Abstract
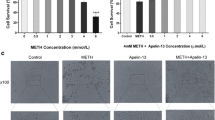
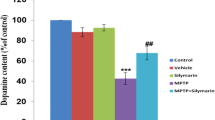
Methamphetamine (METH) abuse causes irreversible neural damages in the brain. It is well-known that Nesfatin-1, a neuropeptide involved in appetite and body weight, has a neuroprotective effect against oxidative stress and apoptotic response in dopaminergic cells. Therefore, the present study aimed to evaluate if Nesfatin-1 could antagonize the neurotoxicity induced by METH in the PC12 cells through suppressing apoptosis, autophagy, and oxidative stress. In this in vitro study, the pretreatment of the PC12 cells was conducted using 1, 5, 10, and 100 ng/ml of Nesfatin-1 for 1 h, followed by exposure to METH (0.5, 1, 2, 3, 4, and 6 mM) for 24 h to determine the appropriate toxic and most protective dose of METH and Nesfatin-1 by MTT assay, respectively. Further investigations were performed to inspect oxidative stress, apoptosis, and autophagy responses. According to the obtained results, Nesfatin-1 could mitigate the overproduction of the reactive oxygen species in the METH-exposed PC12 cells. Moreover, Nesfatin-1 could ameliorate METH-induced apoptotic cell death by augmenting the cell viability and decreasing apoptotic rates. In addition, the amounts of autophagosome formation and microtubule-associated protein-light chain 3 levels were decreased significantly demonstrating the protective effect of Nesfatin-1 against autophagy induced by METH. In conclusion, Nesfatin-1 could be regarded as a therapeutic agent against cell injury triggered by METH by inhibiting oxidative stress, apoptosis, and autophagy.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Açikgöz O, Gönenç S, Kayatekin BM, Pekçetin Ç, Uysal N, Dayi A, Şemin İ, Güre A (2000) The effects of single dose of methamphetamine on lipid peroxidation levels in the rat striatum and prefrontal cortex. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 10:415–418
Alam-mehrjerdi Z, Mokri A, Dolan K (2015) Methamphetamine use and treatment in Iran: a systematic review from the most populated Persian Gulf country. Asian J Psychiatr 16:17–25
Aydin S (2013) Multi-functional peptide hormone NUCB2/nesfatin-1. Endocrine 44:312–325
Bhat AH, Dar KB, Anees S, Zargar MA, Masood A, Sofi MA, Ganie SA (2015) Oxidative stress, mitochondrial dysfunction and neurodegenerative diseases; a mechanistic insight. Biomed Pharmacother 74:101–110
Brailoiu GC, Dun SL, Brailoiu E, Inan S, Yang J, Chang JK, Dun NJ (2007) Nesfatin-1: distribution and interaction with a G protein-coupled receptor in the rat brain. Endocrinology 148:5088–5094
Cadet JL, Jayanthi S, Deng X (2003) Speed kills: cellular and molecular bases of methamphetamine-induced nerve terminal degeneration and neuronal apoptosis. FASEB J 17:1775–1788
Cadet JL, Krasnova IN, Jayanthi S, Lyles J (2007) Neurotoxicity of substituted amphetamines: molecular and cellular mechanisms. Neurotox Res 11:183–202
Cecconi F, Levine B (2008) The role of autophagy in mammalian development: cell makeover rather than cell death. Dev Cell 15:344–357
Chandramani Shivalingappa P, Jin H, Anantharam V, Kanthasamy A, Kanthasamy A (2012) N-acetyl cysteine protects against methamphetamine-induced dopaminergic neurodegeneration via modulation of redox status and autophagy in dopaminergic cells. Parkinson’s Dis 2012:424285
Chen M, Zheng H, Wei T, Wang D, Xia H, Zhao L, Ji J, Gao H (2016) High glucose-induced PC12 cell death by increasing glutamate production and decreasing methyl group metabolism. BioMed Res Int 2016:4125731
Chun Y, Kim J (2018) Autophagy: an essential degradation program for cellular homeostasis and life. Cells 7:278
Cisneros IE, Ghorpade A (2014) Methamphetamine and HIV-1-induced neurotoxicity: role of trace amine associated receptor 1 cAMP signaling in astrocytes. Neuropharmacology 85:499–507
Coelho-Santos V, Gonçalves J, Fontes-Ribeiro C, Silva AP (2012) Prevention of methamphetamine-induced microglial cell death by TNF-α and IL-6 through activation of the JAK-STAT pathway. J Neuroinflamm 9:103
Das GS, Baehrecke EH, Baehrecke EH (2012) Regulation and function of autophagy during cell survival and cell death. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 4:a008813. https://doi.org/10.1101/cshperspect.a008813a13
Erfani S, Moghimi A, Aboutaleb N, Khaksari M (2018) Nesfatin-1 improve spatial memory impairment following transient global cerebral ischemia/reperfusion via inhibiting microglial and caspase-3 activation. J Mol Neurosci 65:377–384
