Abstract
Contex
Soil carbon sequestration is an ecosystem process that can provide important ecosystem services such as climate regulation and mitigation of global warming. Spatiotemporal variation in the soil organic carbon (SOC) stock is the basic information needed for landscape management and determination of regional carbon budgets.
Objectives
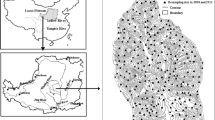
The objective of this study was to evaluate the effect of ecological restoration on SOC stocks and determine the influences of multiple factors in the Yanhe watershed of the Loess Plateau.
Methods
We coupled the Yasso07 soil carbon model with remote sensing indices as model input. The model performance was evaluated by uncertainty and sensitivity analyses as well as validation against field measurement.
Results
The modeling captured the spatial pattern of SOC variability across the landscape generally well. Net primary productivity (NPP) was the foremost factor that affecting the spatiotemporal variation of SOC density. Converting cropland to grassland was the most efficient restoration type in soil carbon sequestration in the study period. Land use change influenced the spatial correlation between NPP and SOC density by altering both litter quantity and quality. The changes in land use area tended to have higher contributions to the changes in SOC stock than did the changes in SOC density for different land use types.
Conclusions
The overall effect of ecological restoration on soil carbon sequestration was dependent on the main vegetation restoration type and the time of recovery. Human-derived land use changes could have more substantial effects on soil carbon budgets compared to natural factors in a short period of time.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adamopoulos S, Voulgaridis E, Passialis C (2005) Variation of certain chemical properties within the stemwood of black locust (Robinia pseudoacacia L.). Eur J Wood Prod 63:327–333
Chang RY, Fu BJ, Liu GH, Wang S, Yao XL (2012) The effects of afforestation on soil organic and inorganic carbon: a case study of the Loess Plateau of China. Catena 95:145–152
Cheng JM, Cheng J, Yang XM (2011) Grassland vegetation and soil carbon sequestration in the Loess Plateau. J Nat Resour 26(3):401–411
Conant RT, Smith GR, Paustian K (2003) Spatial variability of soil carbon in forested and cultivated sites: implications for change detection. J Environ Qual 32:278–286
Dang Y, Ren W, Tao B, Chen G, Lu C, Yang J, Pan S, Wang G, Li S, Tian H (2014) Climate and land use controls on soil organic carbon in the Loess Plateau region of China. PLoS One 9(5):e95548. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0095548
Deng L, Liu GB, Shangguan ZP (2014) Land use conversion and changing soil carbon stocks in China’s grain-for-green’ program: a synthesis. Glob Change Biol 20(11):3544–3556. doi:10.1111/gcb.12508
Falloon P, Smith P, Bradley RI, Milne R, Tomlinson RW, Viner D, Livermore M, Brown TAW (2006) RothCUK—a dynamic modelling system for estimating changes in soil C from mineral soils at 1-km resolution in the UK. Soil Use Manage 22:274–288
Fang JY, Guo ZD, HU HF, Kato T, Muraoka H, Son Y (2014) Forest biomass carbon sinks in East Asia, with special reference to the relative contributions of forest expansion and forest growth. Global Change Biol. doi:10.1111/gcb.12512
Feng X, Fu B, Yang X, Lv Y (2010) Remote sensing of ecosystem services: an opportunity for spatially explicit assessment. Chin Geogr Sci 20(6):522–535
Feng X, Fu B, Lu N, Zeng Y, Wu B (2013) How ecological restoration alters ecosystem services: an analysis of carbon sequestration in China’s Loess Plateau. Sci Rep 2846. doi:10.1038/srep02846
