264. doi:10.1261/rna.1452209
Houwing S, Kamminga LM, Berezikov E et al (2007) A role for Piwi and piRNAs in germ cell maintenance and transposon silencing in Zebrafish. Cell 129:69–82. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2007.03.026
Sasaki T, Shiohama A, Minoshima S, Shimizu N (2003) Identification of eight members of the Argonaute family in the human genome☆. Genomics 82:323–330. doi:10.1016/S0888-7543(03)00129-0
Girard A, Sachidanandam R, Hannon GJ, Carmell MA (2006) A germline-specific class of small RNAs binds mammalian Piwi proteins. Nature 442:199–202. doi:10.1038/nature04917
Grivna ST, Beyret E, Wang Z, Lin H (2006) A novel class of small RNAs in mouse spermatogenic cells. Genes Dev 20:1709–1714. doi:10.1101/gad.1434406
Aravin A, Gaidatzis D, Pfeffer S et al (2006) A novel class of small RNAs bind to MILI protein in mouse testes. Nature 442:203–207. doi:10.1038/nature04916
Watanabe T, Takeda A, Tsukiyama T et al (2006) Identification and characterization of two novel classes of small RNAs in the mouse germline: retrotransposon-derived siRNAs in oocytes and germline small RNAs in testes. Genes Dev 20:1732–1743. doi:10.1101/gad.1425706
Deng W, Lin H (2002) miwi, a murine homolog of piwi, encodes a cytoplasmic protein essential for spermatogenesis. Dev Cell 2:819–830. doi:10.1016/S1534-5807(02)00165-X
Palakodeti D, Smielewska M, Lu Y-C et al (2008) The PIWI proteins SMEDWI-2 and SMEDWI-3 are required for stem cell function and piRNA expression in planarians. RNA 14:1174–1186. doi:10.1261/rna.1085008
Qiao D, Zeeman A-M, Deng W et al (2002) Molecular characterization of hiwi, a human member of the piwi gene family whose overexpression is correlated to seminomas. Oncogene 21:3988–3999. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1205505
Al-Janabi O, Wach S, Nolte E et al (2014) Piwi-like 1 and 4 gene transcript levels are associated with clinicopathological parameters in renal cell carcinomas. Biochim Biophys Acta 1842:686–690. doi:10.1016/j.bbadis.2014.01.014
Jiang J, Zhang H, Tang Q et al (2011) Expression of HIWI in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Cell Biochem Biophys 61:53–58. doi:10.1007/s12013-011-9160-1
Liu X, Sun Y, Guo J et al (2006) Expression of hiwi gene in human gastric cancer was associated with proliferation of cancer cells. Int J Cancer 118:1922–1929. doi:10.1002/ijc.21575
Zhang H, Ren Y, Xu H et al (2013) The expression of stem cell protein Piwil2 and piR-932 in breast cancer. Surg Oncol 22:217–223. doi:10.1016/j.suronc.2013.07.001
Wang X, Tong X, Gao H et al (2014) Silencing HIWI suppresses the growth, invasion and migration of glioma cells. Int J Oncol 45:2385–2392
Siddiqi S, Terry M, Matushansky I (2012) Hiwi mediated tumorigenesis is associated with DNA hypermethylation. PLoS ONE 7:e33711. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0033711
Wang Y, Liu Y, Shen X et al (2012) The PIWI protein acts as a predictive marker for human gastric cancer. Int J Clin Exp Pathol 5:315–325
Yin D-T, Wang Q, Chen L et al (2011) Germline stem cell gene PIWIL2 mediates DNA repair through relaxation of chromatin. PLoS ONE 6:e27154. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0027154
Houwing S, Berezikov E, Ketting RF (2008) Zili is required for germ cell differentiation and meiosis in zebrafish. EMBO J 27:2702–2711. doi:10.1038/emboj.2008.204
Zhang K, Lu Y, Yang P et al (2012) HILI inhibits TGF-β signaling by interacting with Hsp90 and promoting TβR degradation. PLoS ONE 7:e41973. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0041973
Lee JH, Schütte D, Wulf G et al (2006) Stem-cell protein Piwil2 is widely expressed in tumors and inhibits apoptosis through activation of Stat3/Bcl-XL pathway. Hum Mol Genet 15:201–211. doi:10.1093/hmg/ddi430
Sugimoto K, Kage H, Aki N et al (2007) The induction of H3K9 methylation by PIWIL4 at the p16Ink4a locus. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 359:497–502. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2007.05.136
Su C, Ren Z-J, Wang F et al (2012) PIWIL4 regulates cervical cancer cell line growth and is involved in down-regulating the expression of p14ARF and p53. FEBS Lett 586:1356–1362. doi:10.1016/j.febslet.2012.03.053
