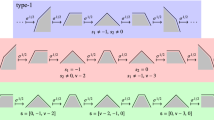
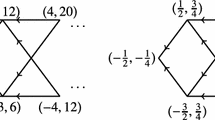Abstract
The first part of this work uses the algorithm recently detailed in Kawasetsu and Ridout (Commun Contemp Math 24:2150037, 2022. arXiv:1906.02935 [math.RT]) to classify the irreducible weight modules of the minimal model vertex operator algebra \({\textsf {L} }_{{\textsf {k} }}(\mathfrak {sl}_{3})\), when the level \({\textsf {k} }\) is admissible. These are naturally described in terms of families parametrised by up to two complex numbers. We also determine the action of the relevant group of automorphisms of \(\widehat{\mathfrak {sl}}_{3}\) on their isomorphism classes and compute explicitly the decomposition into irreducibles when a given family’s parameters are permitted to take certain limiting values. Along with certain character formulae, previously established in Kawasetsu (Adv Math 393:108079, 2021. arXiv:2003.10148 [math.RT]), these results form the input data required by the standard module formalism to consistently compute modular transformations and, assuming the validity of a natural conjecture, the Grothendieck fusion coefficients of the admissible-level \(\mathfrak {sl}_{3}\) minimal models. The second part of this work applies the standard module formalism to compute these explicitly when \({\textsf {k} }=-\frac{3}{2}\). This gives the first nontrivial test of this formalism for a nonrational vertex operator algebra of rank greater than 1 and confirms the expectation that the methodology developed here will apply in much greater generality.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data sharing is not applicable to this article as no datasets were generated or analysed during the current study.
Notes
If we were considering coherent families of \(\mathrm {d}(\mathfrak {l})\)-modules instead of \(\mathfrak {l}\)-modules, then the Weyl reflection appearing here would be \(\mathrm {w}_{2}\).
We remark that under the general definition in [51], all of these modules would be examples of relaxed highest-weight modules. However, in this case the nomenclature introduced here is convenient and so we shall adopt it, hoping that no confusion will arise.
There is a well-known exception to this statement when \({\textsf {u} }\geqslant 3\) and \({\textsf {v} }=1\), so \({\textsf {k} }\in \mathbb {Z}_{\geqslant 0}\). Then, the positive-energy category coincides with \(\widehat{\mathscr {W}}_{{\textsf {u} },1}\) and the category of integrable highest-weight \(\widehat{\mathfrak {sl}}_{3}\)-modules; the latter is of course preserved by spectral flow.
We shall generally drop the hat from affine Dynkin labels, trusting that this will not cause confusion.
As we shall see, this arbitrary choice is convenient because the subsets of admissible weights classifying the relaxed, semirelaxed and highest-weight \({\textsf {A} }_{2} \left({\textsf {u} }, {\textsf {v} } \right)\)-modules then satisfy \(C_{{\textsf {u} },{\textsf {v} }}^2 \subseteq B_{{\textsf {u} },{\textsf {v} }}^1 \subset A_{{\textsf {u} },{\textsf {v} }}\).
It is easy to check that \(\widehat{\lambda } \in C_{{\textsf {u} },{\textsf {v} }}^2\) implies that there are no triple intersections.
We recall that the “−-type” quantum Hamiltonian reduction was introduced by Frenkel, Kac and Wakimoto in [40] for regular (principal) nilpotent elements. It differs from the usual “\(+\)-type” regular reduction in that it gauges the negative root vectors instead of the positive ones. Although both reductions give isomorphic W-algebras, the corresponding functors on modules are different. The reduction functor used in Theorem 5.1 is a generalisation of this −-type functor to all nilpotents due to Kac–Wakimoto [59] and Arakawa [60].
We remark that this name, while quite standard, may be a little misleading. It does not refer to a 1-point correlation function of genus 1 in an appropriate conformal field theory, but rather to a chiral version where the trace is taken over a fixed module. In other words, this concept generalises the definition (5.1) of a character by inserting some fixed zero mode (usually unexponentiated!) inside the trace.
The reader will no doubt recognise the action of \({\textsf {S} }\) and \({\textsf {T} }\) on \(\theta \) as a somewhat strange-looking generalisation of the usual formulae familiar from rational models. The terms involving complex arguments seem to be necessary to deal with the unusual automorphy factor that results from transforming Dirac combs.
