Abstract
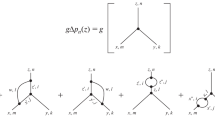
In this survey article, we explain a few ideas behind the fermionic projector approach and summarize recent results which clarify the connection to quantum field theory. The fermionic projector is introduced, which describes the physical system by a collection of Dirac states, including the states of the Dirac sea. Formulating the interaction by an action principle for the fermionic projector, we obtain a consistent description of interacting quantum fields which reproduces the results of perturbative quantum field theory. We find a new mechanism for the generation of boson masses and obtain small corrections to the field equations which violate causality.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bach V., Barbaroux J.-M., Helffer B., Siedentop H.: On the stability of the relativistic electron–positron field. Commun. Math. Phys. 201(2), 445–460 (1999)
Bär, C., Fredenhagen, K. (eds): Quantum Field Theory on Curved Spacetimes. Lecture Notes in Physics, vol. 786. Springer, Berlin (2009)
Christensen S.M.: Vacuum expectation value of the stress tensor in an arbitrary curved background: the covariant point-separation method. Phys. Rev. D (3) 14(10), 2490–2501 (1976)
Collins J.C.: Renormalization, Cambridge Monographs on Mathematical Physics. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (1984)
Deckert, D.-A., Dürr, D., Merkl, F., Schottenloher, M.: Time Evolution of the External Field Problem in QED. arXiv:0906.0046 [math-ph] (2009)
Dirac P.A.M.: A theory of electrons and protons. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. A 126, 360–365 (1930)
Dirac P.A.M.: Discussion of the infinite distribution of electrons in the theory of the positron. Proc. Cambridge Philos. Soc. 30, 150–163 (1934)
Dirac, P.A.M.: Directions in physics. Wiley, New York (Five lectures delivered during a visit to Australia and New Zealand, August–September, 1975) 1978
Dürr H.-P., Heisenberg W., Mitter H., Schlieder S., Yamazaki K.: Zur Theorie der Elementarteilchen. Z. Naturf. 14a, 441–485 (1959)
Dyson F.J.: The S matrix in quantum electrodynamics. Phys. Rev. 75, 1736–1755 (1949)
Epstein H., Glaser V.: The role of locality in perturbation theory. Ann. Inst. H. Poincaré Section A (N.S.) 19, 211–295 (1973)
Feynman R.: The theory of positrons. Phys. Rev. 76, 749–759 (1949)
Fierz H., Scharf G.: Particle interpretation for external field problems in QED. Helv. Phys. Acta 52(4), 437–453 (1979)
Finster, F.: The Principle of the Fermionic Projector, hep-th/0001048, hep-th/0202059, hep-th/0210121. AMS/IP Studies in Advanced Mathematics, vol. 35. American Mathematical Society, Providence (2006)
Finster, F.: An Action Principle for an Interacting Fermion System and its Analysis in the Continuum Limit. arXiv:0908.1542 [math-ph] (2009)
Finster, F.: From discrete space-time to Minkowski space: Basic mechanisms, methods and perspectives. In: Fauser, B., Tolksdorf, J., Zeidler, E. (eds.) Quantum Field Theory. Birkhäuser Verlag, pp. 235–259 (2009). arXiv:0712.0685 [math-ph]
Finster, F.: Entanglement and second quantization in the framework of the fermionic projector. J. Phys. A Math. Theor. 43, 395302 (2010). arXiv:0911.0076 [math-ph]
Finster, F.: The fermionic projector, entanglement, and the collapse of the wave function. In: The Proceedings of DICE2010 (2011). arXiv:1011.2162 [quant-ph]
Finster, F., Grotz, A.: The causal perturbation expansion revisited: rescaling the interacting Dirac sea. J. Math. Phys. 51, 072301 (2010). arXiv:0901.0334 [math-ph]
Fulling S.A., Sweeny M., Wald R.M.: Singularity structure of the two-point function quantum field theory in curved spacetime. Commun. Math. Phys. 63(3), 257–264 (1978)
Glimm J., Jaffe A.: Quantum Physics, a Functional Integral Point of View, 2nd edn. Springer, New York (1987)
Gravejat, P., Lewin, M., Séré, E.: Renormalization and Asymptotic Expansion of Dirac’s Polarized Vacuum (2010). arXiv:1004.1734v1
Hainzl C., Lewin M., Séré E.: Existence of a stable polarized vacuum in the Bogoliubov–Dirac–Fock approximation. Commun. Math. Phys. 257(3), 515–562 (2005) arXiv:math-ph/0403005
Hainzl C., Lewin M., Séré E.: Self-consistent solution for the polarized vacuum in a no-photon QED model. J. Phys. A Math. Theor. 38(20), 4483–4499 (2005) arXiv:physics/0404047
Hainzl C., Lewin M., Séré E., Solovej J.P.: A minimization method for relativistic electrons in a mean-field approximation of quantum electrodynamics. Phys. Rev. A 76, 052104 (2007) arXiv:0706.1486 [physics.atom-ph]
Heisenberg W.: Bemerkungen zur Diracschen Theorie des Positrons. Z. Phys. 90, 209–231 (1934)
Klaus M.: Nonregularity of the Coulomb potential in quantum electrodynamics. Helv. Phys. Acta 53(1), 36–39 (1980)
Klaus M., Scharf G.: The regular external field problem in quantum electrodynamics. Helv Phys. Acta 50(6), 779–802 (1977)
Klaus M., Scharf G.: Vacuum polarization in Fock space. Helv. Phys. Acta 50(6), 803–814 (1977)
Nenciu G., Scharf G.: On regular external fields in quantum electrodynamics. Helv. Phys. Acta 51(3), 412–424 (1978)
Peskin M.E., Schroeder D.V.: An Introduction to Quantum Field Theory. Addison-Wesley, Reading (1995)
Radzikowski M.J.: Micro-local approach to the Hadamard condition in quantum field theory on curved space-time. Commun. Math. Phys. 179(3), 529–553 (1996)
Scharf G.: Finite Quantum Electrodynamics. Texts and Monographs in Physics. Springer, Berlin (1989)
Schwinger J.: Quantum electrodynamics. I. A covariant formulation. Phys. Rev. 74, 1439–1461 (1948)
Serber R.: Linear modifications of the Maxwell field equations. Phys. Rev. 48, 49–54 (1935)
Uehling E.A.: Polarization effects in the positron theory. Phys. Rev. 48, 55–63 (1935)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported in part by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Finster, F. A Formulation of Quantum Field Theory Realizing a Sea of Interacting Dirac Particles. Lett Math Phys 97, 165–183 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11005-011-0473-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11005-011-0473-1