Abstract
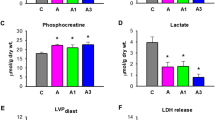
Chemically modified peptide apelin-12 (MA) with enhanced resistance to degradation by proteolytic enzymes is able to protect the heart against myocardial ischemia and reperfusion. This study was aimed to explore the role of mitochondrial ATP-sensitive K+-channels (mitoKATP) in effects of MA on myocardial energy state and membrane integrity in ischemia/reperfusion (I/R) injury. Isolated perfused working rat hearts were used to simulate global ischemia and reperfusion. Acute myocardial infarction was induced by coronary artery occlusion followed by restoration of coronary blood flow in anesthetized rats. Myocardial infarct size and cardiac dysfunction were used as indices of I/R injury at the end of reperfusion. Co-infusion of 5-hydroxydecanoate (5HD), the mitoKATP blocker, along with MA before ischemia significantly decreased functional recovery of isolated hearts as compared to administration of MA alone. These effects were accompanied by increased LDH release in the myocardial effluent, reduced restoration of myocardial ATP, AN, Cr, adenylate energy charge (AEC), and lactate accumulation. Coadministration of 5HD and MA at the onset of reperfusion substantially reduced infarct-limiting effect of the peptide in rats in vivo and increased the plasma LDH and CK-MB activity compared with MA treatment. Additionally, 5HD abolished MA influence on the metabolic state of the area at risk (AAR) at the end of reperfusion. In this case, the contents of metabolites and AEC in the AAR did not differ significantly from the values in control. Therefore, restoration of myocardial energy metabolism and sarcolemma integrity via activation of mitoKATP may be of critical importance for MA-induced protection against I/R injury.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akao M, Ohler A, O’Rourke B, Marban E (2001) Mitochondrial ATP-sensitive potassium channels inhibit apoptosis induced by oxidative stress in cardiac cells. Circ Res 88:1267–1275
Alfarano C, Foussal C, Lairez O, Calise D, Attané C, Anesia R, Daviaud D, Wanecq E, Parini A, Valet P, Kunduzova O (2015) Transition from metabolic adaptation to maladaptation of the heart in obesity: role of apelin. Int J Obes 39:312–320
Attane C, Foussal C, Le Gonidec S, Benani A, Daviaud D, Wanecq E et al (2012) Apelin treatment increases complete Fatty Acid oxidation, mitochondrial oxidative capacity, and biogenesis in muscle of insulin-resistant mice. Diabetes 61:310–320
Azizi Y, Faghihi M, Imani A, Roghani M, Nazari A (2013) Post-infarct treatment with [Pyr1]-apelin-13 reduces myocardial damage through reduction of oxidative injury and nitric oxide enhancement in the rat model of myocardial infarction. Peptides 46:76–82
Bergmeyer HU (ed) (1974) Methods of enzymatic analysis. Academic Press, New York, pp. 1464–1467; 1772–1776; 1777–1781; 2127–2131
Detlef O, Dettwiler S, Favoccia Ch, Scharbatke H, Preckel B, Schlack W (2005) The influence of mitochondrial KATP-channels in the cardioprotection of preconditioning and postconditioning by sevoflurane in the rat in vivo. Anesth Analg 101:1252–1260
Garlid KD, Santos PD, Xie ZJ, Costa ADT, Paucek P (2003) Mitochondrial potassium transport: the role of the mitochondrial ATP-sensitive K+ channel in cardiac function and cardioprotection. Biochim Biophys Acta 1606:1–21
Garnier A, Fortin D, Delomenie C, Momken I, Veksler V, Ventura-Clapier R (2003) Depressed mitochondrial transcription factors and oxidative capacity in rat failing cardiac and skeletal muscles. J Physiol 551(2):491–501
Gerczuk PZ, Kloner RA (2011) Protecting the heart from ischemia: an update on ischemic and pharmacologic conditioning. Hosp pract 39:35–43
Hanley PJ, Gopalan KV, Lareau RA, Srivastava DK, Meltzer VM, Daut J (2003) Beta-Oxidation of 5-hydroxydecanoate, a putative blocker of mitochondrial ATP sensitive potassium channels. J Physiol 547:387–393
Japp AG, Cruden NL, Barnes G, van Gemeren N, Mathews J, Adamson J et al (2010) Acute cardiovascular effects of apelin in humans: potential role in patients with chronic heart failure. Circulation 121:1818–1827
Javadov S, Purdham DM, Asad Zeidan A, Karmazyn M (2006) NHE-1 inhibition improves cardiac mitochondrial function through regulation of mitochondrial biogenesis during postinfarction remodeling. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 291:H1722–H1730
Kleinz MJ, Davenport AP (2005) Emerging roles of apelin in biology and medicine. Pharmacol Ther 107:198–211
