Abstract
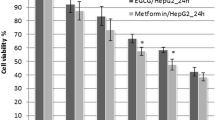
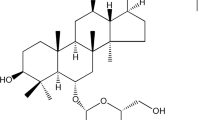
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), the major histological subtype of primary liver cancer, remains one of the most common malignancies worldwide. Due to the complicated pathogenesis of this malignancy, the outcome for comprehensive treatment is limited. Chinese herbal medicine (CHM) is emerging as a promising choice for its multi-targets and coordinated intervention effects against HCC. Ursolic acid (UA), a natural pentacyclic triterpenoid carboxylic acid found in CHM, exerts anti-tumor effects and is emerging as an effective compound for cancer prevention and therapy. However, the molecular mechanisms underlying the action of UA remain largely unknown. In this study, we showed that UA inhibited the growth of HCC cells and induced apoptosis in the dose- and time-dependent fashion. Furthermore, we found that UA induced phosphorylation of AMP-activated protein kinase alpha (AMPKα) and suppressed the protein expression of DNA methyltransferase 1 (DNMT1) in the dose-dependent manner. The inhibitor of AMPK, compound C blocked, while an activator of AMPK, metformin augmented the effect of UA on DNMT1 expression. In addition, UA suppressed the expression of transcription factor Sp1. Conversely, overexpression of Sp1 reversed the effect of UA on DNMT1 expression and cell growth. Collectively, our results show for the first time that UA inhibits growth of HCC through AMPKα-mediated inhibition of Sp1; this in turn results in inhibition of DNMT1. This study reveals a potential novel mechanism by which UA controls growth of HCC cells and suggests that DNMT1 could be novel target for HCC chemoprevention and treatment.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
El-S HB (2011) Hepatocellular carcinoma. N Engl J Med 365:1118–1127. doi:10.1056/NEJMra1001683
Siegel R, Ma J, Zou Z, Jemal A (2014) Cancer statistics, 2014. CA Cancer J Clin 64:9–29. doi:10.3322/caac.21208
Bush DA, Kayali Z, Grove R, Slater JD (2011) The safety and efficacy of high-dose proton beam radiotherapy for hepatocellular carcinoma: a phase 2 prospective trial. Cancer 117:3053–3059. doi:10.1002/cncr.25809
Sun B, Meng J, Xiang T, Chen Z, Li Y, Lu L, Zhang S, Chen X (2013) Jianpijiedu fang improves survival of hepatocarcinoma mice by affecting phosphatase and tensin homolog, phosphoinositide 3-kinase, and focal adhesion kinase. J Tradit Chin Med 33:479–485
Hu F, Han J, Zhai B, Ming X, Zhuang L, Liu Y, Pan S, Liu T (2014) Blocking autophagy enhances the apoptosis effect of bufalin on human hepatocellular carcinoma cells through endoplasmic reticulum stress and JNK activation. Apoptosis 19:210–223. doi:10.1007/s10495-013-0914-7
Wang S, Wang J, Lin P, Li Z, Yao C, Chang G, Li X (2013) Short-term curative effect of endovascular stent-graft treatment for aortic diseases in China: a systematic review. PLoS One 8:e71012. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0071012
Hu Y, Wang S, Wu X, Zhang J, Chen R, Chen M, Wang Y (2013) Chinese herbal medicine-derived compounds for cancer therapy: a focus on hepatocellular carcinoma. J Ethnopharmacol 149:601–612. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2013.07.030
Li X, Zhang J, Gao W, Wang H (2012) Study on chemical composition, anti-inflammatory and anti-microbial activities of extracts from Chinese pear fruit (Pyrus bretschneideri Rehd.). Food Chem Toxicol 50:3673–3679. doi:10.1016/j.fct.2012.07.019
Kong L, Li S, Liao Q, Zhang Y, Sun R, Zhu X, Zhang Q, Wang J, Wu X, Fang X, Zhu Y (2013) Oleanolic acid and ursolic acid: novel hepatitis C virus antivirals that inhibit NS5B activity. Antiviral Res 98:44–53. doi:10.1016/j.antiviral.2013.02.003
Zang LL, Wu BN, Lin Y, Wang J, Fu L, Tang ZY (2014) Research progress of ursolic acid’s anti-tumor actions. Chin J Integr Med 20:72–79. doi:10.1007/s11655-013-1541-4
