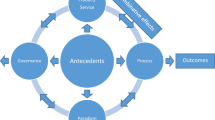
Abstract
Studies on the adoption of innovations in organizations are abundant and have introduced many different factors that are likely to influence adoption decisions yet, somehow, without an integrated view among them and with somehow contradictory empirical results. This study introduces a conceptual framework in which the attributes of innovation–adoption decision linkages in organizations are mediated by both the behavioral preferences of managers and organizations’ resources and moderated by the innovation life cycle. It further meta-analytically tests the framework’s predictions on 185 primary empirical studies. The findings are expected to contribute to the literature on the adoption of innovations by deepening the theoretical conditions and empirical factors that are likely to influence adoption decisions in organizations. The study also has implications for practice, since it sheds light on the factors that practitioners can leverage to manage the diffusion of innovations.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ajzen, I. (1985). From intentions to actions: A theory of planned behavior. In J. Kuhl & J. Beckmann (Eds.), Action-control: From cognition to behavior (pp. 11–39). Heidelberg: Springer.
Ajzen, I. (1987). Attitudes, traits, and actions: Dispositional prediction of behavior in personality and social psychology. In L. Berkowitz (Ed.), Advances in experimental social psychology (pp. 1–63). New York: Academic Press.
Ajzen, I. (1991). The theory of planned behavior. Organizational Behavior and Human Decision Processes,50(2), 179–211.
Ajzen, I. (1996). The social psychology of decision making. In E. T. Higgins & A. W. Kruglanski (Eds.), Social psychology: Handbook of basic principles (pp. 297–325). New York, NY: Guilford.
Ajzen, I., & Driver, B. L. (1992). Contingent value measurement: On the nature and meaning of willingess to pay. Journal of Consumer Psychology,1(4), 297–316.
Alam, S. S., & Noor, M. K. M. (2009). ICT adoption in small and medium enterprises: An empirical evidence of service sectors in Malaysia. International Journal of Business and Management,4(2), 112–125.
Alexandra, V., & Kassim, E. S. (2013). Factors of social networking use as a business tool among micro-enterprises. Paper presented at the 3rd international conference on research and innovation in information systems (ICRIIS), Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, November 27–28, 2013.
Anderson, N., Potočnik, K., & Zhou, J. (2014). Innovation and creativity in organizations a state-of-the-science review, prospective commentary, and guiding framework. Journal of Management,40(5), 1297–1333.
Angle, H. L., & Van de Ven, A. H. (1989). Suggestions for managing the innovation journey. In A. H. Van de Ven, H. L. Angle, & M. S. Poole (Eds.), Research on the management of innovation: The Minnesota studies (pp. 663–698). New York: Oxford University Press.
Arend, R. J. (2014). Social and environmental performance at SMEs: Considering motivations, capabilities, and instrumentalism. Journal of Business Ethics,125(4), 541–561.
Arpaci, I. (2013). Organizational adoption of mobile communication technologies. Ankara: Middle East Technical University.
Arts, J. W. C., Frambach, R. T., & Bijmolt, T. H. A. (2011). Generalizations on consumer innovation adoption: A meta-analysis on drivers of intention and behavior. International Journal of Research in Marketing,28(2), 134–144.
Attewell, P. (1992). Technology diffusion and organizational learning: The case of business computing. Organization Science,3(1), 1–19.
Aubert, B. A., Schroeder, A., & Grimaudo, J. (2012). IT as enabler of sustainable farming: An empirical analysis of farmers’ adoption decision of precision agriculture technology. Decision Support Systems,54(1), 510–520.
Bamberger, P. (2008). From the editors beyond contextualization: Using context theories to narrow the micro-macro gap in management research. Academy of Management Journal,51(5), 839–846.
Bandura, A. (1977). Self-efficacy: Toward a unifying theory of behavioral change. Psychological Review,84(2), 191–215.
Barney, J. (1991). Firm resources and sustained competitive advantage. Journal of Management,17(1), 99–120.
Bass, B. M., & Stogdill, R. M. (1990). Handbook of leadership. New York: The Free Press.
