Abstract
P-selectin-mediated tumor cell adhesion to platelets is a well-established stage in the process of tumor metastasis. Through computerized structural analysis, we found a marine-derived polysaccharide, holothurian glycosaminoglycan (hGAG), behaved as a ligand-competitive inhibitor of P-selectin, indicating its potential to disrupt the binding of P-selectin to cell surface receptor and activation of downstream regulators of tumor cell migration. Our experimental data demonstrated that hGAG significantly inhibited P-selectin-mediated adhesion of tumor cells to platelets and tumor cell migration in vitro and reduced subsequent pulmonary metastasis in vivo. Furthermore, abrogation of the P-selectin-mediated adhesion of tumor cells led to down-regulation of protein levels of integrins, FAK and MMP-2/9 in B16F10 cells, which is a crucial molecular mechanism of hGAG to inhibit tumor metastasis. In conclusion, hGAG has emerged as a novel anti-cancer agent via blocking P-selectin-mediated malignant events of tumor metastasis.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Das Thakur M, Salangsang F, Landman AS, Sellers WR, Pryer NK, Levesque MP, Dummer R, McMahon M, Stuart DD (2013) Modelling vemurafenib resistance in melanoma reveals a strategy to forestall drug resistance. Nature 494(7436):251–255
Mervic L (2012) Time course and pattern of metastasis of cutaneous melanoma differ between men and women. PLoS One 7(3):e32955
Erpenbeck L, Schon MP (2010) Deadly allies: the fatal interplay between platelets and metastasizing cancer cells. Blood 115(17):3427–3436
Gay LJ, Felding-Habermann B (2011) Contribution of platelets to tumour metastasis. Nat Rev Cancer 11(2):123–134
Tsuruo T, Fujita N (2008) Platelet aggregation in the formation of tumor metastasis. Proc Jpn Acad Ser B Phys Biol Sci 84(6):189–198
Bendas G, Borsig L (2012) Cancer cell adhesion and metastasis: selectins, integrins, and the inhibitory potential of heparins. Int J Cell Biol 2012:676731
Bambace NM, Holmes CE (2011) The platelet contribution to cancer progression. J Thromb Haemost 9(2):237–249
Chen C, He Z, Sai P, Faridi A, Aziz A, Kalavar M, Griciene P, Gintautas J, Steier W (2004) Inhibition of human CD24 binding to platelet-bound P-selectin by monoclonal antibody. Proc West Pharmacol Soc 47:28–29
Garcia J, Callewaert N, Borsig L (2007) P-selectin mediates metastatic progression through binding to sulfatides on tumor cells. Glycobiology 17(2):185–196
Mi D, Gao Y, Zheng S, Ba X, Zeng X (2009) Inhibitory effects of chemically modified heparin on the P-selectin-mediated adhesion of breast cancer cells in vitro. Mol Med Rep 2(2):301–306
Raman PS, Alves CS, Wirtz D, Konstantopoulos K (2011) Single-molecule binding of CD44 to fibrin versus P-selectin predicts their distinct shear-dependent interactions in cancer. J Cell Sci 124(Pt 11):1903–1910
Ma YQ, Geng JG (2000) Heparan sulfate-like proteoglycans mediate adhesion of human malignant melanoma A375 cells to P-selectin under flow. J Immunol 165(1):558–565
Ferroni P, Roselli M, Martini F, D’Alessandro R, Mariotti S, Basili S, Spila A, Aloe S, Palmirotta R, Maggini A, Del Monte G, Mancini R, Graziano F, Cosimelli M, Guadagni F (2004) Prognostic value of soluble P-selectin levels in colorectal cancer. Int J Cancer 111(3):404–408
Qi CL, Wei B, Ye J, Yang Y, Li B, Zhang QQ, Li JC, He XD, Lan T, Wang LJ (2014) P-selectin-mediated platelet adhesion promotes the metastasis of murine melanoma cells. PLoS One 9(3):e91320
Chen M, Geng JG (2006) P-selectin mediates adhesion of leukocytes, platelets, and cancer cells in inflammation, thrombosis, and cancer growth and metastasis. Arch Immunol Ther Exp 54(2):75–84
Reyes-Reyes EM, Akiyama SK (2008) Cell-surface nucleolin is a signal transducing P-selectin binding protein for human colon carcinoma cells. Exp Cell Res 314(11–12):2212–2223
Reyes-Reyes ME, George MD, Roberts JD, Akiyama SK (2006) P-selectin activates integrin-mediated colon carcinoma cell adhesion to fibronectin. Exp Cell Res 312(20):4056–4069