This second identity is well known for delta functions with real arguments. Here, as in many other applications of the standard module formalism, we assume that it may be extended to complex arguments. We expect that this formula can be established rigorously by finding the correct space of test functions to pair with and hope to pursue this in future work.
This rigidity conjecture is very natural as all rational vertex operator algebras are known to produce rigid module categories (modular tensor categories even) [8] and a growing number of nonrational vertex operator algebras are also known to admit rigid module categories [32, 68,69,70,71,72]. There is, however, a known counterexample [73]. A modified Grothendieck fusion ring for this counterexample was studied in detail in [74].
We thank an anonymous referee for this suggestion.
That \(\widehat{\mathcal {L}}_{0}\) is the Grothendieck fusion unit follows directly from the standard Verlinde formula and the fact that the standard S-matrix is unitary.
References
Kawasetsu, K., Ridout, D.: Relaxed highest-weight modules II: classifications for affine vertex algebras. Commun. Contemp. Math. 24, 2150037 (2022). arXiv:1906.02935 [math.RT]
Kawasetsu, K.: Relaxed highest-weight modules III: character formulae. Adv. Math. 393, 108079 (2021). arXiv:2003.10148 [math.RT]
Frenkel, I., Zhu, Y.: Vertex operator algebras associated to representations of affine and Virasoro algebras. Duke Math. J. 66, 123–168 (1992)
Witten, E.: Non-abelian bosonization in two dimensions. Commun. Math. Phys. 92, 455–472 (1984)
Gepner, D., Witten, E.: String theory on group manifolds. Nucl. Phys. B 278, 493–549 (1986)
Verlinde, E.: Fusion rules and modular transformations in 2D conformal field theory. Nucl. Phys. B 300, 360–376 (1988)
Moore, G., Seiberg, N.: Classical and quantum conformal field theory. Commun. Math. Phys. 123, 177–254 (1989)
Huang, Y.-Z.: Vertex operator algebras and the Verlinde conjecture. Commun. Contemp. Math. 10, 103–154 (2008). arXiv:math/0406291 [math.QA]
Huang, Y.-Z.: Vertex operator algebras, the Verlinde conjecture, and modular tensor categories. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 102, 5352–5356 (2005). arXiv:math/0412261 [math.QA]
Kac, V., Wakimoto, M.: Modular invariant representations of infinite-dimensional Lie algebras and superalgebras. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 85, 4956–4960 (1988)
Koh, I., Sorba, P.: Fusion rules and (sub)modular invariant partition functions in nonunitary theories. Phys. Lett. B 215, 723–729 (1988)
Kent, A. Infinite-dimensional algebras and the conformal bootstrap. PhD thesis, Department of Applied Mathematics and Theoretical Physics, Cambridge University (1986)
Feigin, B., Frenkel, E.: Quantization of the Drinfeld–Sokolov reduction. Phys. Lett. B 246, 75–81 (1990)
Kac, V., Roan, S., Wakimoto, M.: Quantum reduction for affine superalgebras. Commun. Math. Phys. 241, 307–342 (2003). arXiv:math-ph/0302015
Ridout, D.: \(\widehat{\mathfrak{sl} } \left(2 \right)_{-1/2}\): a case study. Nucl. Phys. B 814, 485–521 (2009). arXiv:0810.3532 [hep-th]
Creutzig, T., Ridout, D.: Modular data and Verlinde formulae for fractional level WZW models I. Nucl. Phys. B 865, 83–114 (2012). arXiv:1205.6513 [hep-th]
Creutzig, T., Ridout, D.: Modular data and Verlinde formulae for fractional level WZW models II. Nucl. Phys. B 875, 423–458 (2013). arXiv:1306.4388 [hep-th]
Creutzig, T., Ridout, D.: Relating the archetypes of logarithmic conformal field theory. Nucl. Phys. B 872, 348–391 (2013). arXiv:1107.2135 [hep-th]