Kowaltowski AJ, Seetharaman S, Paucek P, Garlid KD (2001) Bioenergetic consequences of opening the ATP-sensitive K+ channel of heart mitochondria. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 280:H649–H657
Larsson NG, Wang J, Wilhelmsson H, Oldfors A, Rustin P, Lewandoski M, Barsh GS, Clayton DA (1998) Mitochondrial transcription factor A is necessary for mtDNA maintenance and nembryogenesis in mice. Nat Genet 18:231–236
Lim KHH, Javadov SA, Das M, Clarke SJ, Suleiman MS, Halestrap AP (2002) The effects of ischaemic preconditioning, diazoxide and 5-hydroxydecanoate on rat heart mitochondrial volume and respiration. J Physiol 545:961–974
Liu Q, Yao JY, Qian C, Chen R, Li XY, Liu SW et al (2012) Effects of propofol on ischemia-induced ventricular arrhythmias and mitochondrial ATP-sensitive potassium channels. Acta Pharmacol Sin 33:1495–1501
Lopaschuk GD (1997) Alterations in fatty acid oxidation during reperfusion of the heart after myocardial ischemia. Am J Cardiol 80:11A–16A
Oldenburg O, Cohen MV, Yellon DM, Downey JM (2002) Mitochondrial K+ channels: role in cardioprotection. Cardiovasc Res 55:429–437
Pisarenko OI, Serebryakova LI, Studneva IM, Pelogeykina YuA, Tskitishvili OV, Bespalova ZhD et al (2013) Effects of structural analogues of apelin 12 in acute myocardial infarction in rats. J Pharmacol Pharmacother 4:198–203
Pisarenko OI, Lankin VZ, Konovalova GG, Serebryakova LI, Shulzhenko VS, Timoshin AA et al (2014) Apelin-12 and its structural analogue enhance antioxidant defense in experimental myocardial ischemia and reperfusion. Mol Cell Biochem 391:241–250
Pisarenko OI, Shulzhenko VS, Studneva IM, Serebryakova LI, Pelogeykina YuA, Veselova OM (2015) Signaling pathways of a structural analogue of apelin-12 involved in myocardial protection against ischemia/reperfusion injury. Peptides 73:67–76
Rastaldo R, Cappello S, Folino A, Berta GN, Sprio AE, Losano G et al (2011) Apelin-13 limits infarct size and improves cardiac postischemic mechanical recovery only if given after ischemia. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 300:H2308–H2315
Sidorova MV, Az’muko AA, Pal’keeva ME, Molokoedov AS, Bushuev VN, Dvoryantsev SN et al (2012) Synthesis and cardioprotective properties of apelin-12 and its structural analogues. Russ J Bioorg Chem 38:40–45
Simpkin JC, Yellon DM, Davidson SM, Lim SY, Wynne AM, Smith CC (2007) Apelin-13 and apelin-36 exhibit direct cardioprotective activity against ischemia-reperfusion injury. Basic Res Cardiol 102:518–528
Tinker A, Aziz Q, Thomas A (2014) The role of ATP-sensitive potassium channels in cellular function and protection in the cardiovascular system. Br J Pharmacol 171:12–23
Ventura-Clapier R, Garnier A, Vladimir Veksler V (2008) Transcriptional control of mitochondrial biogenesis: the central role of PGC-1α. Cardiovasc Res 79:208–217
Vinten-Johansen J, Granfeldt A, Mykytenko J, Undyala VV, Dong Y, Przyklenk K (2011) The multidimensional physiological responses to postconditioning. Antioxid Redox Signal 14:791–810
Wang C, Liu N, Luan R, Li Y, Wang D, Zou W et al (2013) Apelin protects sarcoplasmic reticulum function and cardiac performance by attenuating oxidation of sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+-ATPase and ryanodine receptor. Cardiovasc Res 100:114–124
Yu XH, Tang ZB, Liu LJ, Qian H, Tang SL, Zhang DW et al (2014) Apelin and its receptor APJ in cardiovascular diseases. Clin Chim Acta 428:1–8
Zeng XJ, Zhang LK, Wang HX, Lu LQ, Ma LQ, Tang CS (2009) Apelin protects heart against ischemia/reperfusion injury in rat. Peptides 30:1144–1152
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Russian Foundation for Basic Research (Grant No. 14-04-00012a). The authors are grateful to Dr. M.V. Sidorova for synthesis of peptide MA and discussion of the results.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
All procedures performed in studies involving animals were in accordance with the European Convention for the Protection of Vertebrate Animals Used for Experimental and other Scientific Purposes (No 123 of 18 March 1986).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pisarenko, O., Shulzhenko, V., Studneva, I. et al. 5-Hydroxydecanoate Abolishes Cardioprotective Effects of a Structural Analogue of Apelin-12 in Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury. Int J Pept Res Ther 23, 333–341 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10989-016-9565-1
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10989-016-9565-1