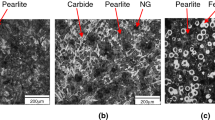
Abstract
The new generation of acid-lined medium-frequency coreless induction furnaces revolutionized the iron foundries, resulting higher overheating and lower S and Al content iron melt, characterized by higher eutectic undercooling solidification and consequently high chill [carbides] and unfavourable undercooled graphite morphologies sensitiveness. Having established that Al, Zr, Ti, Ca, Ba and La appear to have a key role in graphite nucleation in grey cast iron, thermal [cooling curves] investigations are undertaken to explore their effects on solidification parameters. The experimental heats are obtained in acid-lined coreless induction melting. Some important active elements are added to FeSi-based alloy, usually used as conventional inoculant in cast iron foundry industry, resulting complex inoculating systems [Al, Ca–La; Al, Ca–La, Zr; Al, Ca–La, Ba; Al, Ca–La, Zr, Ba; Al, Ca–La, Zr, Ti and Al, Ca–La, Zr, Ba, Ti]. In-mould [ceramic cup, cooling modulus of approximately 0.75 cm] inoculation is applied directly in the Quik-cup™ cooling curve analysis equipment, for the same alloy addition rate. The La effects are evaluated in low S and Al, high overheated electric grey iron solidification pattern with and without any other oxide-sulphides forming elements contribution. Study is focused on the representative temperatures during eutectic reaction and at the end of solidification, and it results in an undercooling referring to equilibrium eutectic temperature in the stable and metastable solidification system. As primary evaluation for general application, La, Ca, Al–FeSi alloy have a high efficiency in low S and Al and higher carbon equivalent grey cast irons, electrically melting, without any other active elements contribution. For specific applications, more complex La-bearing alloys are recommended, such as for higher dendritic austenite amount promotion [LaBaZrTi–FeSi alloy] or for lower eutectic recalescence [LaBaZr–FeSi alloy].










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chisamera M, Stan S, Riposan I, Costache G, Barstow M. Solidification pattern of In-Mold and ladle inoculated low sulfur hypoeutectic gray cast irons. AFS Trans. 2008;116:641–52.
Riposan I, Chisamera M, Stan S, Skaland T, Onsoien MI. Analyses of possible nucleation sites in Ca/Sr overinoculated grey irons. AFS Trans. 2001;109:1151–62.
Riposan I, Chisamera M, Stan S, Hartung C, White D. Three-stage model for the nucleation of graphite in grey cast iron. Mater Sci Technol. 2010;26(12):1439–47.
Riposan I, Chisamera M, Stan S, Stefan E, Hartung C. Role of lanthanum in graphite nucleation in grey cast iron. Key Eng Mater. 2011;457:19–24.
Anton IV, Riposan I. Structure characteristics of Ce-inoculated, low sulphur grey cast irons. Solid State Phenom. 2012;188:318–23.
Riposan I, Stefan IC, Firican MC, Stan S, Naro RL, Williams DC. Increasing the inoculant potency of commercial inoculating alloys in induction melting grey cast iron. AFS Trans. 2015;123:227–42.
Riposan I, Chisamera M, Stan S. Enhanced quality in electric melt grey cast irons. ISIJ Int. 2013;53(10):1683–95.
Riposan I, Chisamera M, Stan S. The role of compounds in graphite formation in cast iron—a review. Mater Sci Forum. 2018;925:3–11.
Riposan I, Chisamera M, Stan S, Uta V, Stefan IC, Firican MC, Naro RL, Williams DC. Demystifying the effects of sulphur in cast irons. AFS Trans. 2016;124:247–66.
Stefanescu DM. Thermal analysis-theory and applications in metalcasting. Int J Metalcast. 2015;9(1):7–22.
Sparkman D, Bhaskaram CA. Chill measurement by thermal analysis. AFS Trans. 1996;104:969–76.
Kanno T, Fukuda Y, Kang I, Morinaka M, Nakae H. Prediction of chilling tendency in cast iron using three cups thermal analysis system. J JFS. 1998;70:773–8.
Kanno T, Nakae H. Prediction of graphite types and mechanical properties in cast iron using three cups thermal analysis. J JFS. 2000;72:175–80.
Emadi D, Whiting LV, Nafisi S, Ghomashchi R. Applications of thermal analysis in quality control of solidification processes. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2005;81:235–42.
Dioszegi A, Svensson IL. On the problems of thermal analysis of solidification. Mater Sci Eng A. 2005;413–414:474–9.
Sparkman D. Microstructure by thermal analysis. AFS Trans. 2011;119:413–9.
Upadhya KG, Stefanescu DM, Lieu K, Yeager DP. Computer-aided cooling curve analysis: principles and applications in metal casting. AFS Trans. 1989;97:61–6.
Barlow JO, Stefanescu DM. Computer-aided cooling curve analysis revisited. AFS Trans. 1997;104:349–54.
Stefanescu DM, Moran M, Boonmee S, Guesser WL. The use of combined liquid displacement and cooling curve analysis in understanding the solidification of cast irons. AFS Trans. 2012;120:365–74.
Stan S, Chisamera M, Riposan I, Barstow M. Applications of thermal analysis to monitor the quality of hypoeutectic cast irons during solidification in sand and metal moulds. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2012;110(3):1185–92.
Riposan I, Chisamera M, Stan S, Barstow M. Identifying chill tendency of cast iron melts by thermal analysis. Int J Cast Met Res. 2013;26(3):152–9.
Klancnik U, Habjan J, Klancnik G, Medved J. Thermal analysis of indefinite chill cast iron modified with ferrovanadium and ferrotungsten. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2017;127:71–8.
Riposan I, Chisamera M, Stan S. Application of cooling curve analysis in solidification pattern and structure control of grey cast irons. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2018;132:1017–28.
Chisamera M, Riposan I, Stan S, Stefan E, Costache G. Thermal analysis control of in-mould and ladle inoculated grey cast irons. China Foundry. 2009;6:145–51.
Zhou J. Color metallography of cast irons. China Foundry. 2009;6:52–69.
Wang B, Fu D, Shan G. Effect of Rare-earth element lanthanum on structure and performance of gray casting iron. Hot Working Technology. 2008. http://en.cnki.com.cn/Journal_en/B-B022-SJGY-2008-13.htm.
Sofroni L, Riposan I, Brabie V, Chisamera M. Cast iron. Bucharest, Romania: Editura Didactica si Pedagogica Publisher [Romanian language]; 1985, p. 36–49.
Riposan I, Chisamera M, Stan S, Toboc P, Grasmo G, White D, Ecob C, Hartung C. Benefits of residual aluminum in ductile iron. J Mater Eng Perform. 2011;20(1):57–64.
Sillen RV. Novacast technologies. 2006. www.novacast.se.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stefan, E., Riposan, I. & Chisamera, M. Application of thermal analysis in solidification pattern control of La-inoculated grey cast irons. J Therm Anal Calorim 138, 2491–2503 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-019-08714-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-019-08714-7