Gong J, Chen LD, Fu BJ, Huang Y, Huang Z, Peng H (2006) Effects of land use on soil nutrients in the loess hilly area of the Loess Plateau, China. Land Degrad Dev 17:453–465
Grunwald S, Vasques GM (2010) Synthesis of knowledge on soil carbon spatial patterns across a large subtropical soil-landscape in Southern U.S. 19th world congress of soil science, soil solutions for a changing world. 1–6 August 2010, Brisbane, Australia
Hashimoto S, Wattenbach M, Smith P (2011) Litter carbon inputs to the mineral soil of Japanese Brown forest soils: comparing estimates from the RothC model with estimates from MODIS. J For Res 16:16–25. doi:10.1007/s10310-010-0209-6
Jandl R, Lindner M, Vesterdal L, Bauwens B, Baritz R, Hagedorn F, Johnson DW, Minkkinen K, Byrne KA (2007) How strongly can forest management influence soil carbon sequestration? Geoderma 137:253–268
Jastrow JD, Miller RM, Matamala R (2005) Elevated atmospheric carbon dioxide increases soil carbon. Global Change Biol 11:2057–2064
Jensen LS, Salo Y, Palmason F, Breland TA, Henriksen TM, Stenberg B, Pedersen A, Lundstro C, Esala M (2005) Influence of biochemical quality on C and N mineralisation from a broad variety of plant materials in soil. Plant Soil 273:307–326
Jobbágy E, Jackson R (2000) The vertical distribution of soil organic carbon and its relation to climate and vegetation. Ecol Appl 10:423–436
Lal R (2004) Soil carbon sequestration to mitigate climate change. Geoderma 123:1–22
Lauenroth WK (2000) Methods of estimating belowground net primary production. In: Sala OE, Jackson RB, Mooney HA et al (eds) Methods in ecosystem science. Springer, New York, pp 58–71
Li LB, Tu CL, Zhao ZQ, Cui LF, Liu WJ (2011) Distribution characteristics of soil organic carbon and its isotopic composition for soil profiles of Loess Plateau under different vegetation conditions. Earth Environ 39(4):441–448
Liu W, Cheng JM, Chen FR, Gao Y (2010) Characteristic of organic carbon density and organic carbon storage in the natural grassland of center Loess Plateau. Acta Agrestia Sin 19(3):425–431
Liu YC, Wang QF, Yu GR, Zhu XJ, Zhan XY, Guo Q, Yang H, Li SG, Hu ZM (2011a) Ecosystems carbon storage and carbon sequestration potential of two main tree species for the grain for green project on China’s hilly Loess Plateau. Acta Ecol Sin 31(15):4277–4286
Liu ZP, Shao MA, Wang YQ (2011b) Effect of environmental factors on regional soil organic carbon stocks across the Loess Plateau region, China. Agric Ecosyst Environ 142:184–194
Liu ZP, Shao MA, Wang YQ (2012) Large-scale spatial variability and distribution of soil organic carbon across the entire Loess Plateau, China. Soil Res 50:114–124
Lu N, Liski J, Chang RY, Akujärvi A, Wu X, Jin TT, Wang YF, Fu BJ (2013) Soil organic carbon dynamics of black locust plantations in the middle Loess Plateau area of China. Biogeosciences 10:7053–7063
Luo ZK, Wang EL, Bryan BA, King D, Zhao G, Pan XB, Bende-Michl U (2013) Meta-modeling soil organic carbon sequestration potential and its application at regional scale. Ecol Appl 23(2):408–420
Meersmans J, De Ridder F, Canters F, De Baets S, Van Molle M (2009) A multiple regression approach to assess the spatial distribution of soil organic carbon (SOC) at the regional scale (Flanders, Belgium). Geoderma 152:43–52
Mueller TG, Pierce FJ (2003) Soil carbon maps: enhancing spatial estimates with simple terrain attributes at multiple scales. Soil Sci Soc Am J 67:258–267
Ogle SM, Breidt FJ, Easter M, Williams S, Killian K, Paustian K (2010) Scale and uncertainty in modeled soil organic carbon stock changes for US croplands using a process-based model. Global Change Biol 16:810–822
Piao S, Fang J, He J (2006) Variations in vegetation net primary production in the Qinghai–Xizang Plateau, China, from 1982 to 1999. Clim Change 74:253–267. doi:10.1007/s10584-005-6339-8