Erfani S, Moghimi A, Aboutaleb N, Khaksari M (2019) Protective effects of Nesfatin-1 peptide on cerebral ischemia reperfusion injury via inhibition of neuronal cell death and enhancement of antioxidant defenses. Metab Brain Dis 34:79–85
Filomeni G, De Zio D, Cecconi F (2015) Oxidative stress and autophagy: the clash between damage and metabolic needs. Cell Death Differ 22:377–388
Foo KS, Brismar H, Broberger C (2008) Distribution and neuropeptide coexistence of nucleobindin-2 mRNA/nesfatin-like immunoreactivity in the rat CNS. Neuroscience 156:563–579
Foroughi K, Khaksari M, Rahmati M, Bitaraf FS, Shayannia A (2019) ’Apelin-13 protects PC12 cells against methamphetamine-induced oxidative stress, autophagy and apoptosis. Neurochem Res 44:2103–2112
Garcia-Galiano D, Navarro VM, Gaytan F, Tena-Sempere M (2010) Expanding roles of NUCB2/nesfatin-1 in neuroendocrine regulation. J Mol Endocrinol 45:281–290
Ghanbari F, Khaksari M, Vaezi G, Hojati V, Shiravi A (2019) Hydrogen sulfide protects hippocampal neurons against methamphetamine neurotoxicity via inhibition of apoptosis and neuroinflammation. J Mol Neurosci 67:133–141
Giovanni A, Liang LP, Hastings TG, Zigmond MJ (1995) Estimating hydroxyl radical content in rat brain using systemic and intraventricular salicylate: impact of methamphetamine. J Neurochem 64:1819–1825
Gupta SC, Hevia D, Patchva S, Park B, Koh W, Aggarwal BB (2012) Upsides and downsides of reactive oxygen species for cancer: the roles of reactive oxygen species in tumorigenesis, prevention, and therapy. Antioxid Redox Signal 16:1295–1322
Halpin LE, Collins SA, Yamamoto BK (2014) Neurotoxicity of methamphetamine and 3, 4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine. Life Sci 97:37–44
Huang W, Xie WB, Qiao D, Qiu P, Huang E, Li B, Chen C, Liu C, Wang Q, Lin Z, Wang H (2015) Caspase-11 plays an essential role in methamphetamine-induced dopaminergic neuron apoptosis. Toxicol Sci 145:68–79
Jayanthi S, Ladenheim B, Cadet JL (1998) Methamphetamine-induced changes in antioxidant enzymes and lipid peroxidation in copper/zinc-superoxide dismutase transgenic mice. Ann N Y Acad Sci 844:92–102
Jayanthi S, Deng X, Bordelon MA, Mccoy MT, Cadet JL (2001) Methamphetamine causes differential regulation of pro-death and anti-death Bcl-2 genes in the mouse neocortex. FASEB J 15:1745–1752
Jiang G, Wang M, Wang L, Chen H, Chen Z, Guo J, Weng X, Liu X (2015) The protective effect of nesfatin-1 against renal ischemia–reperfusion injury in rats. Ren Fail 37:882–889
Kang Y, Lee JH, Seo YH, Jang JH, Jeong CH, Lee S, Jeong GS, Park B (2019) Epicatechin prevents methamphetamine-induced neuronal cell death via inhibition of ER stress. Biomol Ther 27:145
Kanthasamy A, Anantharam V, Ali SF, Kanthasamy AG (2006) Methamphetamine induces autophagy and apoptosis in a mesencephalic dopaminergic neuronal culture model: role of cathepsin-D in methamphetamine-induced apoptotic cell death. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1074:234–244
Kolgazi M, Cantali-Ozturk C, Deniz R, Ozdemir-Kumral ZN, Yuksel M, Sirvanci S, Yeğen BC (2015) Nesfatin-1 alleviates gastric damage via direct antioxidant mechanisms. J Surg Res 193:111–118
Kourtis N, Tavernarakis N (2009) Autophagy and cell death in model organisms. Cell Death Differ 16:21–30
Krasnova IN, Cadet JL (2009) Methamphetamine toxicity and messengers of death. Brain Res Rev 60:379–407
Li Y, Hu Z, Chen B, Bu Q, Lu W, Deng Y, Zhu R, Shao X, Hou J, Zhao J, Li H (2012) Taurine attenuates methamphetamine-induced autophagy and apoptosis in PC12 cells through mTOR signaling pathway. Toxicol Lett 215:1–7
Li C, Zhang F, Shi L, Zhang H, Tian Z, Xie J, Jiang H (2014a) Nesfatin-1 decreases excitability of dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra. J Mol Neurosci 52:419–424
Li Y, Wang S, Ni HM, Huang H, Ding WX (2014b) Autophagy in alcohol-induced multiorgan injury: mechanisms and potential therapeutic targets. Biomed Res Int 2014:498491–498591
Lin MT, Beal MF (2006) Mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress in neurodegenerative diseases. Nature 443:787–795
Méndez-Armenta M, Nava-Ruíz C, Juárez-Rebollar D, Rodríguez-Martínez E, Yescas GP (2014) Oxidative stress associated with neuronal apoptosis in experimental models of epilepsy. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2014:29368937
Merz F (2018) United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime: World Drug Report 2017. 2017. SIRIUS–Zeitschrift für Strategische Analysen 2: 85–86.