Bauer, T. N., Bodner, T., Erdogan, B., Truxillo, D. M., & Tucker, J. S. (2007). Newcomer adjustment during organizational socialization: A meta-analytic review of antecedents, outcomes, and methods. Journal of Applied Psychology,92(3), 707.
Begg, C. B. (1994). Publication bias. In H. Cooper & L. V. Hedges (Eds.), The handbook of research synthesis (pp. 399–409). New York: Russel Sage Foundation.
Bentler, P. M. (1990). Comparative fit indexes in structural models. Psychological Bulletin,107(2), 238–246.
Blalock, H. (1961). Causal inferences in nonexperimental research. Chapel Hill: University of North Carolina Press.
Bobko, P., & Rieck, A. (1980). Large sample estimators for standard errors of functions of correlation coefficients. Applied Psychological Measurement,4(3), 385–398.
Borenstein, M., Hedges, L. V., Higgins, J. P., & Rothstein, H. R. (2009). Introduction to meta-analysis. West Sussex: Wiley.
Brown, R. L. (1997). Assessing specific mediational effects in complex theoretical models. Structural Equation Modeling: A Multidisciplinary Journal,4(2), 142–156.
Bruque, S., & Moyano, J. (2007). Organisational determinants of information technology adoption and implementation in SMEs: The case of family and cooperative firms. Technovation,27(5), 241–253.
Brynjolfsson, E., Hitt, L. M., & Yang, S. (2002). Intangible assets: Computers and organizational capital. Brookings Papers on Economic Activity,2002(1), 137–181.
Bullock, R. J., & Svyantek, D. J. (1985). Analyzing meta-analysis: Potential problems, an unsuccessful replication, and evaluation criteria. Journal of Applied Psychology,70(1), 108–115.
Caiazza, R. (2016). A cross-national analysis of policies affecting innovation diffusion. Journal of Technology Transfer,41(6), 1406–1419.
Camisón-Zornoza, C., Lapiedra-Alcamí, R., Segarra-Ciprés, M., & Boronat-Navarro, M. (2004). A meta-analysis of innovation and organizational size. Organization Studies,25(3), 331–361.
Camisón-Zornoza, C., & Villar-López, A. (2014). Organizational innovation as an enabler of technological innovation capabilities and firm performance. Journal of Business Research,67(1), 2891–2902.
Carney, M., Gedajlovic, E. R., Heugens, P. P., Van Essen, M., & Van Oosterhout, J. H. (2011). Business group affiliation, performance, context, and strategy: A meta-analysis. Academy of Management Journal,54(3), 437–460.
Chen, M.-J. (1996). Competitor analysis and interfirm rivalry: Toward a theoretical integration. Academy of Management Review,21(1), 100–134.
Chen, J., Damanpour, F., & Reilly, R. R. (2010). Understanding antecedents of new product development speed: A meta-analysis. Journal of Operations Management,28(1), 17–33.
Cheung, M. W. L. (2009). Comparison of methods for constructing confidence intervals of standardized indirect effects. Behavior Research Methods,41(2), 425–438.
Cheung, M. W. L., & Chan, W. (2005). Meta-analytic structural equation modeling: A two-stage approach. Psychological Methods,10(1), 40–64.
Cohen, J., & Cohen, P. (1983). Applied multiple regression/correlation analysis for the behavioral sciences (2nd ed.). Hillsdale, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates Inc.
Cohen, W. M., & Levinthal, D. A. (1990). Absorptive capacity: A new perspective on learning and innovation. Administrative Science Quarterly,35(1), 128–152.
Colquitt, J. A., LePine, J. A., & Noe, R. A. (2000). Toward an integrative theory of training motivation: A meta-analytic path analysis of 20 years of research. Journal of Applied Psychology,85(5), 678.
Cordano, M., & Frieze, I. H. (2000). Pollution reduction preferences of U.S. environmental managers: Applying Ajzen’s theory of planned behavior. Academy of Management Journal,43(4), 627–641.
Crespo, Á. H., & del Bosque, I. R. (2008). The effect of innovativeness on the adoption of B2C e-commerce: A model based on the theory of planned behaviour. Computers in Human Behavior,24(6), 2830–2847.
