Abstract
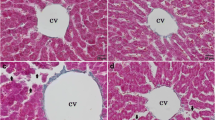
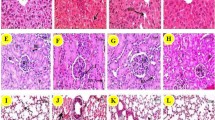
In the present study, we have evaluated the effects of dietary selenite (Se) on polyamine levels and its influence on N-nitrosodiethylamine (DEN) initiated and Phenobarbital (PB) promoted in rat liver carcinogenesis. Dietary selenite at a concentration of 4 ppm (through drinking water) was administered in rats either before initiation (4 weeks), or during promotion (16 weeks) and entire experimental period (20 weeks). Male Wistar strain of albino rats was treated with single intra peritoneal dose of DEN (200 mg kg−1 body weight), after 2 weeks the carcinogenic effect was promoted by PB (0.05%; through diet). Alpha fetoprotein (AFP) was investigated after the 20th-week of experimental period. Selenite-treated animals markedly reduced the AFP during the time of pre-selenite [before initiation (4 weeks)] and entire experimental period (20 weeks), administration rather than the promotion period. This infers that anticancer property of selenite depends on the stage of carcinogenesis, rather than duration of treatment. Evaluation of polyamine levels in hepatoma and surrounding liver tissue showed significant difference in the selenite-treated groups compared with pair-fed control groups. Furthermore, histopathological examination showing remarkable difference between control and treated groups. These results demonstrate that selenite can modulate the development of DEN-induced and PB-promoted rat liver carcinogenesis through a polyamine-dependent mechanism. (Mol Cell Biochem xxx: 165–172, 2005)
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- DEN:
-
N-nitrosodiethylamine
- PB:
-
Phenobarbital
- AFP:
-
Alpha-fetoprotein
- Se:
-
Selenium
References
Combs GF Jr, Gray WP: Chemopreventive agents: selenium. Pharmacol Ther 79:179–192, 1998
Clark LC, Combs GF Jr, Turnbull WB, Slate EH, Chalker DK, Chow J, Davis LS, Glover RA, Graham GF, Gross EG, Krongrad A, Lesh JL, Park K, Sanders BB, Smith CL, Taylor JR: Effects of selenium. Supplementation for cancer prevention in patients with carcinoma of the skin: A randomized controlled trial. J Am Med Assoc 276: 1957–1963, 1996
Thirunavukkarasu C, Sakthisekaran D: Sodium selenite, dietary micronutrient, prevents the lymphocytes DNA damage induced by N-nitrosodiethylamine and phenobarbital promoted experimental hepatocarcinogenesis. J Cell Biochem 88: 578–588, 2003
Ip C, el-Bayoumy K, Upadhyaya P, Ganther H, Vadhanavikit S: Comparative effect of inorganic and organic selenocyanate derivatives in mammary cancer chemoprevention. Carcinogenesis 15: 187–192, 1994
el-Bayoumy K, Upadhyaya P, Desai DH, Amin S, Hecht SS: Inhibition of 4-(methylnitrosamino)-1-(3-pyridyl)-1-butanone tumorigenicity in mouse lung by the synthetic organoselenium compound, 1,4-phenylenebis(methylene)selenocyanate. Carcinogenesis 14: 1111–1113, 1993
Schrauzer GN: Selenium: mechanistic aspects of anticarcinogenic action. Biol Trace Elem Res 33: 1657–1666, 1999
Gopalakrishna R, Chen ZH, Gundimeda U: Selenocompounds induce a redox modulation of protein kinase C in the cell, compartmentally independent from cytosolic glutathione: its role in inhibition of tumor promotion. Arch Biochem Biophys 348: 37–48, 1997
Beutler L, Beutler B, Matumato F: Glutathione peroxidase activity of inorganic selenium and seleno-DL-cysteine. Experimentia 31: 669–670, 1975
Berggren M, Gallego SA, Gasdarka JR, Gasdarka PY, Warneke J, Powis G: Thioredoxin and thioredoxin reductase gene expression in human tumors and cell lines and the effects of selenium stimulation and hypoxia. Anti Cancer Res 16: 3459–3466, 1996
Rafferty TS, Mckenzie RC, Hunter JA, Howie AF, Artghur AR, Nicol F, Beckett GJ: Differential expression of selenoproteins by human skin cells and protection by selenium from UVB-radiation-induced cell death. Biochem J 332: 231–236, 1998
Pattersen BH, Levander OA, Helzlsouer K, McAdam PA, Lewis SA, Taylor PR, Veillon C, Zech LA: Human selenite metabolism: a kinetic model. Am J Physiol 257: R556–R567, 1989
Ganther HE: Selenium metabolism, selenoproteins and mechanisms of cancer prevention: complexities with thioredoxin reductase. Carcinogenesis 20: 1657–1666, 1999
Lanfear J, Wu L, Fleming J, Wu L, Webster G, Harrison PR: The selenium metabolite selenodiglutathione induces P53 and apoptosis: relevance to the chemopreventive effects of selenium? Carcinogenesis 15: 1387–1392, 1994
Wu L, Lanfear J, Harrison PR: The selenium metabolite selenodiglutathione induced cell death by a mechanism distinct from H2O2 toxicity. Carcinogenesis 16: 1579–1584, 1995