Liu W, Tan X, Shu L, Sun H, Song J, Jin P, Yu S, Sun M, Jia X (2012) Ursolic acid inhibits cigarette smoke extract-induced human bronchial epithelial cell injury and prevents development of lung cancer. Molecules 17:9104–9115. doi:10.3390/molecules17089104
Tang Q, Ji Q, Tang Y, Chen T, Pan G, Hu S, Bao Y, Peng W, Yin P (2014) Mitochondrial translocation of cofilin-1 promotes apoptosis of gastric cancer BGC-823 cells induced by ursolic acid. Tumour Biol 35:2451–2459. doi:10.1007/s13277-013-1325-7
Li J, Liang X, Yang X (2012) Ursolic acid inhibits growth and induces apoptosis in gemcitabine-resistant human pancreatic cancer via the JNK and PI3K/Akt/NF-kappaB pathways. Oncol Rep 28:501–510. doi:10.3892/or.2012.1827
Son HS, Kwon HY, Sohn EJ, Lee JH, Woo HJ, Yun M, Kim SH, Kim YC (2013) Activation of AMP-activated protein kinase and phosphorylation of glycogen synthase kinase3 beta mediate ursolic acid induced apoptosis in HepG2 liver cancer cells. Phytother Res 27:1714–1722. doi:10.1002/ptr.4925
Wang J, Liu L, Qiu H, Zhang X, Guo W, Chen W, Tian Y, Fu L, Shi D, Cheng J, Huang W, Deng W (2013) Ursolic acid simultaneously targets multiple signaling pathways to suppress proliferation and induce apoptosis in colon cancer cells. PLoS One 8:e63872. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0063872
Scott A, Song J, Ewing R, Wang Z (2014) Regulation of protein stability of DNA methyltransferase 1 by post-translational modifications. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai) 46:199–203. doi:10.1093/abbs/gmt146
Mudbhary R, Hoshida Y, Chernyavskaya Y, Jacob V, Villanueva A, Fiel MI, Chen X, Kojima K, Thung S, Bronson RT, Lachenmayer A, Revill K, Alsinet C, Sachidanandam R, Desai A, SenBanerjee S, Ukomadu C, Llovet JM, Sadler KC (2014) UHRF1 overexpression drives DNA hypomethylation and hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Cell 25:196–209. doi:10.1016/j.ccr.2014.01.003
Azizi M, Teimoori-Toolabi L, Arzanani MK, Azadmanesh K, Fard-Esfahani P, Zeinali S (2014) MicroRNA-148b and microRNA-152 reactivate tumor suppressor genes through suppression of DNA methyltransferase-1 gene in pancreatic cancer cell lines. Cancer Biol Ther 15(4):419–427
Gao J, Wang L, Xu J, Zheng J, Man X, Wu H, Jin J, Wang K, Xiao H, Li S, Li Z (2013) Aberrant DNA methyltransferase expression in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma development and progression. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 32:86. doi:10.1186/1756-9966-32-86
Fan H, Zhao ZJ, Cheng J, Su XW, Wu QX, Shan YF (2009) Overexpression of DNA methyltransferase 1 and its biological significance in primary hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol 15:2020–2026
Flis S, Gnyszka A, Flis K (2014) DNA methyltransferase inhibitors improve the effect of chemotherapeutic agents in SW48 and HT-29 colorectal cancer cells. PLoS One 9:e92305. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0092305
Konac E, Varol N, Yilmaz A, Menevse S, Sozen S (2013) DNA methyltransferase inhibitor-mediated apoptosis in the Wnt/beta-catenin signal pathway in a renal cell carcinoma cell line. Exp Biol Med (Maywood) 238:1009–1016. doi:10.1177/1535370213498984
Nakamura K, Aizawa K, Nakabayashi K, Kato N, Yamauchi J, Hata K, Tanoue A (2013) DNA methyltransferase inhibitor zebularine inhibits human hepatic carcinoma cells proliferation and induces apoptosis. PLoS One 8:e54036. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0054036
Zheng F, Tang Q, Wu J, Zhao S, Liang Z, Li L, Wu W, Hann S (2014) p38alpha MAPK-mediated induction and interaction of FOXO3a and p53 contribute to the inhibited-growth and induced-apoptosis of human lung adenocarcinoma cells by berberine. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 33:36. doi:10.1186/1756-9966-33-36