Crossan, M. M., & Apaydin, M. (2010). A multi-dimensional framework of organizational innovation: A systematic review of the literature. Journal of Management Studies,47(6), 1154–1191.
Daft, R. L. (1978). A dual-core model of organizational innovation. Academy of Management Journal,21(2), 193–210.
Damanpour, F. (1991). Organizational innovation: A meta-analysis of effects of determinants and moderators. Academy of Management Journal,34(3), 555–590.
Damanpour, F., Walker, R. M., & Avellaneda, C. N. (2009). Combinative effects of innovation types and organizational performance: A longitudinal study of service organizations. Journal of Management Studies,46(4), 650–675.
Daryanto, A., Khan, H., Matlay, H., & Chakrabarti, R. (2013). Adoption of country-specific business websites. The case of UK small businesses entering the Chinese market. Journal of Small Business and Enterprise Development,20(3), 650–660.
Davis, F. D. (1989). Perceived usefulness, perceived ease of use, and user acceptance of information technology. MIS Quarterly,13(4), 319–340.
Downs, J. G. W., & Mohr, L. B. (1976). Conceptual issues in the study of innovation. Administrative Science Quarterly,21(4), 700–714.
Dulany, D. E., Jr. (1961). Hypotheses and habits in verbal “operant conditioning”. Journal of Abnormal and Social Psychology,63(2), 251–263.
Dutton, J. E., & Jackson, S. E. (1987). Categorizing strategic issues: Links to organizational action. Academy of Management Review,12(1), 76–90.
Ettlie, J. E. (1983). Organizational policy and innovation among suppliers to the food processing sector. Academy of Management Journal,26(1), 27–44.
Fern, E. F., & Monroe, K. B. (1996). Effect-size estimates: Issues and problems in interpretation. Journal of Consumer Research,23(2), 89–105.
Fiedler, K., Schott, M., & Meiser, T. (2011). What mediation analysis can (not) do. Journal of Experimental Social Psychology,47(6), 1231–1236.
Fishbein, M., & Ajzen, I. (1975). Belief, attitude, intention and behavior: An introduction to theory and research. Reading, MA: Addison-Wesley.
Fisher, J. D., Fisher, W. A., Bryan, A. D., & Misovich, S. J. (2002). Information-motivation-behavioral skills model-based HIV risk behavior change intervention for inner-city high school youth. Health Psychology,21(2), 177–186.
Frambach, R. T., & Schillewaert, N. (2002). Organizational innovation adoption. A multi-level framework of determinants and opportunities for future research. Journal of Business Research,55(2), 163–176.
Gajendran, R. S., & Harrison, D. A. (2007). The good, the bad, and the unknown about telecommuting: Meta-analysis of psychological mediators and individual consequences. Journal of Applied Psychology,92(6), 1524–1541.
Gallivan, M. J. (2001). Organizational adoption and assimilation of complex technological innovations: Development and application of a new framework. ACM SIGMIS Database,32(3), 51–85.
Gamal Aboelmaged, M. (2010). Predicting e-procurement adoption in a developing country: An empirical integration of technology acceptance model and theory of planned behaviour. Industrial Management and Data Systems,110(3), 392–414.
Ghobakhloo, M., & Tang, S. H. (2013). The role of owner/manager in adoption of electronic commerce in small businesses: The case of developing countries. Journal of Small Business and Enterprise Development,20(4), 754–787.
Gómez, J., & Vargas, P. (2012). Intangible resources and technology adoption in manufacturing firms. Research Policy,41(9), 1607–1619.
Gooding, R. Z., & Wagner, J. A. (1985). A meta-analytic review of the relationship between size and performance. Administrative Science Quarterly,30(3), 462–481.
Gu, V. C., Cao, Q., & Duan, W. (2012). Unified Modeling Language (UML) IT adoption—A holistic model of organizational capabilities perspective. Decision Support Systems,54(1), 257–269.
Gupta, P., Seetharaman, A., & Raj, J. R. (2013). The usage and adoption of cloud computing by small and medium businesses. International Journal of Information Management,33(5), 861–874.