Pickett STA, Cadenasso ML (1995) Landscape ecology: spatial heterogeneity in ecological systems. Science 269:331–334
Poeplau C, Don A (2013) Sensitivity of soil organic carbon stocks and fractions to different land-use changes across Europe. Geoderma 192:189–201
Poeplau C, Don A, Vesterdal L, Leifeld J, Van Wesemael B, Schumacher J, Gensior A (2011) Temporal dynamics of soil organic carbon after land-use change in the temperate zone- carbon response functions as a model approach. Glob Change Bio 17:2415–2427. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2486.2011.02408.x
Post WM, Kwon KC (2000) Soil carbon sequestration and land-use change: processes and potential. Global Change Biol 6:317–328
Potter CS, Randerson JT, Field CB, Matson PA, Vitousek PM, Mooney HA, Klooster SA (1993) Terrestrial ecosystem production: a process model based on global satellite and surface data. Global Biogeochem Cy 7:811–841
Schulp CJE, Verburg PH (2009) Effect of land use history and site factors on spatial variation of soil organic carbon across a physiographic region. Agric Ecosyst Environ 133:86–97
Schulp CJE, Nabuurs GN, Verburg PH (2008) Future carbon sequestration in Europe—effects of land use change. Agric Ecosyst Environ 127:251–264
Shi H, Wen Z, Paull D (2013a) Estimation of carbon carrying capacity in the Yanhe River catchment of China’s Loess Plateau. Acta Agric Scand Sect B Soil Plant Sci 63(6):543–553. doi:10.1080/09064710.2013.820786
Shi SW, Zhang W, Zhang P, Yu YQ, Ding F (2013b) A synthesis of change in deep soil organic carbon stores with afforestation of agricultural soils. For Ecol Manage 296:53–63
Sievänen R, Salminen O, Lehtonen A, Ojanen P, Liski J, Ruosteenoja K, Tuomi M (2014) Carbon stock changes of forest land in Finland under different levels of wood use and climate change. Ann For Sci 71:255–265. doi:10.1007/s13595-013-0295-7
Song XZ, Peng CH, Zhou GM, Jiang H, Wang WF (2014) Chinese grain for green program led to highly increased soil organic carbon levels: a meta-analysis. Sci Rep 4:4460. doi:10.1038/srep04460
Thum T, Räisänen P, Sevanto S, Tuomi M, Reick C, Vesala T, Raddatz T, Aalto T, Järvinen H, Altimir N, Pilegaard K, Zoltan N, Rambal S, Liski J (2011) Soil carbon model alternatives for ECHAM5/JSBACH climate model: evaluation and impacts on global carbon cycle estimates. J Geophys Res 116:G02028. doi:10.1029/2010JG001612
Todd-Brown KEO, Randerson JT, Hopkins F, Arora V, Hajima T, Jones C, Shevliakova E, Tjiputra J, Volodin E, Wu T, Zhang Q, Allison SD (2014) Changes in soil organic carbon storage predicted by earth system models during the 21st century. Biogeosciences 11:2341–2356
Tuomi M, Vanhala P, Karhu K, Fritze H, Liski J (2008) Heterotrophic soil respiration—comparison of different models describing its temperature dependence. Ecol Model 211(1–2):182–190
Tuomi M, Thum T, Jarvinen H, Fronzek S, Berg B, Harmon M, Trofymow JA, Sevanto S, Liski J (2009) Leaf litter decomposition-estimates of global variability based on Yasso07 model. Ecol Model 220(23):3362–3371
Tuomi M, Laiho R, Repo A, Liski J (2011a) Wood decomposition model for boreal forests. Ecol Model 222(3):709–718
Tuomi M, Rasinmaki J, Repo A, Vanhala P, Liski J (2011b) Soil carbon model Yasso07 graphical user interface. Environ Model Softw 26(11):1358–1362
Upadhyay TP, Solberg B, Sankhayan PL, Shahi C (2013) Land-use changes, forest/soil conditions and carbon sequestration dynamics: a bio-economic model at watershed level in Nepal. J Bioecon 15:135–170
Vagen TG, Winowiecki LA (2013) Mapping of soil organic carbon stocks for spatially explicit assessments of climate change mitigation potential. Environ Res Lett 8:015011
