Abstract
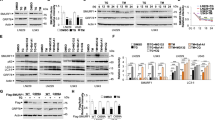
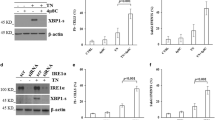
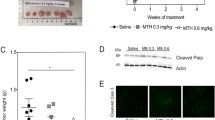
The mammalian unfolded protein response (UPR) protects the cell against the stress of misfolded proteins in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER). Failure to adapt to ER stress causes the UPR to trigger apoptosis. Inositol-requiring enzyme-1α (IRE1α), as one of three unfolded protein sensors in UPR signaling pathways, senses ER unfolded proteins through an ER lumenal domain that becomes oligomerized during ER stress. It is known to be important for ER stress-mediated apoptosis and cell growth, but the exact molecular mechanism underlying these processes remains unexplored. In this study, we report that knockdown of IRE1α by an siRNA silencing approach enhanced, whereas its overexpression inhibited, cell proliferation in Hepatoma cells. Besides, overexpression of IRE1α induced, while its repression inhibited, ER stress-mediated apoptosis in Hepatomas cells. Furthermore, we found that overexpressed IRE1α can down-regulate Polo-like kinase 1(PLK1) from mRNA and protein two levels. IRE1α-mediated induction of apoptosis and inhibition of proliferation in response to ER stress is through downregulation PLK1, an early trigger for G2/M transition known to be participated in regulating cell proliferation and cell apoptosis. Collectively, these findings reveal a novel critical role of IRE1α in ER stress-mediated apoptosis and the molecular mechanisms involved. IRE1α may be a useful molecular target for the development of novel predictive and therapeutic strategies in cancer.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Korennykh AV, Egea PF, Korostelev AA, Finer-Moore J, Zhang C, Shokat KM, Stroud RM, Walter P (2009) The unfolded protein response signals through high-order assembly of Ire1. Nature 457(7230):687–693
Back SH, Lee K, Vink E, Kaufman RJ (2006) Cytoplasmic IRE1alpha-mediated XBP1 mRNA splicing in th absence of nuclear processing and endoplasmic reticulum stress. J Biol Chem 281(27):18691–18706
Marciniak SJ, Ron D (2006) Endoplasmic reticulum stress signaling in disease. Physiol Rev 86(4):1133–1149
Hotamisligil GS (2010) Endoplasmic reticulum stress and the inflammatory basis of metabolic disease. Cell 140(6):900–917
Kaser A, Lee AH, Franke A, Glickman JN, Zeissig S, Tilg H, Nieuwenhuis EE, Higgins DE, Schreiber S, Glimcher LH, Blumberg RS (2008) XBP1 links ER stress to intestinal inflammation and confers genetic risk for human inflammatory bowel disease. Cell 134(5):743–756
Zhang K, Kaufman RJ (2004) Signaling the unfolded protein response from the endoplasmic reticulum. J Biol Chem 279(25):25935–25938
Urano F, Wang X, Bertolotti A et al (2000) Coupling of stress in the ER to activation of JNK protein kinases by transmembrane protein kinase IRE1. Science 287(5453):664–666
Yoshida H, Oku M, Suzuki M, Mori K (2006) pXBP1(U) encoded in XBP1 pre-mRNA negatively regulates unfolded protein response activator pXBP1(S) in mammalian ER stress response. J Cell Biol 172(4):565–575
van de Weerdt BC, Medema RH (2006) Polo-like kinases: a team in control of the division. Cell Cycle 5(8):853–864
Petronczki M, Lenart P, Peters JM (2008) Polo on the rise-from mitotic entry to cytokinesis with Plk1. Dev Cell 14(5):646–659
Feng YB, Lin DC, Shi ZZ, Wang XC, Shen XM, Zhang Y, Du XL, Luo ML, Xu X, Han YL et al (2009) Overexpression of PLK1 is associated with poor survival by inhibiting apoptosis via enhancement of survivin level in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Cancer 124(3):578–588
Lin JH, Li H, Yasumura D, Cohen HR, Zhang C, Panning B, Shokat KM, Lavail MM, Walter P (2007) IRE1 signaling affects cell fate during the unfolded protein response. Science 318(5852):944–949
Fulda S, Gorman AM, Hori O, Samali A (2010) Cellular stress responses: cell survival and cell death. Int J Cell Biol 2010:214074. Epub 2010 Feb 21