Hambrick, D. C., & Mason, P. A. (1984). Upper echelons: The organization as a reflection of its top managers. Academy of Management Review,9(2), 193–206.
Hameed, M. A., Counsell, S., & Swift, S. (2012). A meta-analysis of relationships between organizational characteristics and IT innovation adoption in organizations. Information and Management,49(5), 218–232.
Harland, P., Staats, H., & Wilke, H. A. (1999). Explaining proenvironmental intention and behavior by personal norms and the theory of planned behavior. Journal of Applied Social Psychology,29(12), 2505–2528.
Harrison, D. A., Mykytyn, P. P., Jr., & Riemenschneider, C. K. (1997). Executive decisions about adoption of information technology in small business: Theory and empirical tests. Information Systems Research,8(2), 171–195.
Hauser, J., Tellis, G. J., & Griffin, A. (2006). Research on innovation: A review and agenda for marketing science. Marketing Science,25(6), 687–717.
He, Q., Duan, Y., Fu, Z., & Li, D. (2006). An innovation adoption study of online e-payment in chinese companies. Journal of Electronic Commerce in Organizations,4(1), 48–69.
Henderson, D., Sheetz, S. D., & Trinkle, B. S. (2012). The determinants of inter-organizational and internal in-house adoption of XBRL: A structural equation model. International Journal of Accounting Information Systems,13(2), 109–140.
Heyder, M., Theuvsen, L., & Hollmann-Hespos, T. (2012). Investments in tracking and tracing systems in the food industry: A PLS analysis. Food Policy,37(1), 102–113.
Higgins, J., & Thompson, S. G. (2004). Controlling the risk of spurious findings from meta-regression. Statistics in Medicine,23(11), 1663–1682.
Hossain, M. A., & Quaddus, M. (2015). Radio frequency identification (RFID) adoption: A cross-sectional comparison of voluntary and mandatory contexts. Information Systems Frontiers,17(5), 1057–1076.
Hsing Wu, C., Kao, S.-C., & Lin, H.-H. (2013). Acceptance of enterprise blog for service industry. Internet Research,23(3), 260–297.
Hsu, P.-F., Ray, S., & Li-Hsieh, Y.-Y. (2014). Examining cloud computing adoption intention, pricing mechanism, and deployment model. International Journal of Information Management,34(4), 474–488.
Hung, S.-Y., Hung, W.-H., Tsai, C.-A., & Jiang, S.-C. (2010). Critical factors of hospital adoption on CRM system: Organizational and information system perspectives. Decision Support Systems,48(4), 592–603.
Hussin, H., Nor, R. M., & Suhaimi, M. A. (2008). Perceived attributes of e-commerce and the adoption decision: The case of Malaysian SMEs. Jurnal Teknologi Maklumat and Multimedia,5(1), 107–125.
Jackson, E. L. (2008). Behavioural determinants of the adoption of forward contracts by Western Australian wool producers. Curtin: Curtin University of Technology.
Jarrett, S. M. (2003). Factors affecting the adoption of e-business in the aerospace industry. Nova: Nova Southeastern University.
Jeon, B. N., Han, K. S., & Lee, M. J. (2006). Determining factors for the adoption of e-business: The case of SMEs in Korea. Applied Economics,38(16), 1905–1916.
Jeyaraj, A., Rottman, J. W., & Lacity, M. C. (2006). A review of the predictors, linkages, and biases in IT innovation adoption research. Journal of Information Technology,21(1), 1–23.
Kaplan, S. (2008). Cognition, capabilities, and incentives: Assessing firm response to the fiber-optic revolution. Academy of Management Journal,51(4), 672–695.
Kapoor, K. K., Dwivedi, Y. K., & Williams, M. D. (2014a). Innovation adoption attributes: A review and synthesis of research findings. European Journal of Innovation Management,17(3), 327–348.
Kapoor, K. K., Dwivedi, Y. K., & Williams, M. D. (2014b). Rogers’ innovation adoption attributes: A systematic review and synthesis of existing research. Information Systems Management,31(1), 74–91.
Kaufmann, D., Kraay, A., & Mastruzzi, M. (2010). The worldwide governance indicators: A summary of methodology, data and analytical issues. World Bank policy research working paper (Vol. 5430).