Babichenko, A., Ridout, D.: Takiff superalgebras and conformal field theory. J. Phys. A 46, 125204 (2013). arXiv:1210.7094 [math-ph]
Ridout, D., Wood, S.: Bosonic ghosts at \(c=2\) as a logarithmic CFT. Lett. Math. Phys. 105, 279–307 (2015). arXiv:1408.4185 [hep-th]
Morin-Duchesne, A., Rasmussen, J., Ridout, D.: Boundary algebras and Kac modules for logarithmic minimal models. Nucl. Phys. B 899, 677–769 (2015). arXiv:1503.07584 [hep-th]
Canagasabey, M., Rasmussen, J., Ridout, D.: Fusion rules for the \(N=1\) superconformal logarithmic minimal models I: the Neveu–Schwarz sector. J. Phys. A 48, 415402 (2015). arXiv:1504.03155 [hep-th]
Canagasabey, M., Ridout, D.: Fusion rules for the logarithmic \(N=1\) superconformal minimal models II: including the Ramond sector. Nucl. Phys. B 905, 132–187 (2016). arXiv:1512.05837 [hep-th]
Ridout, D., Snadden, J., Wood, S.: An admissible level \(\widehat{\mathfrak{osp} } \left(1 | \vert 2 \right)\)-model: modular transformations and the Verlinde formula. Lett. Math. Phys. 108, 2363–2423 (2018). arXiv:1705.04006 [hep-th]
Babichenko, A., Kawasetsu, K., Ridout, D., Stewart, W.: Representations of the Nappi–Witten vertex operator algebra. Lett. Math. Phys. 111, 131 (2021). arXiv:2011.14453 [math-ph]
Fehily, Z., Ridout, D.: Modularity of Bershadsky–Polyakov minimal models. Lett. Math. Phys. 122, 46 (2022). arXiv:2110.10336 [math.QA]
Creutzig, T., Ridout, D.: Logarithmic conformal field theory: beyond an introduction. J. Phys. A 46, 494006 (2013). arXiv:1303.0847 [hep-th]
Ridout, D., Wood, S.: The Verlinde formula in logarithmic CFT. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 597, 012065 (2015). arXiv:1409.0670 [hep-th]
Gaberdiel, M.: Fusion rules and logarithmic representations of a WZW model at fractional level. Nucl. Phys. B 618, 407–436 (2001). arXiv:hep-th/0105046
Ridout, D.: Fusion in fractional level \(\widehat{\mathfrak{sl} } \left(2 \right)\)-theories with \(k=-\tfrac{1}{2}\). Nucl. Phys. B 848, 216–250 (2011). arXiv:1012.2905 [hep-th]
Adamović, D., Pedić, V.: On fusion rules and intertwining operators for the Weyl vertex algebra. J. Math. Phys. 60, 081701 (2019). arXiv:1903.10248 [math.QA]
Allen, R., Wood, S. Bosonic ghostbusting—the bosonic ghost vertex algebra admits a logarithmic module category with rigid fusion (2022). arXiv:2001.05986 [math.QA]
Arakawa, T., Futorny, V., Ramirez, L.: Weight representations of admissible affine vertex algebras. Commun. Math. Phys. 353, 1151–1178 (2017). arXiv:1605.07580 [math.RT]
Futorny, V., Morales, O., Ramirez, L. Simple modules for affine vertex algebras in the minimal nilpotent orbit. arXiv:2002.05568 [math.RT]
Futorny, V., Křižka, L.: Positive energy representations of affine vertex algebras. Commun. Math. Phys. 383, 841–891 (2021). arXiv:2002.05586 [math.RT]
Futorny, V., Morales, O., Křižka, L. Admissible representations of simple affine vertex algebras. arXiv:2107.11128 [math.RT]
Arakawa, T.: Rationality of admissible affine vertex algebras in the category \(\cal{O} \). Duke Math. J. 165, 67–93 (2016). arXiv:1207.4857 [math.QA]
Mathieu, O.: Classification of irreducible weight modules. Ann. Inst. Fourier (Grenoble) 50, 537–592 (2000)
Zamolodchikov, A.: Infinite additional symmetries in two-dimensional conformal quantum field theory. Theoret. Math. Phys. 65, 1205–1213 (1985)
Frenkel, E., Kac, V., Wakimoto, M.: Characters and fusion rules for W-algebras via quantized Drinfeld–Sokolov reduction. Commun. Math. Phys. 147, 295–328 (1992)
