Abstract
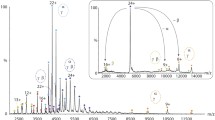
Gene encoding a novel translation initiation factor PeIF5B from Pisum sativum with sequence similarity to eIF5B from H. sapiens, D. melanogaster, S. cerevisiae as well as archaeal aIF5B from M. thermoautotrophicum was earlier reported by us. We now describe the expression and purification of 96 kDa recombinant PeIF5B (rPeIF5B) protein. Using fluorescence and circular dichroism spectra analyses, we show that Mg2+ binding does not lead to any change in PeIF5B aromatic amino acid micro-environment, whereas GTP binding induces significant changes in the local environment of the aromatic amino acids. However, the protein undergoes changes in secondary structure upon metal ion and nucleotide binding. Charged initiator tRNA binding to PeIF5B is found to be cofactor dependent. PeIF5B binds to GTP in vitro as evident from autoradiography. Based on homology modeling of the catalytic domain of PeIF5B, we could confirm the conformational changes in PeIF5B following ligand binding.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kozak M (1999) Initiation of translation in prokaryotes and eukaryotes. Gene 234:187–208
Gualerzi CO, Pon CL (1990) Initiation of mRNA translation in prokaryotes. Biochemistry 29:5881–5889
Wu X-Q, Iyengar P, RajBhandary UL (1996) Ribosome-initiator tRNA complex as an intermediate in translation initiation in Escherichia coli revealed by use of mutant initiator tRNAs and specialized ribosomes. EMBO J 15:4734–4739
Laalami S, Sacerdot C, Vachon G, Mortensen K, Sperling-Petersen HU, Cenatiempo Y, Grunberg-Manago M (1991) Structural and functional domains of E coli initiation factor IF2. Biochimie 73:1557–1566
Spurio R, Brandi L, Caserta E, Pon CL, Gualerzi CO, Misselwitz R, Krafft C, Welfle K, Welfle H (2000) The C-terminal subdomain (IF2 C-2) contains the entire fMet-tRNA binding site of initiation factor IF2. J Biol Chem 275:2447–2454
Ma L, Spremulli LL (1995) Cloning and sequence analysis of the human mitochondrial translational initiation factor 2 cDNA. J Biol Chem 270:1859–1865
Ma J, Spremulli LL (1996) Expression, purification, and mechanistic studies of bovine mitochondrial translational initiation factor 2. J Biol Chem 271:5805–5811
Vambutas A, Ackerman SH, Tzagoloff A (1991) Mitochondrial translational-initiation and elongation factors in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Eur J Biochem 201:643–652
Ma L, Spremulli LL (1990) Identification and characterization of large, complex forms of chloroplast translational initiation factor 2 from Euglena gracilis. J Biol Chem 265:13560–13565
Stern DB, Higgs DC, Yang J (1997) Transcription and translation in chloroplasts. Trends Plant Sci 2:308–315
Gillham NW, Boynton JE, Hauser CR (1994) Translational regulation of gene expression in chloroplasts and mitochondria. Annu Rev Genet 28:71–93
Kyrpides NC, Woese CR (1998) Universally conserved translation initiation factors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:224–228
Choi SK, Lee JH, Zoll WL, Merrick WC, Dever TE (1998) Promotion of Met-tRNA Meti binding to ribosomes by yIF2, a bacterial IF2 homolog in yeast. Science 280:1757–1760
Pestova TV, Lomakin IB, Lee JH, Choi SK, Dever TE, Hellen CU (2000) The joining of ribosomal subunits in eukaryotes requires eIF5B. Nature 403:332–335
Unbehaun A, Borukhov SI, Hellen CUT, Pestova TV (2004) Release of initiation factors from 48S complexes during ribosomal subunit joining and the link between establishment of codon-anticodon base-pairing and hydrolysis of eIF2-bound GTP. Genes Dev 18:3078–3093
Lee JH, Pestova TV, Shin BS, Cao C, Choi SK, Dever TE (2002) Initiation factor eIF5B catalyzes second GTP-dependent step in eukaryotic translation initiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:16689–16694