Wang HQ, Cornell JD, Hall CAS, Marley DP (2002) Spatial and seasonal dynamics of surface soil carbon in the Luquillo experimental forest, Puerto Rico. Ecol Model 147:105–122
Wang CY, Zhou JB, Wang X, Xia ZM (2011a) Contents and biodegradation of soluble organic carbon in different plant residues from the Loess Plateau. Environ Sci 32:1139–1145
Wang W, Dungan J, Hashimoto H, Michaelis A, Milesi C, Ichii K, Nemani R (2011b) Diagnosing and assessing uncertainties of terrestrial ecosystem models in multimodel ensemble experiment: 1. Primary production. Global Change Biol 17:1350–1366. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2486.2010.02309.x
Wang Z, Liu GB, Xu MX, Zhang J, Wang Y, Tang L (2012) Temporal and spatial variations in soil organic carbon sequestration following revegetation in the hilly Loess Plateau, China. Catena 99:26–33
Wiesmeier M, Prietzel J, Barthold F, Spörlein P, Geu U, Hangen E, Reischl A, Schilling B, von Lützow M, Kögel-Knabner I (2013) Storage and drivers of organic carbon in forest soils of southeast Germany (Bavaria)—implications for carbon sequestration. For Ecol Manage 295:162–172
Wu X, Lu N, Liski J, Akujärvi A, Liu GH, Wang YF, Li F, Zeng Y, Fu BJ (2014) Dynamics of soil organic carbon stock at the catchment scale in the Loess Plateau—Comparison of model simulation with measurements. Landscape Ecol. doi:10.1007/s10980-014-0110-3
Xu GC, Li ZB, Li P, Lu KX, Wang Y (2013) Spatial variability of soil organic carbon in a typical watershed in the source area of the middle Dan River, China. Soil Res 51:41–49
Yadav V, Malanson G (2008) Spatially explicit historical land use land cover and soil organic carbon transformations in Southern Illinois. Agric Ecosyst Environ 123:280–292
Yang S (2010) The evaluation of carbon in farmland in Yanhe River Catchment in Loess Hilly and Gully Region. Thesis of Northwest A & F University, China
Yang YH, Monhammat A, Feng JM, Zhou R, Fang JY (2007) Storage, patterns and environmental controls of soil organic carbon in China. Biogeochemistry 84:131–141
Yang XM, Cheng JM, Meng L, Han JJ, Fan WJ (2010) Analysis on soil organic carbon and nutrients storages in different forests in Ziwuling. Res Soil Water Conserv 17(3):130–134
Zhang N, Liang YM (2002) Studies on the below-ground/above-ground biomass ratio of natural grassland in loess hilly region. Acta Pratacult Sin 11(2):72–78
Zhang XB, Shangguan ZP (2005) The bio-cycle patterns of nutrient elements and stand biomass in forest communities in hilly loess regions. Acta Ecol Sin 25(3):527–537
Zhang C, Liu GB, Xue S, Sun C (2013) Soil organic carbon and total nitrogen storage as affected by land use in a small watershed of the Loess Plateau, China. Eur J Soil Biol 54:16–24
Zhang K, Dang H, Tan S, Cheng X, Zhang Q (2010) Change in soil organic carbon following the ‘grain-for-green’ programme in China. Land Degrad Dev 21:16–28
Zhao SW, Lu L, Liu NN, Wu JS, Su J, Yang YH (2006) Effects of ecosystem conversion on the characteristics of soil organic carbon in Ziwuling forest region. Acta Bot Boreal Occident Sin 26(5):1030–1035
Acknowledgments
This study is financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 41230745, 41201182), the Chinese Academy of Sciences (Nos. XDA05050602-05-01 and GJHZ1215), and the Academy of Finland (No. 256231). We thank the three anonymous reviewers for their constructive comments and suggestions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lu, N., Akujärvi, A., Wu, X. et al. Changes in soil carbon stock predicted by a process-based soil carbon model (Yasso07) in the Yanhe watershed of the Loess Plateau. Landscape Ecol 30, 399–413 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10980-014-0132-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10980-014-0132-x