Kennedy, M. T., & Fiss, P. C. (2009). Institutionalization, framing, and diffusion: The logic of TQM adoption and implementation decisions among U.S. hospitals. Academy of Management Journal,52(5), 897–918.
Keupp, M. M., Palmié, M., & Gassmann, O. (2012). The strategic management of innovation: A systematic review and paths for future research. International Journal of Management Reviews,14(4), 367–390.
Kimberly, J. R., & Evanisko, M. R. (1981). Organizational innovation: The influence of individual, organizational, and contextual factors on hospital adoption of technological and administrative innovations. Academy of Management Journal,24(4), 689–713.
King, W. R., & He, J. (2006). A meta-analysis of the technology acceptance model. Information and Management,43(6), 740–755.
Kurnia, S., Choudrie, J., Mahbubur, R. M., & Alzougool, B. (2015). E-commerce technology adoption: A Malaysian grocery SME retail sector study. Journal of Business Research,68(9), 1906–1918.
Lau, R. R., Sigelman, L., Heldman, C., & Babbitt, P. (1999). The effects of negative political advertisements: A meta-analytic assessment. American Political Science Review,93(4), 851–875.
Lee, Y., & Larsen, K. R. T. (2009). Threat or coping appraisal: Determinants of SMB executives’ decision to adopt anti-malware software. European Journal of Information Systems,18(2), 177–187.
Lefebvre, L. A., Lefebvre, E., Elia, E., & Boeck, H. (2005). Exploring B-to-B e-commerce adoption trajectories in manufacturing SMEs. Technovation,25(12), 1443–1456.
Lefebvre, L. A., Lefebvre, E., & Harvey, J. (1996). Intangible assets as determinants of advanced manufacturing technology adoption in SME’s: Toward an evolutionary model. IEEE Transactions on Engineering Management,43(3), 307–322.
Leung, M. T. (2005). Determinants of the adoption of technological innovations in organizations. Hong Kong: Hong Kong Polythechnic University.
Levin, S. G., Levin, S. L., & Meisel, J. B. (1987). A dynamic analysis of the adoption of a new technology: The case of optical scanners. Review of Economics and Statistics,69(1), 12–17.
Li, X., Troutt, M. D., Brandyberry, A., & Wang, T. (2011). Decision factors for the adoption and continued use of online direct sales channels among SMEs. Journal of the Association for Information Systems,12(1), 1–31.
Lieberman, M. B., & Montgomery, D. B. (1988). First-mover advantages. Strategic Management Journal,9(S1), 41–58.
Lin, C.-Y., & Ho, Y.-H. (2011). Determinants of green practice adoption for logistics companies in China. Journal of Business Ethics,98(1), 67–83.
Lin, C.-H., Lin, I.-C., Roan, J.-S., & Yeh, J.-S. (2012). Critical factors influencing hospitals’ adoption of HL7 version 2 standards: An empirical investigation. Journal of Medical Systems,36(3), 1183–1192.
Lipsey, M. W., & Wilson, D. B. (2001). Practical meta-analysis. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage.
Livengood, R. S., & Reger, R. K. (2010). That’s our turf! Identity domains and competitive dynamics. Academy of Management Review,35(1), 48–66.
Marcati, A., Guido, G., & Peluso, A. M. (2008). The role of SME entrepreneurs’ innovativeness and personality in the adoption of innovations. Research Policy,37(9), 1579–1590.
March, J. G., & Simon, H. A. (1958). Organizations. New York: Wiley.
Martinez-Garcıa, C. G., Dorward, P., & Rehman, T. (2013). Factors influencing adoption of improved grassland management by small-scale dairy farmers in central Mexico and the implications for future research on small holder adoption in developing countries. Livestock Science,152(2–3), 228–238.
Messerschmidt, C. M., & Hinz, O. (2013). Explaining the adoption of grid computing: An integrated institutional theory and organizational capability approach. Journal of Strategic Information Systems,22(2), 137–156.
Meyers, L. S., Gamst, G., & Guarino, A. J. (2006). Applied multivariate research: Design and interpretation. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage.