Kambe A, Iguchi G, Moon Y, Kamitani H, Watanabe T, Eling TE (2008) Regulation of EP4 expression via the Sp-1 transcription factor: inhibition of expression by anti-cancer agents. Biochim Biophys Acta 1783:1211–1219. doi:10.1016/j.bbamcr.2008.01.032
Hann SS, Tang Q, Zheng F, Zhao S, Chen J, Wang Z (2014) Repression of phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase 1 expression by ciglitazone via Egr-1 represents a new approach for inhibition of lung cancer cell growth. Mol Cancer 13:149. doi:10.1186/1476-4598-13-149
Yu Z, Xiao Q, Zhao L, Ren J, Bai X, Sun M, Wu H, Liu X, Song Z, Yan Y, Mi X, Wang E, Jin F, Wei M (2014) DNA methyltransferase 1/3a overexpression in sporadic breast cancer is associated with reduced expression of estrogen receptor-alpha/breast cancer susceptibility gene 1 and poor prognosis. Mol Carcinog. doi:10.1002/mc.22133
Liu WB, Cui ZH, Ao L, Zhou ZY, Zhou YH, Yuan XY, Xiang YL, Liu JY, Cao J (2011) Aberrant methylation accounts for cell adhesion-related gene silencing during 3-methylcholanthrene and diethylnitrosamine induced multistep rat lung carcinogenesis associated with overexpression of DNA methyltransferases 1 and 3a. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 251:70–78. doi:10.1016/j.taap.2010.12.002
Lin RK, Wu CY, Chang JW, Juan LJ, Hsu HS, Chen CY, Lu YY, Tang YA, Yang YC, Yang PC, Wang YC (2010) Dysregulation of p53/Sp1 control leads to DNA methyltransferase-1 overexpression in lung cancer. Cancer Res 70:5807–5817. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-09-4161
Huang SK, Scruggs AM, Donaghy J, McEachin RC, Fisher AS, Richardson BC, Peters-Golden M (2012) Prostaglandin E(2) increases fibroblast gene-specific and global DNA methylation via increased DNA methyltransferase expression. FASEB J 26:3703–3714. doi:10.1096/fj.11-203323
Li X, Shen Q, Zhang D, Mei X, Ran W, Xu Y, Yu G (2013) Functional groups determine biochar properties (pH and EC) as studied by two-dimensional C NMR correlation spectroscopy. PLoS One 8:e65949. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0065949
Hoenerhoff MJ, Pandiri AR, Snyder SA, Hong HH, Ton TV, Peddada S, Shockley K, Witt K, Chan P, Rider C, Kooistra L, Nyska A, Sills RC (2013) Hepatocellular carcinomas in B6C3F1 mice treated with Ginkgo biloba extract for two years differ from spontaneous liver tumors in cancer gene mutations and genomic pathways. Toxicol Pathol 41:826–841. doi:10.1177/0192623312467520
Prasad S, Yadav VR, Sung B, Reuter S, Kannappan R, Deorukhkar A, Diagaradjane P, Wei C, Baladandayuthapani V, Krishnan S, Guha S, Aggarwal BB (2012) Ursolic acid inhibits growth and metastasis of human colorectal cancer in an orthotopic nude mouse model by targeting multiple cell signaling pathways: chemosensitization with capecitabine. Clin Cancer Res 18:4942–4953. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.ccr-11-2805
Yu YX, Gu ZL, Yin JL, Chou WH, Kwok CY, Qin ZH, Liang ZQ (2010) Ursolic acid induces human hepatoma cell line SMMC-7721 apoptosis via p53-dependent pathway. Chin Med J (Engl) 123:1915–1923
Liang J, Mills GB (2013) AMPK: a contextual oncogene or tumor suppressor? Cancer Res 73:2929–2935. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-12-3876
He Y, Li Y, Zhao T, Wang Y, Sun C (2013) Ursolic acid inhibits adipogenesis in 3T3-L1 adipocytes through LKB1/AMPK pathway. PLoS One 8:e70135. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0070135
Zheng QY, Jin FS, Yao C, Zhang T, Zhang GH, Ai X (2012) Ursolic acid-induced AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) activation contributes to growth inhibition and apoptosis in human bladder cancer T24 cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 419:741–747. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2012.02.093
Liu X, Goldstein AS (2014) Inflammation promotes prostate differentiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 111:1666–1667. doi:10.1073/pnas.1323181111