Rajasethupathy P, Antonov I, Sheridan R et al (2012) A role for neuronal piRNAs in the epigenetic control of memory-related synaptic plasticity. Cell 149:693–707. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2012.02.057
Lin H, Yin H (2008) A novel epigenetic mechanism in drosophila somatic cells mediated by Piwi and piRNAs. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol 73:273–281. doi:10.1101/sqb.2008.73.056
Lee EJ, Banerjee S, Zhou H et al (2011) Identification of piRNAs in the central nervous system. RNA 17:1090–1099. doi:10.1261/rna.2565011
Gonzalez J, Qi H, Liu N, Lin H (2015) Piwi is a key regulator of both somatic and germline stem cells in the drosophila testis. Cell Rep 12:150–161. doi:10.1016/j.celrep.2015.06.004
Cheng E-C, Kang D, Wang Z, Lin H (2014) PIWI proteins are dispensable for mouse somatic development and reprogramming of fibroblasts into pluripotent stem cells. PLoS ONE 9:e97821. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0097821
Sharma AK, Nelson MC, Brandt JE et al (2001) Human CD34(+) stem cells express the hiwi gene, a human homologue of the Drosophila gene piwi. Blood 97:426–434
Nolde MJ, Cheng E-C, Guo S, Lin H (2013) Piwi genes are dispensable for normal hematopoiesis in mice. PLoS ONE 8:e71950. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0071950
Kotaja N, Bhattacharyya SN, Jaskiewicz L et al (2006) The chromatoid body of male germ cells: similarity with processing bodies and presence of Dicer and microRNA pathway components. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:2647–2652. doi:10.1073/pnas.0509333103
Rajan KS, Velmurugan G, Pandi G, Ramasamy S (2014) miRNA and piRNA mediated Akt pathway in heart: antisense expands to survive. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 55:153–156. doi:10.1016/j.biocel.2014.09.001
Peng L, Song L, Liu C et al (2015) piR-55490 inhibits the growth of lung carcinoma by suppressing mTOR signaling. Tumour Biol. doi:10.1007/s13277-015-4056-0
Berzal S, Alique M, Ruiz-Ortega M et al (2012) GSK3, snail, and adhesion molecule regulation by cyclosporine A in renal tubular cells. Toxicol Sci 127:425–437. doi:10.1093/toxsci/kfs108
Severson EA, Kwon M, Hilgarth RS et al (2010) Glycogen synthase kinase 3 (GSK-3) influences epithelial barrier function by regulating occludin, claudin-1 and E-cadherin expression. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 397:592–597. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2010.05.164
Chen R, Chang G, Zhang Y et al (2012) Cloning of the quail PIWI gene and characterization of PIWI binding to small RNAs. PLoS ONE 7:e51724. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0051724
Brower-Toland B, Findley SD, Jiang L et al (2007) Drosophila PIWI associates with chromatin and interacts directly with HP1a. Genes Dev 21:2300–2311. doi:10.1101/gad.1564307
Ross RJ, Weiner MM, Lin H (2014) PIWI proteins and PIWI-interacting RNAs in the soma. Nature 505:353–359. doi:10.1038/nature12987
Cunha-Vaz J (2012) Blood-retinal barrier and its relevance in retinal disease. Med Retin 1:6–10. doi:10.1159/000336698
Matter K, Balda MS (2003) Signalling to and from tight junctions. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 4:225–236. doi:10.1038/nrm1055
González-Mariscal L, Tapia R, Chamorro D (2008) Crosstalk of tight junction components with signaling pathways. Biochim Biophys Acta Biomembr 1778:729–756. doi:10.1016/j.bbamem.2007.08.018
Kim B, Breton S (2016) The MAPK/ERK-signaling pathway regulates the expression and distribution of tight junction proteins in the mouse proximal epididymis. Biol Reprod 94:22. doi:10.1095/biolreprod.115.134965
Bachelder RE, Yoon S-O, Franci C et al (2005) Glycogen synthase kinase-3 is an endogenous inhibitor of Snail transcription: implications for the epithelial-mesenchymal transition. J Cell Biol 168:29–33. doi:10.1083/jcb.200409067
Ohkubo T, Ozawa M (2004) The transcription factor Snail downregulates the tight junction components independently of E-cadherin downregulation. J Cell Sci 117:1675–1685. doi:10.1242/jcs.01004
Huang XA, Yin H, Sweeney S et al (2013) A major epigenetic programming mechanism guided by piRNAs. Dev Cell 24:502–516. doi:10.1016/j.devcel.2013.01.023