Miller, C. C., & Cardinal, L. B. (1994). Strategic planning and firm performance: A synthesis of more than two decades of research. Academy of Management Journal,37(6), 1649–1665.
Miller, D., & Friesen, P. H. (1982). Innovation in conservative and entrepreneurial firms: Two models of strategic momentum. Strategic Management Journal,3(1), 1–25.
Mitchell, T. R. (1985). An evaluation of the validity of correlational research conducted in organizations. Academy of Management Review,10(2), 192–205.
Montazemi, A. R., & Qahri-Saremi, H. (2015). Factors affecting adoption of online banking: A meta-analytic structural equation modeling study. Information and Management,52(2), 210–226.
Nasco, S. A., Toledo, E. G., & Mykytyn, P. P. (2008). Predicting electronic commerce adoption in Chilean SMEs. Journal of Business Research,61(6), 697–705.
Nigbur, D., Lyons, E., & Uzzell, D. (2010). Attitudes, norms, identity and environmental behaviour: Using an expanded theory of planned behaviour to predict participation in a kerbside recycling programme. British Journal of Social Psychology,49(2), 259–284.
North, D. C. (1990). Institutions, institutional change and economic performance. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Oliver, R. L., & Bearden, W. O. (1985). Crossover effects in the theory of reasoned action: A moderating influence attempt. Journal of Consumer Research,12(3), 324–340.
Ozusaglam, S., Robin, S., & Wong, C. Y. (2018). Early and late adopters of ISO 14001-type standards: Revisiting the role of firm characteristics and capabilities. Journal of Technology Transfer,43(5), 1318–1345.
Perrow, C. (1994). Accidents in high-risk systems. Technology Studies,1(1), 1–20.
Pierce, J. L., & Delbecq, A. L. (1977). Organization structure, individual attitudes and innovation. Academy of Management Review,2(1), 27–37.
Porter, B. E. (2005). Time and implementing change. British Journal of Educational Technology,36(6), 1063–1065.
Powell, W. W., & DiMaggio, P. J. (2012). The new institutionalism in organizational analysis. Chicago: University of Chicago Press.
Premkumar, G. (2003). A meta-analysis of research on information technology implementation in small business. Journal of Organizational Computing and Electronic Commerce,13(2), 91–121.
Premkumar, G., & Roberts, M. (1999). Adoption of new information technologies in rural small businesses. Omega,27(4), 467–484.
Quaddus, M., & Hofmeyer, G. (2007). An investigation into the factors influencing the adoption of B2B trading exchanges in small businesses. European Journal of Information Systems,16(3), 202–215.
Reed, R., & DeFillippi, R. J. (1990). Causal ambiguity, barriers to imitation, and sustainable competitive advantage. Academy of Management Review,15(1), 88–102.
Riemenschneider, C. K., Harrison, D. A., & Mykytyn, P. P. (2003). Understanding IT adoption decisions in small business: Integrating current theories. Information and Management,40(4), 269–285.
Rivkin, J. W. (2000). Imitation of complex strategies. Management Science,46(6), 824–844.
Riyadh, A. N., Rahman, A., & Tanha, M. (2012). Factors affecting internet adoption in the garments industry in Bangladesh: A structural equation modeling (SEM) approach. D.U. Journal of Marketing,15(1), 1–29.
Rogers, E. M. (1983). Diffusion of innovations. New York: The Free Press.
Rosenbusch, N., Brinckmann, J., & Bausch, A. (2011). Is innovation always beneficial? A meta-analysis of the relationship between innovation and performance in SMEs. Journal of Business Venturing,26(4), 441–457.
Rosenbusch, N., Rauch, A., & Bausch, A. (2013). The mediating role of entrepreneurial orientation in the task environment–performance relationship: A meta-analysis. Journal of Management,39(3), 633–659.
Rosenthal, R. (1979). The “file drawer problem” and tolerance for null results. Psychological Bulletin,86(3), 638–641.
Rosenthal, R. (1991). Meta-analytical procedures for social research. Newbury Park, CA: Sage.