Sontag RL, Weber TJ (2012) Ectopic ERK expression induces phenotypic conversion of C10 cells and alters DNA methyltransferase expression. BMC Res Notes 5:217. doi:10.1186/1756-0500-5-217
Kassis ES, Zhao M, Hong JA, Chen GA, Nguyen DM, Schrump DS (2006) Depletion of DNA methyltransferase 1 and/or DNA methyltransferase 3b mediates growth arrest and apoptosis in lung and esophageal cancer and malignant pleural mesothelioma cells. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 131:298–306. doi:10.1016/j.jtcvs.2005.05.022
Takata A, Otsuka M, Yoshikawa T, Kishikawa T, Hikiba Y, Obi S, Goto T, Kang YJ, Maeda S, Yoshida H, Omata M, Asahara H, Koike K (2013) MicroRNA-140 acts as a liver tumor suppressor by controlling NF-kappaB activity by directly targeting DNA methyltransferase 1 (Dnmt1) expression. Hepatology 57:162–170. doi:10.1002/hep.26011
Brodie SA, Li G, El-Kommos A, Kang H, Ramalingam SS, Behera M, Gandhi K, Kowalski J, Sica GL, Khuri FR, Vertino PM, Brandes JC (2014) Class I HDACs are mediators of smoke carcinogen-induced stabilization of DNMT1 and serve as promising targets for chemoprevention of lung cancer. Cancer Prev Res (Phila) 7:351–361. doi:10.1158/1940-6207.CAPR-13-0254
Wang W, Cheng X, Lu J, Wei J, Fu G, Zhu F, Jia C, Zhou L, Xie H, Zheng S (2010) Mitofusin-2 is a novel direct target of p53. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 400:587–592. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2010.08.108
Huang J, Wang Y, Guo Y, Sun S (2010) Down-regulated microRNA-152 induces aberrant DNA methylation in hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting DNA methyltransferase 1. Hepatology 52:60–70. doi:10.1002/hep.23660
Saito Y, Kanai Y, Nakagawa T, Sakamoto M, Saito H, Ishii H, Hirohashi S (2003) Increased protein expression of DNA methyltransferase (DNMT) 1 is significantly correlated with the malignant potential and poor prognosis of human hepatocellular carcinomas. Int J Cancer 105:527–532. doi:10.1002/ijc.11127
Karpe PA, Tikoo K (2014) Heat shock prevents insulin resistance-induced vascular complications by augmenting angiotensin-(1-7) signaling. Diabetes 63:1124–1139. doi:10.2337/db13-1267
Chai G, Li L, Zhou W, Wu L, Zhao Y, Wang D, Lu S, Yu Y, Wang H, McNutt MA, Hu YG, Chen Y, Yang Y, Wu X, Otterson GA, Zhu WG (2008) HDAC inhibitors act with 5-aza-2′-deoxycytidine to inhibit cell proliferation by suppressing removal of incorporated abases in lung cancer cells. PLoS One 3:e2445. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0002445
Li J, Zou WX, Chang KS (2014) Inhibition of Sp1 functions by its sequestration into PML nuclear bodies. PLoS One 9:e94450. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0094450
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to Dr. Thomas E Eling (NIEHS, USA) for providing the Sp1 expression vectors. This work was supported in part by the Specific Science and Technology Research Fund from Guangdong Provincial Hospital of Chinese Medicine (Grant No. YK2013B2N13), the Research Fund from Guangdong Province Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine (Grant No. 20132149), the Special Science and Technology Join fund from Guangdong Provincial Department of Science and Technology-Guangdong Academy of Traditional Chinese Medicine (Grant No. 2012A032500011), and a grant from the National Nature Scientific Foundation of China (Grant No. 81272614).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Yinyi Yie and Shunyu Zhao have contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yie, Y., Zhao, S., Tang, Q. et al. Ursolic acid inhibited growth of hepatocellular carcinoma HepG2 cells through AMPKα-mediated reduction of DNA methyltransferase 1. Mol Cell Biochem 402, 63–74 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-014-2314-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-014-2314-x