Shin BS, Maag D, Roll-Mecak A, Arefin MS, Burley SK, Lorsch JR, Dever TE (2002) Uncoupling of initiation factor eIF5B/IF2 GTPase and translational activities by mutations that lower ribosome affinity. Cell 111:1015–1025
Rasheedi S, Ghosh S, Suragani M, Tuteja N, Sopory SK, Hasnain SE, Ehtesham NZ (2007) Pisum sativum contains a factor with strong homology to eIF5B. Gene 399:144–151
Khurana R, Udgaonkar JB (1994) Equilibrium unfolding studies of barstar: evidence for an alternative conformation which resembles a molten globule. Biochemistry 33:106–115
Hackeng TM, Fernández JA, Dawson PE, Kent SBH, Griffin JH (2000) Chemical synthesis and spontaneous folding of a multidomain protein: anticoagulant microprotein S. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:14074–14078
Laskowski RA, MacArthur MW, Moss DS, Thornton JM (1993) PROCHECK: a program to check the stereochemical quality of protein structures. J Appl Cryst 26:283–291
Morris AL, MacArthur MW, Hutchinson EG, Thornton JM (1992) Stereochemical quality of protein structure coordinates. Proteins 12:345–364
Wiederstein M, Sippl MJ (2007) ProSA-web: interactive web service for the recognition of errors in three-dimensional structures of proteins. Nucleic Acids Res 35:W407–W410
Benzaghou I, Bougie I, Bisaillon M (2004) Effect of metal ion binding on the structural stability of the hepatitis C virus RNA polymerase. J Biol Chem 279:49755–49761
Roll-Mecak A, Cao C, Dever TE, Burley SK (2000) X-ray structures of the universal translation initiation factor IF2/eIF5B: conformational changes on GDP and GTP binding. Cell 103:781–792
Brock S, Szkaradkiewicz K, Sprinzl M (1998) Initiation factors of protein biosynthesis in bacteria and their structural relationship to elongation and termination factors. Mol Microbiol 29:409–417
Lee JH, Choi SK, Roll-Mecak A, Burley SK, Dever TE (1999) Universal conservation in translation initiation revealed by human and archaeal homologs of bacterial translation initiation factor IF2. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96:4342–4347
Ng KKS, Cherney MM, Vázquez AL, Machín Á, Alonso JMM, Parra F, James MNG (2002) Crystal structures of active and inactive conformations of a caliciviral RNA-dependent RNA polymerase. J Biol Chem 277:1381–1387
Huang H, Chopra R, Verdine GL, Harrison SC (1998) Structure of a covalently trapped catalytic complex of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase: implications for drug resistance. Science 282:1669–1675
Doublié S, Tabor S, Long AM, Richardson CC, Ellenberger T (1998) Crystal structure of a bacteriophage T7 DNA replication complex at 2.2 Å resolution. Nature 391:251–258
Berchtold H, Reshetnikova L, Reiser COA, Schirmer NK, Sprinzl M, Hilgenfeld R (1993) Crystal structure of active elongation factor Tu reveals major domain rearrangements. Nature 365:126–132
Shin BS, Acker MG, Maag D, Kim J-R, Lorsch JR, Dever TE (2007) Intragenic suppressor mutations restore GTPase and translation functions of a eukaryotic initiation factor 5B Switch II mutant. Mol Cell Biol 27:1677–1685
Acknowledgements
S.R. and M.S. thank the CSIR and ICMR, respectively, for Senior Research Fellowship. S.E.H. is a JC Bose National Fellow.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
11010_2010_526_MOESM1_ESM.ppt
The following supplementary material is available: Fig. S1 Ramachandran plots for free (a), inactive (b) and active (c) forms of PeIF5B vs. 1g7r, 1g7 s and 1g7t forms of aIF5B from M. thermoautotrophicum, respectively. (PPT 911 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rasheedi, S., Suragani, M., Haq, S.K. et al. Expression, purification and ligand binding properties of the recombinant translation initiation factor (PeIF5B) from Pisum sativum . Mol Cell Biochem 344, 33–41 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-010-0526-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-010-0526-2