Rosenthal, R., & Rubin, D. B. (1982). A simple, general purpose display of magnitude of experimental effect. Journal of Educational Psychology,74(2), 166.
Ross, L. (1977). The intuitive psychologist and his short-comings. In L. Berkowitz (Ed.), Advances in experimental social psychology (Vol. 10, pp. 173–220). New York: Academic Press.
Ryan, M. J. (1982). Behavioral intention formation: The interdependency of attitudinal and social influence variables. Journal of Consumer Research,9(3), 263–278.
Schmidt, F. L., & Hunter, J. E. (2004). Methods of meta-analysis: Correcting error and bias in research findings. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage.
Schumpeter, J. A. (1934). The theory of economic development: An inquiry into profits, capital, credit, interest, and the business cycle. Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press.
Schwartz, S. H., & Howard, J. A. (1984). Internalized values as moderators of altruism. In E. Staub, D. Bar-Tal, J. Karylowski, & J. Reykowski (Eds.), Development and maintenance of prosocial behavior (pp. 229–255). New York, NY: Plenum.
Scott, W. R. (2001). Institutions and organizations. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage.
Segaar, D., Bolman, C., Willemsen, M. C., & de Vries, H. (2006). Determinants of adoption of cognitive behavioral interventions in a hospital setting: Example of a minimal-contact smoking cessation intervention for cardiology wards. Patient Education and Counseling,61(2), 262–271.
Seyal, A. H., & Rahman, M. N. A. (2003). A preliminary investigation of e-commerce adoption in small & medium enterprises in Brunei. Journal of Global Information Technology Management,6(2), 6–26.
Shadish, W. R. (1996). Meta-analysis and the exploration of causal mediating processes: A primer of examples, methods, and issues. Psychological Methods,1(1), 47–65.
Sheth, J. N. (1973). A model of industrial buyer behavior. Journal of Marketing,37(4), 50–56.
Sobel, M. E. (1982). Asymptotic intervals for indirect effects in structural equations models. In S. Leinhart (Ed.), Sociological methodology (pp. 290–312). San Francisco: Jossey-Bass.
Steadman, L., Rutter, D., & Field, S. (2002). Individually elicited versus modal normative beliefs in predicting attendance at breast screening: Examining the role of belief salience in the theory of planned behaviour. British Journal of Health Psychology,7(3), 317–330.
Stern, P. C., Dietz, T., Abel, T., Guagnano, G. A., & Kalof, L. (1999). A value-belief-norm theory of support for social movements: The case of environmentalism. Human Ecology Review,6(2), 81–97.
Subramanian, A., & Nilakanta, S. (1996). Organizational innovativeness: Exploring the relationship between organizational determinants of innovation, types of innovations, and measures of organizational performance. Omega,24(6), 631–647.
Swanson, E. B. (1994). Information systems innovation among organizations. Management Science,40(9), 1069–1092.
Tabachnick, B. G., & Fidell, L. S. (1996). Using multivariate statistics. New York: Harper & Collins.
Tajfel, H., & Turner, J. C. (2004). The social identity theory of intergroup behavior. In J. T. Jost & J. Sidanius (Eds.), Key readings in social psychology. Political psychology (pp. 276–293). New York, NY: Psychology Press.
Taylor, S., & Todd, P. (1995). Decomposition and crossover effects in the theory of planned behavior: A study of consumer adoption intentions. International Journal of Research in Marketing,12(2), 137–155.
Teece, D. J. (1986). Profiting from technological innovation: Implications for integration, collaboration, licensing and public policy. Research Policy,15(6), 285–305.
Thompson, S. H. T., Sijie, L., & Kee-hung, L. (2009). Adopters and non-adopters of e-procurement in Singapore: An empirical study. Omega,37(5), 972–987.
Thong, J. Y. (1999). An integrated model of information systems adoption in small businesses. Journal of Management Information Systems,15(4), 187–214.
Thong, J. Y. (2001). Resource constraints and information systems implementation in Singaporean small businesses. Omega,29(2), 143–156.
Thong, J. Y., & Yap, C.-S. (1995). CEO characteristics, organizational characteristics and information technology adoption in small businesses. Omega,23(4), 429–442.