Chen Z, Che Q, Jiang F-Z et al (2015) Piwil1 causes epigenetic alteration of PTEN gene via upregulation of DNA methyltransferase in type I endometrial cancer. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 463:876–880. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2015.06.028
Gebert D, Ketting RF, Zischler H, Rosenkranz D (2015) piRNAs from pig testis provide evidence for a conserved role of the piwi pathway in post-transcriptional gene regulation in mammals. PLoS ONE 10:e0124860. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0124860
Xu H-Z, Le Y-Z (2011) Significance of outer blood-retina barrier breakdown in diabetes and ischemia. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 52:2160–2164. doi:10.1167/iovs.10-6518
Jacot JL, Sherris D (2011) Potential therapeutic roles for inhibition of the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway in the pathophysiology of diabetic retinopathy. J Ophthalmol 2011:589813. doi:10.1155/2011/589813
Friemel C, Ammerpohl O, Gutwein J et al (2014) Array-based DNA methylation profiling in male infertility reveals allele-specific DNA methylation in PIWIL1 and PIWIL2. Fertil Steril 101(1097–1103):e1. doi:10.1016/j.fertnstert.2013.12.054
Suzuki R, Honda S, Kirino Y (2012) PIWI expression and function in cancer. Front Genet 3:204. doi:10.3389/fgene.2012.00204
Srinivasan V, Palanisamy K, Karunakaran C et al (2014) Expression and localisation of adiponectin and its receptors in human ocular tissues. Int J Pharma Bio Sci 5:639–646
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge the financial assistance provided by Department of Science and Technology under the project “SR/FT/LS-145/2010”, Indian Council of Medical Research “BMS/FW/BIOCHEM/2015-23270/OCT-2015/24/TN/PVT” and Max Planck-India mobility grant ‘IGSTC/MPG/FS(SC)2012’. CS thanks University Grants Commission, New Delhi for the award of Assistant Professorship under its Faculty Recharge Program (UGC-FRP). We acknowledge the facilities, the scientific technical assistance of Advanced Microscopy facility at NCTB, Department of Biotechnology, IIT Madras, Chennai, India. We thank Dr. R.Baskaran, Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Pondicherry University, for critical reading of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interests
The authors declare that no conflict of interests exist.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Human and animal rights statement
All applicable international, national, and/or institutional guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed. If applicable (where such a committee exists): “All procedures performed in studies involving animals were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institution or practice at which the studies were conducted.”
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
11010_2016_2906_MOESM1_ESM.tif
Supplementary material 1: S1 figure. Specificity of the primers. a) Agarose gel images showing the specificity of the primers. b) Melting curve of the real time PCR primers showing the amplification was only due to PIWIL transcripts (TIFF 3196 kb)
11010_2016_2906_MOESM2_ESM.tif
Supplementary material 2: S2 figure. Validation of HIWI and HILI antibodies. a) Expression of HIWI in rat testis and rat liver as a positive and negative control respectively. The band at 99 kDa in rat testis has reduced intensity when the HIWI antibody was incubated with the respective blocking peptide. b) Expression of HILI in rat testis and rat liver as a positive and negative control respectively. The band at 110 kDa in rat testis has reduced intensity when the HILI antibody was incubated with the respective blocking peptide. (Positive control (PC) – rat testis; Negative control (NC)—Rat liver; BP—blocking peptide). (TIFF 1947 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sivagurunathan, S., Palanisamy, K., Arunachalam, J.P. et al. Possible role of HIWI2 in modulating tight junction proteins in retinal pigment epithelial cells through Akt signaling pathway. Mol Cell Biochem 427, 145–156 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-016-2906-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-016-2906-8