Kim YJ, Borsig L, Varki NM, Varki A (1998) P-selectin deficiency attenuates tumor growth and metastasis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95(16):9325–9330
Borsig L, Wong R, Hynes RO, Varki NM, Varki A (2002) Synergistic effects of L- and P-selectin in facilitating tumor metastasis can involve non-mucin ligands and implicate leukocytes as enhancers of metastasis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99(4):2193–2198
Laubli H, Stevenson JL, Varki A, Varki NM, Borsig L (2006) L-selectin facilitation of metastasis involves temporal induction of Fut7-dependent ligands at sites of tumor cell arrest. Cancer Res 66(3):1536–1542
Laubli H, Borsig L (2010) Selectins as mediators of lung metastasis. Cancer Microenviron 3(1):97–105
Gao Y, Wei M, Zheng S, Ba X, Hao S, Zeng X (2006) Chemically modified heparin inhibits the in vitro adhesion of nonsmall cell lung cancer cells to P-selectin. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 132(4):257–264
Kozlowski EO, Pavao MS, Borsig L (2011) Ascidian dermatan sulfates attenuate metastasis, inflammation and thrombosis by inhibition of P-selectin. J Thromb Haemost 9(9):1807–1815
Sasisekharan R, Shriver Z, Venkataraman G, Narayanasami U (2002) Roles of heparan-sulphate glycosaminoglycans in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 2(7):521–528
Borsig L, Wong R, Feramisco J, Nadeau DR, Varki NM, Varki A (2001) Heparin and cancer revisited: mechanistic connections involving platelets, P-selectin, carcinoma mucins, and tumor metastasis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98(6):3352–3357
Schlesinger M, Roblek M, Ortmann K, Naggi A, Torri G, Borsig L, Bendas G (2014) The role of VLA-4 binding for experimental melanoma metastasis and its inhibition by heparin. Thromb Res 133(5):855–862
Li Y, Luo JY, Cui HF, Zheng L, Du SS (2010) Study on anti-metastasis of heparin derivatives as ligand antagonist of p-selectin. Biomed Pharmacother 64(10):654–658
Zhao Y, Zhang D, Wang S, Tao L, Wang A, Chen W, Zhu Z, Zheng S, Gao X, Lu Y (2013) Holothurian glycosaminoglycan inhibits metastasis and thrombosis via targeting of nuclear factor-kappaB/tissue factor/factor Xa pathway in melanoma B16F10 cells. PLoS One 8(2):e56557
Zhang W, Lu Y, Xu B, Wu J, Zhang L, Gao M, Zheng S, Wang A, Zhang C, Chen L, Lei N (2009) Acidic mucopolysaccharide from Holothuria leucospilota has antitumor effect by inhibiting angiogenesis and tumor cell invasion in vivo and in vitro. Cancer Biol Ther 8(15):1489–1499
Liang D, Jia W, Li J, Li K, Zhao Q (2012) Retinoic acid signaling plays a restrictive role in zebrafish primitive myelopoiesis. PLoS One 7(2):e30865
Rouhi P, Jensen LD, Cao Z, Hosaka K, Lanne T, Wahlberg E, Steffensen JF, Cao Y (2010) Hypoxia-induced metastasis model in embryonic zebrafish. Nat Protoc 5(12):1911–1918
McDermott KM, Crocker PR, Harris A, Burdick MD, Hinoda Y, Hayashi T, Imai K, Hollingsworth MA (2001) Overexpression of MUC1 reconfigures the binding properties of tumor cells. Int J Cancer 94(6):783–791
Xu J, Cai J, Anderson B, Wagner B, Albrecht R, Peek SF, Suresh M, Darien BJ (2007) Cloning and functional characterization of recombinant equine P-selectin. Vet Immunol Immunopathol 116(3–4):115–130
Hostettler N, Naggi A, Torri G, Ishai-Michaeli R, Casu B, Vlodavsky I, Borsig L (2007) P-selectin- and heparanase-dependent antimetastatic activity of non-anticoagulant heparins. FASEB J 21(13):3562–3572
Ludwig RJ, Schon MP, Boehncke WH (2007) P-selectin: a common therapeutic target for cardiovascular disorders, inflammation and tumour metastasis. Expert Opin Ther Targ 11(8):1103–1117
Barkalow FJ, Barkalow KL, Mayadas TN (2000) Dimerization of P-selectin in platelets and endothelial cells. Blood 96(9):3070–3077
Koedam JA, Cramer EM, Briend E, Furie B, Furie BC, Wagner DD (1992) P-selectin, a granule membrane protein of platelets and endothelial cells, follows the regulated secretory pathway in AtT-20 cells. J Cell Biol 116(3):617–625