Mizushima N, Levine B, Cuervo AM, Klionsky DJ (2008) Autophagy fights disease through cellular self-digestion. Nature 451:1069–1075
Nazarnezhad S, Rahmati M, Shayannia A, Abbasi Z, Salehi M, Khaksari M (2019a) Nesfatin-1 protects PC12 cells against high glucose-induced cytotoxicity via inhibiting oxidative stress, autophagy and apoptosis. Neurotoxicology 74:196–202
Nazarnezhad S, Rahmati M, Shayannia A, Abbasi Z, Salehi M, Khaksari M (2019b) Nesfatin-1 protects PC12 cells against high glucose-induced cytotoxicity via inhibiting oxidative Stress, autophagy and apoptosis. Neurotoxicology 74:106–204
Nopparat C, Porter JE, Ebadi M, Govitrapong P (2010) The mechanism for the neuroprotective effect of melatonin against methamphetamine-induced autophagy. J Pineal Res 49:382–389
O’Donnell LA, Agrawal A, Sabnekar P, Dichter MA, Lynch DR, Kolson DL (2007) Apelin, an endogenous neuronal peptide, protects hippocampal neurons against excitotoxic injury. J Neurochem 102:1905–1917
Oh-I S, Shimizu H, Satoh T, Okada S, Adachi S, Inoue K, Eguchi H, Yamamoto M, Imaki T, Hashimoto K, Tsuchiya T (2006) Identification of nesfatin-1 as a satiety molecule in the hypothalamus. Nature 443:709–712
Özsavcí D, Erşahin M, Şener A, Özakpinar ÖB, Toklu HZ, Akakín D, Şener G, Yeğen BÇ (2011) The novel function of nesfatin-1 as an anti-inflammatory and antiapoptotic peptide in subarachnoid hemorrhage–induced oxidative brain damage in rats. Neurosurgery 68:1699–1708
Ozturk CC, Oktay S, Yuksel M, Akakin D, Yarat A, Kasimay CO (2015) Anti-inflammatory effects of nesfatin-1 in rats with acetic acid-induced colitis and underlying mechanisms. J Physiol Pharmacol 66:741–750
Pitaksalee R, Sanvarinda Y, Sinchai T, Sanvarinda P, Thampithak A, Jantaratnotai N, Jariyawat S, Tuchinda P, Govitrapong P, Sanvarinda P (2015) Autophagy inhibition by caffeine increases toxicity of methamphetamine in SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cell line. Neurotox Res 27:421–429
Psilopanagioti A, Nikou S, Papadaki H (2019) Nucleobindin-2/nesfatin-1 in the human hypothalamus is reduced in obese subjects and colocalizes with oxytocin, vasopressin, melanin-concentrating hormone, and cocaine-and amphetamine-regulated transcript. Neuroendocrinology 108:190–200
Radfar SR, Rawson RA (2014) Current research on methamphetamine: epidemiology, medical and psychiatric effects, treatment, and harm reduction efforts. Addict Health 6:146
Riddle EL, Fleckenstein AE, Hanson GR (2006) Mechanisms of methamphetamine-induced dopaminergic neurotoxicity. AAPS J 8:E413–E418
Ru Q, Xiong Q, Tian X, Chen L, Zhou M, Li Y, Li C (2019) Tea polyphenols attenuate methamphetamine-induced neuronal damage of PC12 cells by alleviating oxidative stress and promoting DNA repair. Front Physiol 10:1450
Scherz-Shouval R, Shvets E, Fass E, Shorer H, Gil L, Elazar Z (2007) Reactive oxygen species are essential for autophagy and specifically regulate the activity of Atg4. EMBO J 26:1749–1760
Shakeel M (2015) Recent advances in understanding the role of oxidative stress in diabetic neuropathy. Diabetes Metab Syndr 9:373–378
Sharifi H, Shokoohi M, Ahmad RafieiRad A, Sargolzaie Moghadam M, Haghdoost AA, Mirzazadeh A, Karamouzian M (2017) Methamphetamine use among Iranian youth: a population-based knowledge, attitude, and practice study. Subst Use Misuse 52:1214–1221