Qiu Y, Mao T, Zhang Y, Shao M, You J, Ding Q, Chen Y, Wu D, Xie D, Lin X, Gao X, Kaufman RJ, Li W, Liu Y (2010) A crucial role for RACK1 in the regulation of glucose-stimulated IRE1α activation in pancreatic β-cells. Sci Signal 3(106):ra7
Kaufman RJ (1999) Stress signaling from the lumen of the endoplasmic reticulum: coordination of gene transcriptional and translational controls. Genes Dev 13(10):1211–1233
Yoshida H, Matsui T, Yamamoto A, Okada T, Mori K (2001) XBP1 mRNA is induced by ATF6 and spliced by IRE1 in response to ER stress to produce a highly active transcription factor. Cell 107:881–891
Calfon M, Zeng H, Urano F, Till JH, Hubbard SR, Harding HP, Clark SG, Ron D (2002) IRE1 couples endoplasmic reticulum load to secretory capacity by processing the XBP1 mRNA. Nature 415:92–96
Nakanishi K, Sudo T, Morishima N (2005) Endoplasmic reticulum stress signaling transmitted by ATF6 mediates apoptosis during muscle development. J Cell Biol 169(4):555–560
Guo F, Lin EA, Liu P, Lin J, Liu C (2010) XBP1U inhibits the XBP1S-mediated upregulation of the iNOS gene expression in mammalian ER stress response. Cell Signal 22:1818–1828
Han D, Lerner AG, Vande Walle L, Upton JP, Xu W, Hagen A, Backes BJ, Oakes SA, Papa FR (2009) IRE1 alpha kinase activation modes control alternate endoribonuclease outputs to determine divergent cell fates. Cell 138:562–575
Pincus D, Chevalier MW, Aragón T, van Anken E, Vidal SE, El-Samad H, Walter P (2010) BiP binding to the ER-stress sensor Ire1 tunes the homeostatic behavior of the unfolded protein response. PLoS Biol 8(7):1–14
Elia AE, Rellos P, Haire LF, Chao JW, Ivins FJ, Hoepker K, Mohammad D, Cantley LC, Smerdon SJ, Yaffe MB (2003) The molecular basis for phosphodependent substrate targeting and regulation of Plks by the Polo-box domain. Cell 115(1):83–95
Lu LY, Yu X (2009) The balance of polo-like kinase 1 in tumorigenesis. Cell Div 4(4):1–6
Qi W, Tang Z, Yu H (2006) Phosphorylation- and polo-box-dependent binding of Plk1 to Bub1 is required for the kinetochore localization of Plk1. Mol Biol Cell 17(8):3705–3716
Malumbres M, Barbacid M (2007) Cell cycle kinases in cancer. Curr Opin Genet Dev 17(1):60–65
Elowe S, Hummer S, Uldschmid A, Li X, Nigg EA (2007) Tension-sensitive Plk1 phosphorylation on BubR1 regulates the stability of kinetochore microtubule interactions. Genes Dev 21(17):2205–2219
Goto H, Kiyono T, Tomono Y, Kawajiri A, Urano T, Furukawa K, Nigg EA, Inagaki M (2006) Complex formation of Plk1 and INCENP required for metaphase-anaphase transition. Nat Cell Biol 8(2):180–187
Nakagawa T, Yuan J (2000) Cross-talk between two cysteine protease families. Activation of caspase-12 by calpain in apoptosis. J Cell Biol 150:887–894
Hitomi J, Katayama T, Eguchi Y et al (2004) Involvement of caspase-4 in endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced apoptosis and Aβ-induced cell death. J Cell Biol 165(3):347–356
Szegezdi E, Logue SE, Gorman AM, Samali A (2006) Mediators of endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced apoptosis. EMBO Rep 7(9):880–885
Kim R, Emi M, Tanabe K, Murakami S (2006) Role of the unfolded protein response in cell death. Apoptosis 11(1):5–13
Puthalakath H, O’Reilly LA, Gunn P et al (2007) ER stress triggers apoptosis by activating BH3-only protein Bim. Cell 129(7):1337–1349
McCullough KD, Martindale JL, Klotz LO, Aw TY, Holbrook NJ (2001) Gadd153 sensitizes cells to endoplasmic reticulum stress by down-regulating Bc12 and perturbing the cellular redox state. Mol Cell Biol 21(4):1249–1259
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Science Foundation of China (No. 31040019 and No. 81171697); and the Natural Science Foundation Project of CQ CSTC (No. 2011jjA10047).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, X., Zhu, H., Huang, H. et al. Study on the effect of IRE1α on cell growth and apoptosis via modulation PLK1 in ER stress response. Mol Cell Biochem 365, 99–108 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-012-1248-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-012-1248-4