Felding-Habermann B, Habermann R, Saldivar E, Ruggeri ZM (1996) Role of beta3 integrins in melanoma cell adhesion to activated platelets under flow. J Biol Chem 271(10):5892–5900
Shin S, Wolgamott L, Yoon SO (2012) Integrin trafficking and tumor progression. Int J Cell Biol 2012:516789
Shibue T, Weinberg RA (2009) Integrin beta1-focal adhesion kinase signaling directs the proliferation of metastatic cancer cells disseminated in the lungs. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106(25):10290–10295
Mitra SK, Schlaepfer DD (2006) Integrin-regulated FAK-Src signaling in normal and cancer cells. Curr Opin Cell Biol 18(5):516–523
Golubovskaya VM (2010) Focal adhesion kinase as a cancer therapy target. Anti-Cancer Agents Med Chem 10(10):735–741
Varki A, Varki NM (2001) P-selectin, carcinoma metastasis and heparin: novel mechanistic connections with therapeutic implications. Braz J Med Biol Res 34(6):711–717
Varki NM, Varki A (2002) Heparin inhibition of selectin-mediated interactions during the hematogenous phase of carcinoma metastasis: rationale for clinical studies in humans. Semin Thromb Hemost 28(1):53–66
Wei M, Tai G, Gao Y, Li N, Huang B, Zhou Y, Hao S, Zeng X (2004) Modified heparin inhibits P-selectin-mediated cell adhesion of human colon carcinoma cells to immobilized platelets under dynamic flow conditions. J Biol Chem 279(28):29202–29210
Borsig L, Wang L, Cavalcante MC, Cardilo-Reis L, Ferreira PL, Mourao PA, Esko JD, Pavao MS (2007) Selectin blocking activity of a fucosylated chondroitin sulfate glycosaminoglycan from sea cucumber. Effect on tumor metastasis and neutrophil recruitment. J Biol Chem 282(20):14984–14991
Stevenson JL, Varki A, Borsig L (2007) Heparin attenuates metastasis mainly due to inhibition of P- and L-selectin, but non-anticoagulant heparins can have additional effects. Thromb Res 120(Suppl 2):S107–S111
Borsig L (2007) Antimetastatic activities of modified heparins: selectin inhibition by heparin attenuates metastasis. Semin Thromb Hemost 33(5):540–546
Stone JP, Wagner DD (1993) P-selectin mediates adhesion of platelets to neuroblastoma and small cell lung cancer. J Clin Investig 92(2):804–813
Wong CH, MorisVara F, Hung SC, Marron TG, Lin CC, Gong KW, WeitzSchmidt G (1997) Small molecules as structural and functional mimics of sialyl Lewis X tetrasaccharide in selectin inhibition: a remarkable enhancement of inhibition by additional negative charge and/or hydrophobic group. J Am Chem Soc 119(35):8152–8158
Acknowledgments
This Project was supported in part by National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 81173174, 81202655), Doctoral Program of the Ministry of Education (20113237110008), 2013’ Program for Excellent Scientific and Technological Innovation Team of Jiangsu Higher Education, Jiangsu Ordinary University Graduate Students Scientific Research Innovation Program (CXLX11-0772), and a project of the Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions (PAPD).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that no competing interests exist.
Additional information
Zhiqiang Yue and Aiyun Wang have contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary Fig. 1
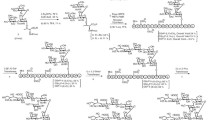
Plot of hGAG interaction between TGF-β (a), PDGF-B (b), TNF-α (c), vWF (d), ADP (e), Platelet factor 4 (f), GPIIb/IIIa (g), Thrombin (h) and Thromboxane A2 (i). hGAG is shown in ball and stick fashion, putative hydrogen bonds are shown as green dashed lines, and residues involved in hydrogen bond formation are shown in flat lines
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yue, Z., Wang, A., Zhu, Z. et al. Holothurian glycosaminoglycan inhibits metastasis via inhibition of P-selectin in B16F10 melanoma cells. Mol Cell Biochem 410, 143–154 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-015-2546-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-015-2546-4