Shen XL, Song N, Du XX, Li Y, Xie JX, Jiang H (2017) Nesfatin-1 protects dopaminergic neurons against MPP+/MPTP-induced neurotoxicity through the C-Raf–ERK1/2-dependent anti-apoptotic pathway. Sci Rep 7:1–13
Shintani T, Klionsky DJ (2004) Autophagy in health and disease: a double-edged sword. Science 306:990–995
Solmaz A, Bahadır E, Gülçiçek OB, Yiğitbaş H, Çelik A, Karagöz A, Özsavcı D, Şirvancı S, Yeğen BÇ (2016) Nesfatin-1 improves oxidative skin injury in normoglycemic or hyperglycemic rats. Peptides 78:1–10
Stumm G, Schlegel J, Schafer T, Wurz C, Mennel HD, Krieg J-C, Vedder H (1999) Amphetamines induce apoptosis and regulation of bcl-x splice variants in neocortical neurons. FASEB J 13:1065–1072
Su Y, Zhang J, Tang Y, Bi F, Liu JN (2010) The novel function of nesfatin-1: anti-hyperglycemia. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 391:1039–1042
Tan Z, Xu H, Shen X, Jiang H (2015) Nesfatin-1 antagonized rotenone-induced neurotoxicity in MES23. 5 dopaminergic cells. Peptides 69:109–114
Tang Z, Zhao L, Yang Z, Liu Z, Gu J, Bai B, Liu J, Xu J, Yang H (2018) Mechanisms of oxidative stress, apoptosis, and autophagy involved in graphene oxide nanomaterial anti-osteosarcoma effect. Int J Nanomed 13:2907
Thorburn A (2008) Apoptosis and autophagy: regulatory connections between two supposedly different processes. Apoptosis 13:1–9
Tian X, Ru Q, Xiong Q, Yue K, Chen L, Ma B, Gan W, Si Y, Xiao H, Li C (2017) Neurotoxicity induced by methamphetamine-heroin combination in PC12 cells. Neurosci Lett 647:1–7
Travis ER, Wightman RM (1998) Spatio-temporal resolution of exocytosis from individual cells. Annu Rev Biophys Biomol Struct 27:77–103
Westerink RHS, Ewing AG (2008) The PC12 cell as model for neurosecretion. Acta Physiol 192:273–285
Xu X, Huang E, Tai Y, Zhao X, Chen X, Chen C, Chen R, Liu C, Lin Z, Wang H, Xie WB (2017) Nupr1 modulates methamphetamine-induced dopaminergic neuronal apoptosis and autophagy through CHOP-Trib3-mediated endoplasmic reticulum stress signaling pathway. Front Mol Neurosci 10:203
Yamamoto BK, Raudensky J (2008) The role of oxidative stress, metabolic compromise, and inflammation in neuronal injury produced by amphetamine-related drugs of abuse. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol 3:203–217
Yun HR, Jo YH, Kim J, Shin Y, Kim SS, Choi TG (2020) Roles of autophagy in oxidative stress. Int J Mol Sci 21:3289
Acknowledgements
This study was financially supported by the Research Deputy of Shahroud University of Medical Sciences, Shahroud, Iran (Grant No. 97181).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
ZA and MR wrote the paper and analyzed the data. ZA and SN performed the experiments. MJ was a scientific advisor. MR, MKH, ASH, and GHA conceived and designed the experiments. All authors read and approved the manuscript and all data were generated in-house and no paper mill was used.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of financial and non-financial interest regarding the publication of the study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abbasi, Z., Khaksari, M., Shayannia, A. et al. Protection of the PC12 Cells by Nesfatin-1 Against Methamphetamine-Induced Neurotoxicity. Int J Pept Res Ther 28, 107 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10989-022-10417-x
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10989-022-10417-x