Arakawa, T., van Ekeren, J.: Modularity of relatively rational vertex algebras and fusion rules of principal affine \(W\)-algebras. Commun. Math. Phys. 370, 205–247 (2019). arXiv:1612.09100 [math.RT]
Zhu, Y.: Modular invariance of characters of vertex operator algebras. J. Am. Math. Soc. 9, 237–302 (1996)
Adamović, D.: Realizations of simple affine vertex algebras and their modules: the cases \(\widehat{sl(2)}\) and \(\widehat{osp(1,2)}\). Commun. Math. Phys. 366, 1025–1067 (2019). arXiv:1711.11342 [math.QA]
Semikhatov, A. Inverting the Hamiltonian reduction in string theory. In: 28th International Symposium on Particle Theory, Wendisch-Rietz, Germany, pp. 156–167 (1994). arXiv:hep-th/9410109
Adamović, D., Creutzig, T., Genra, N. Relaxed and logarithmic modules of \(\widehat{\mathfrak{sl}_3}\). arXiv:2110.15203 [math.RT]
Adamović, D., Kawasetsu, K., Ridout, D.: A realisation of the Bershadsky-Polyakov algebras and their relaxed modules. Lett. Math. Phys. 111, 38 (2021). arXiv:2007.00396 [math.QA]
Adamović, D.: A construction of admissible \(A_1^{\left(1\right)}\)-modules of level \(-\frac{4}{3}\). J. Pure Appl. Algebra 196, 119–134 (2005). arXiv:math.QA/0401023
Creutzig, T., Ridout, D., Rupert, M. A Kazhdan–Lusztig correspondence for \(L_{-3/2}(\mathfrak{sl}_3)\). arXiv:2112.13167 [math.RT]
Fernando, S.: Lie algebra modules with finite-dimensional weight spaces. I. Trans. Am. Math. Soc. 322, 757–781 (1990)
Gorelik, M., Kac, V.: On simplicity of vacuum modules. Adv. Math. 211, 621–677 (2007). arXiv:math-ph/0606002
Ridout, D., Wood, S.: Relaxed singular vectors, Jack symmetric functions and fractional level \(\widehat{\mathfrak{sl} } \left(2 \right)\) models. Nucl. Phys. B 894, 621–664 (2015). arXiv:1501.07318 [hep-th]
Kac, V., Wakimoto, M.: Classification of modular invariant representations of affine algebras. In: Infinite-Dimensional Lie Algebras and Groups (Luminy-Marseille. 1988), volume 7 of Advanced Series in Mathematical Physics, pp. 138–177. World Scientific, New Jersey (1989)
Joseph, A.: On the associated variety of a primitive ideal. J. Algebra 93, 509–523 (1985)
Adamović, D.: A realization of certain modules for the \(N=4\) superconformal algebra and the affine Lie algebra \(A_2^{(1)}\). Transform. Groups 21, 299–327 (2016). arXiv:1407.1527 [math.QA]
Adamović, D., Milas, A., Wang, Q. On parafermion vertex algebras of \(\mathfrak{s}\mathfrak{l}(2)_{-3/2}\) and \(\mathfrak{s}\mathfrak{l} (3)_{-3/2}\). Commun. Contemp. Math. 24, 2050086 (2022). arXiv:2005.02631 [math.QA]
Semikhatov, A. A note on the logarithmic \(W_3\) octuplet algebra and its Nichols algebra. arXiv:1301.2227 [math.QA]
Kac, V., Wakimoto, M.: A remark on boundary level admissible representations. C. R. Acad. Sci. Paris Sér. I Math. 355, 128–132 (2017). arXiv:1612.07423 [math.RT]
Kawasetsu, K., Ridout, D.: Relaxed highest-weight modules I: rank \(1\) cases. Commun. Math. Phys. 368, 627–663 (2019). arXiv:1803.01989 [math.RT]
Kac, V., Wakimoto, M.: On rationality of W-algebras. Transform. Groups 13, 671–713 (2008). arXiv:0711.2296 [math-ph]
Arakawa, T. Representation theory of \(W\)-algebras, II: Ramond twisted representations. In Exploring New Structure and Natural Constructions in Mathematical Physics, volume 61 of Advanced Studies in Pure Mathematics, pp. 51–90, Tokyo, 2011. Mathematical Society of Japan. arXiv:0802.1564 [math.QA]
Kac, V., Wakimoto, M.: Quantum reduction and representation theory of superconformal algebras. Adv. Math. 185, 400–458 (2004). arXiv:math-ph/0304011
Arakawa, T.: Representation theory of superconformal algebras and the Kac–Roan–Wakimoto conjecture. Duke Math. J. 130, 435–478 (2005). arXiv:math-ph/0405015