Tidd, J. (2001). Innovation management in context: Environment, organization and performance. International Journal of Management Reviews,3(3), 169–183.
Tolbert, P. S., & Zucker, L. G. (1983). Institutional sources of change in the formal structure of organizations: The diffusion of civil service reform, 1880–1935. Administrative Science Quarterly,28(1), 22–39.
Tornatzky, L. G., & Klein, K. J. (1982). Innovation characteristics and innovation adoption-implementation: A meta-analysis of findings. IEEE Transactions on Engineering Management,29(1), 28–43.
Triandis, H. C. (1979). Values, attitudes, and interpersonal behavior. Nebraska Symposium on Motivation,27(1), 195–259.
Tsai, M.-C., Lee, W., & Wu, H.-C. (2010). Determinants of RFID adoption intention: Evidence from Taiwanese retail chains. Information and Management,47(5–6), 255–261.
Tung, L. L., & Rieck, O. (2005). Adoption of electronic government services among business organizations in Singapore. Journal of Strategic Information Systems,14(4), 417–440.
Uzoka, F.-M. E., & Ndzinge, T. (2009). Empirical analysis of biometric technology adoption and acceptance in Botswana. Journal of Systems and Software,82(9), 1550–1564.
Vagnani, G., & Volpe, L. (2017). Innovation attributes and managers’ decisions about the adoption of innovations in organizations: A meta-analytical review. International Journal of Innovation Studies,1(2), 107–133.
van Oorschot, J. A. W. H., Hofman, E., & Halman, J. I. M. (2018). A bibliometric review of the innovation adoption literature. Technological Forecasting and Social Change,134(9), 1–21.
Viswesvaran, C., & Ones, D. S. (1995). Theory testing: Combining psychometric meta-analysis and strucutural equations modeling. Personnel Psychology,48(4), 865.
Waarts, E., Everdingen, Y. M., & Hillegersberg, J. (2002). The dynamics of factors affecting the adoption of innovations. Journal of Product Innovation Management,19(6), 412–423.
Wang, M. C., & Bushman, B. J. (1999). Integrating results through meta-analytic review using SAS software. Cary, NC: SAS Institute.
Weigel, F. K., Hazen, B. T., Cegielski, C. G., & Hall, D. J. (2014). Diffusion of innovations and the theory of planned behavior in information systems research: A meta-analysis. Communications of the Association for Information Systems,34(1), 31–43.
Weng, M.-H., & Lin, C.-Y. (2011). Determinants of green innovation adoption for small and medium-size enterprises (SMES). African Journal of Business Management,5(22), 9154–9163.
Westphal, J. D., Gulati, R., & Shortell, S. M. (1997). Customization or conformity? An institutional and network perspective on the content and consequences of TQM adoption Administrative Science Quarterly,42(2), 366–394.
Wolfe, R. A. (1994). Organizational innovation: Review, critique and suggested research. Journal of Management Studies,31(3), 405–431.
Wolfswinkel, J. F., Furtmueller, E., & Wilderom, C. P. (2013). Using grounded theory as a method for rigorously reviewing literature. European Journal of Information Systems,22(1), 45–55.
Wozniak, G. D. (1987). Human capital, information, and the early adoption of new technology. The Journal of Human Resources,22(1), 101–112.
Xu, J., & Quaddus, M. (2012). Examining a model of knowledge management systems adoption and diffusion: A partial least square approach. Knowledge-Based Systems,27(1), 18–28.
Zaltman, G., Duncan, R., & Holbek, J. (1973). Innovations and organizations. New York: Wiley.
Zmud, R. W., & Apple, L. E. (1992). Measuring technology incorporation/infusion. Journal of Product Innovation Management,9(2), 148–155.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Details of all works included in the meta-analysis are reported in an electronic companion available from both the journal’s website and the home page of Gianluca Vagnani on the Department of Management, Sapienza, University of Rome.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vagnani, G., Gatti, C. & Proietti, L. A conceptual framework of the adoption of innovations in organizations: a meta-analytical review of the literature. J Manag Gov 23, 1023–1062 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10997-019-09452-6
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10997-019-09452-6