Heby O, Persson L: Molecular genetics of polyamine synthesis in eukaryotic cells. Trends Biol Sci 15: 153–158, 1990
Marquet R, Houssier C: Different binding modes of spermine to A-T and G-C base pairs modulate the bending and stiffening of the DNA double helix. Biochem Pharmacol 37: 1857–1858, 1998
Pegg AE: Recent advance in the biochemistry of polyamines in eukaryotes. Biochem J 234: 240–262, 1998
Kajander SO, Harvima R, Kauppinen L, Akerman KK, Martikainen H, Pajula RL, Karenkampi SO: Effects of selenomethionine on cell growth and on S-adenosylmethionine metabolism in cultured malignant cell. Biochem J 267: 767–774, 1990
McGarrity T, Peiffer L, Hartle R: Effects of selenium on growth, S-adenosylmethionine and polyamine biosynthesis in human colon cancer cells. Anticancer Res 13: 811–816, 1993
Newberne PM, Bieri JG, Briggs GM, Nesheim MC: Control of diets in laboratory animal experimentation. Inst Lab Anim Resour News 21: A1–A12, 1978
Yoshiji H, Nakae D, Kinugasa T, Matsuzaki M, Denda A, Suiji T: Inhibitory effect of the iron deficiency on the induction of putative preneoplastic foci rat liver initiated with diethylnitrosamine and promoted by Phenobarbital. Br J Cancer 64: 839–842, 1991
Schneider WC: Determination of nucleic acid in tissues. In: S.P. Colowick and N.O. Kaplan (eds) Methods in Enzymology, Vol. III, Academic Press, New York, 1957, pp 680–684
Burton K: A study of the conditions and mechanisms of diphenylamine reaction for colorimetric estimation of deoxyribonucleic acid. Biochem J 62: 315–323, 1956
Rawal UM, Patel US, Rao GN, Desai RR: Clinical and biochemical studies on cateractous human lens III. Quantitative study of protein, RNA and DNA, Arogya J Health Sci 3: 69–72, 1977
Endo Y: A simple and sensitive method of analysis of histamine, putrescine and polyamines without the use of an amino acid analyzer. Anal Biochem 89: 235–246, 1978
Thirunavukkarasu C, Sakthisekaran D: Sodium selenite modulates tumour marker indices in N-nitrosodiethylamine-initiated and phenobarbital-promoted rat liver carcinogenesis. Cell Biochem Funct 21: 147–153, 2003
Thirunavukkarasu C, Jagadeeswaran R, Babu E, Sakthisekaran D: Inhibitory effect of selenium on N-nitrosodiethylamine-induced and phenobarbital promoted rat liver carcinogenesis. J Clin Biochem Nutr 28: 69–80, 2000
Enzmann H, Bomhard E, Iatropoulos M, Ahr HJ, Schlueter G, Williams GM: Short- and intermediate-term carcinogenicity testing. A review. Part I: The prototypes mouse skin tumour assay and rat liver focus assay. Food Chem Toxicol 36: 979–995, 1998
Heby O: Role of polyamines in the control of cell proliferation and differentiation. Differentiation 14: 1–20, 1981
Verma DS, Sunkara PS: An essential role for polyamine biosynthesis during granulopoetic differentiation. Cancer Res 42: 3046–3048, 1982
Seiler N: Pharmacological properties of the natural polyamines and their depletion by biosynthesis inhibitors as a therapeutic approach. Prog Drug Res 37: 107–109, 1991
Tamori A: Point mutation of ornithine decarboxylase gene in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Res 55: 3500–3503, 1995
Homma Y, Kakioe Y, Samma S, Oyasu R: Inhibition of N-butyl-N-(4-hydroxybutyl)nitrosamine-induced rat urinary bladder carcinogenic by alpha-difluoromethylornithine. Cancer Res 47: 6167–6179, 1987
Chen DS, Snug JL, Shen JC: Pleural effusion coinciding with acute exacerbations in a patient with chronic hepatitis B. Gastroenterology 96: 1604–1606, 1989
Bisceglie AM, Dusheiko GM, Paterson AC, Alexander S, Shoural D, Lee CS, Beasley RP, Kew MC: Detection of alpha fetoprotein messanger RNA in human hepatocellular carcinoma and hepatoblastoma tissue. Br J Cancer 54: 779–785, 1986
Kumar R, Sukumar S, Barbacid M: Activation of ras oncogenes preceding the onset of neoplasia. Science 248: 1100–1102, 1990
Tanaka T, Kojima T, Suzuki M, Mori H: Chemoprevention of diethylnitrosamine-induced hepatocarcinogenesis by a simple phenolic acid protocatechuic acid in rats. Cancer Res 53: 3908–3913, 1993
Dorado RD, Porta EA, Aquino TM: Effects of dietary selenium on hepatic and renal tumorigenesis induced in rats by diethylnitrosamine. Hepatology 5: 1201–1208, 1985
Archer MC: Mechanism of action of N-nitrosocompounds. Cancer Surv 8: 241–250, 1987
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Thirunavukkarasu, C., Premkumar, K., Jagadeeswaran, R. et al. The inhibitory effect of sodium selenite on N-nitrosodiethylamine-induced and phenobarbital promoted liver tumourigenesis in rats based on the modulation of polyamine levels. Mol Cell Biochem 280, 165–172 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-005-8907-7
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-005-8907-7