Arakawa, T., van Ekeren, J. Rationality and fusion rules of exceptional W-algebras. arXiv:1905.11473 [math.RT]
Perše, O.: Vertex operator algebras associated to certain admissible modules for affine Lie algebras of type \(A\). Glas. Mat. Ser. III(43), 41–57 (2008). arXiv:0707.4129 [math.QA]
Beem, C., Lemos, M., Liendo, P., Peelaers, W., Rastelli, L., van Rees, B.: Infinite chiral symmetry in four dimensions. Commun. Math. Phys. 336, 1359–1433 (2015). arXiv:1312.5344 [hep-th]
Adamović, D.: A realization of certain modules for the \(N=4\) superconformal algebra and the affine Lie algebra \(A_2^{(1)}\). Transform. Groups 21, 299–327 (2016). arXiv:1407.1527 [math.QA]
Arakawa, T., Kawasetsu, K. Quasi-lisse vertex algebras and modular linear differential equations. In: Lie Groups, Geometry and Representation Theory, volume 326 of Progress in Mathematics, pp. 41–57. Birkhäuser/Springer (2018). arXiv:1610.05865 [math.QA]
Tsuchiya, A., Wood, S.: The tensor structure on the representation category of the \(\cal{W} _p\) triplet algebra. J. Phys. A 46, 445203 (2013). arXiv:1201.0419 [hep-th]
Creutzig, T., Jiang, C., Orosz Hunziker, F., Ridout, D., Yang, J.: Tensor categories arising from the Virasoro algebra. Adv. Math. 380, 107601 (2021). arXiv:2002.03180 [math.RT]
Creutzig, T., Yang, J.: Tensor categories of affine Lie algebras beyond admissible levels. Math. Ann. 380, 1991–2040 (2021). arXiv:2002.05686 [math.QA]
Creutzig, T., McRae, R., Yang, J.: On ribbon categories for singlet vertex algebras. Commun. Math. Phys. 387, 865–925 (2021). arXiv:2007.12735 [math.QA]
Creutzig, T., McRae, R., Yang, J. Tensor structure on the Kazhdan–Lusztig category for affine \(\mathfrak{gl}(1|1)\). Int. Math. Res. Not. (to appear). arXiv:2009.00818 [math.QA]
Gaberdiel, M., Runkel, I., Wood, S.: Fusion rules and boundary conditions in the \(c=0\) triplet model. J. Phys. A 42, 325403 (2009). arXiv:0905.0916 [hep-th]
Ridout, D., Wood, S.: Modular transformations and Verlinde formulae for logarithmic \(\left( p_+, p_- \right)\)-models. Nucl. Phys. B 880, 175–202 (2014). arXiv:1310.6479 [hep-th]
Li, H.: The physics superselection principle in vertex operator algebra theory. J. Algebra 196, 436–457 (1997)
Creutzig, T., Ridout, D., Wood, S.: Coset constructions of logarithmic \(\left(1, p \right)\)-models. Lett. Math. Phys. 104, 553–583 (2014). arXiv:1305.2665 [math.QA]
Creutzig, T.: Logarithmic W-algebras and Argyres–Douglas theories at higher rank. J. High Energy Phys. 2018, 188 (2018). arXiv:1809.01725 [hep-th]
Acknowledgements
KK’s research is partially supported by the Australian Research Council Discovery Project DP160101520, MEXT Japan “Leading Initiative for Excellent Young Researchers (LEADER)”, JSPS Kakenhi Grant numbers 19KK0065 and 21K3775. DR’s research is supported by the Australian Research Council Discovery Projects DP160101520 and DP210101502, as well as an Australian Research Council Future Fellowship FT200100431. SW’s research is supported by the Australian Research Council Discovery Project DP160101520 and the Humboldt Fellowship for Experience Researchers GBR-1212053-HFST-E.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Kawasetsu, K., Ridout, D. & Wood, S. Admissible-level \(\mathfrak {sl}_3\) minimal models. Lett Math Phys 112, 96 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11005-022-01580-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11005-022-01580-9
Keywords
- Vertex operator algebras
- Conformal field theory
- Affine Kac-Moody algebras
- Representation theory
- Verlinde formula