Abstract
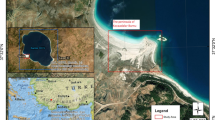
We present a large-scale quantitative test of a hyperspectral remote-sensing reflectance algorithm. We show that coastal bathymetry can be adequately derived through model inversions using data from the Airborne Visible-Infrared Imaging Spectrometer instrument. Data are analyzed from a shore-perpendicular transect 5 km offshore Sarasota, Florida at water depths ranging from 10 m to 15.5 m. Derived bottom depths are compared to a high-resolution multibeam bathymetry survey. Model-derived depths are biased 4.9% shallower than the mean of the multibeam depths with an RMS error of 7.83%. These results suggest that the model performs well for retrieving bottom depths from hyperspectral data in subtropical coastal areas in water depths ranging from 10 m to 15.5 m.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bierwirth P.N., Lee T.J. and Burne R.V. (1993). Shallow sea-floor reflectance and water depth derived by unmixing multispectral imagery. Photogramm. Eng. Rem. S. 59: 331–338
Carder K.L., Reinersman P., Chen R.F. and Muller-Karger F.E. (1993). AVIRIS calibration and application in coastal oceanic environments. Remote Sens. Environ. 44: 205–216
Carder K.L., Liu C., Lee Z.P., English D.C., Patten J., Chen R.F. and Ivey J.E. (2003). Illumination and turbidity effects on observing faceted bottom elements with uniform lambertian albedos. Limnol. Oceanogr. 48: 355–363
Clark R.K., Fay T.H. and Walker C.L. (1987). Bathymetry calculations with Landsat 4 TM imagery under a generalized ratio assumption. Appl. Optics 26: 4036–4038
Durand D., Bijaoui J. and Cauneau F. (2000). Optical remote sensing of shallow-water environmental parameters: A feasibility study. Remote Sens. Environ. 73: 152–161
Eastwood, M.L., Green, R.O., Sarture, C.M., Chippindale, B.J., Chovit, C.J., Faust, J.A., Johnson, D.L., Monacos, S.P. and Raney, J., 2000, Recent improvements to the AVIRIS sensor: Flight season 2000. in: Proceedings of the Tenth Annual JPL Airborne Geoscience Workshop, Pasadena, California
Green E.P., Mumby P.J., Edwards A.J. and Clark C.D. (1996). A review of remote sensing for the assessment and management of tropical coastal resources. Coast. Manage. 24: 1–40
Gordon H.R. and Brown O. (1974). Influence of bottom depth and albedo on the diffuse reflectance of a flat homogeneous ocean. Appl. Optics 13: 2153–2159
He R. and Weisberg R.H. (2003). West Florida shelf circulation and temperature budget for the 1998 fall transition. Cont. Shelf Res. 23: 777–800
Jerlov N.G. (1976). Marine Optics. Elsevier, New York
Lee Z., Carder K.L., Hawes S.K., Steward R.G., Peacock T.G. and Davis C.O. (1994). Model for the interpretation of hyperspectral remote-sensing reflectance. Appl. Optics 33: 5721–5732
Lee Z., Carder K.L., Mobley C.D., Steward R.G. and Patch J.S. (1999). Hyperspectral remote sensing for shallow waters II. Deriving bottom depths and water properties by optimization. Appl. Optics 38: 3831–3843
Lee Z., Carder K.L., Chen R.F. and Peacock T.G. (2001). Properties of the water column and bottom derived from AVIRIS data. J. Geophys. Res. 106: 11639–11651
Louchard E., Reid P.R., Stephens F.C., Davis C.O., Leathers R.A. and Downes T.V. (2003). Optical remote sensing of benthic habitats and bathymetry in coastal environments at Lee Stocking Island, Bahamas: A comparative spectral classification approach. Limnol. Oceanogra. 48: 511–521
Lyzenga D.R. (1978). Passive remote sensing techniques for mapping water depth and bottom features. Appl. Optics 17: 379–383
Lyzenga D.R. (1985). Shallow-water bathymetry using combined Lidar and passive multispectral scanner data. Int. J. Remote Sen. 6: 115–125
Maritorena R.J., Morel A. and Gentilli B. (1994). Diffuse reflectance of oceanic shallow waters: Influence of water depth and bottom albedo. Limnol. Oceanogr. 39: 1689–1703
McIntyre, M.L., Naar, D.F., Carder, K.L., Howd, P.A., Lewis, J.M., Donahue, B.T. and Chen, R.F., 2002, Comparison of bathymetry and bottom characteristics from hyperspectral remote sensing data and shipborne acoustic measurements. in: Eos Transactions of the American Geophysical Union Fall Meeting Supplements, 6–10 December 2002, p. 47. San Francisco, California
McIntyre M.L. (2003). Testing a model for deriving bathymetry from airborne hyperspectral data by comparing with multibeam sonar data. MS thesis. University of South Florida, St. Petersburg, Florida
Mobley C.D. (1993). Comparison of numerical models for computing underwater light fields. Appl. Optics 32: 7484–75041
Mustard J.F., Staid M.I. and Fripp W.J. (2001). A semianalytical approach to the calibration of AVIRIS data to reflectance over water application in a temperate estuary. Remote Sens. Environ. 75: 335–349
Naar, D.F., Donahue, B.T., DeWitt, N., Farmer, A.S., Jarrett, B., Palmsten, M., Reynolds, B.J. and Wilder, D., 1999, Preliminary results from a EM 3000 multibeam class survey along the west coast of the Florida carbonate platform. in: Eos Transactions of the American Geophysical Union Fall Meeting Supplements, 13–17 December 1999, p 46. San Francisco, California
O’Neill N.T. and Miller J.R. (1989). On calibration of passive optical bathymetry through depth soundings analysis and treatment of errors resulting from the spatial variation of environmental parameters. Int. J. Remote Sen. 10: 1481–1501
Philpot W.D. (1989). Bathymetric mapping with passive multispectral imagery. Appl. Optics 28: 1569–1578
Sandidge J.C. and Holyer R.J. (1998). Coastal bathymetry from hyperspectral observations of water radiance. Remote Sens. Environ. 65: 341–352
Vane G., Green R.O., Chrien T.G., Enmark H.T., Hansen E.G. and Porter W.M. (1993). The Airborne Visible/Infrared Imaging Spectrometer (AVIRIS). Remote Sens. Environ. 44: 127–143
Werdell P.J. and Roesler C.S. (2003). Remote assessment of benthic substrate composition in shallow waters using multispectral reflectance. Limnol. Oceanogr. 48(1, part 2): 557–567
Zhan H, Lee Z.P., Shi P., Chen C. and Carder K.L. (2003). Retrieval of water optical properties for optically deep waters using genetic algorithms. IEEE T. Geosci. Remote Sens. 41: 1123–1128
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
McIntyre, M.L., Naar, D.F., Carder, K.L. et al. Coastal Bathymetry from Hyperspectral Remote Sensing Data: Comparisons with High Resolution Multibeam Bathymetry. Mar Geophys Res 27, 129–136 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11001-005-0266-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11001-005-0266-y