Abstract
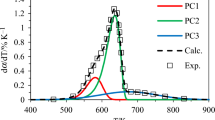
This work involved the prediction of the concentration profiles and theoretical yields in lignocellulosic biomass pyrolysis under real pyrolysis conditions. The competing reaction model was used and verified by the experimental data of the pyrolysis of oilseed rape straw and sesame stalk. The pyrolysis kinetic behaviors of the pyrolysis of peach branch, cotton stalk, and corn stalk under various conditions were simulated based on the model and their chemical compositions. The influences of the heating rate and final temperature on the theoretical yields of pyrolysis products and the pyrolysis time were obtained. Under the same conditions, the pyrolysis of peach branch gave the highest yield of volatile products, while the pyrolysis of cotton stalk gave the highest yield of char. The method presented in this work enables us to predict the concentration profiles and theoretical yields of different lignocellulosic materials under various pyrolysis conditions.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bridgwater AV. Review of fast pyrolysis of biomass and product upgrading. Biomass Bioenergy. 2012;38:68–94.
Wu W, Mei Y, Zhang L, Liu R, Cai J. Effective activation energies of lignocellulosic biomass pyrolysis. Energy Fuels. 2014;28(6):3916–23.
Mohan D, Pittman CU, Steele PH. Pyrolysis of wood/biomass for bio-oil: a critical review. Energy Fuels. 2006;20(3):848–89.
Yin C. Microwave-assisted pyrolysis of biomass for liquid biofuels production. Bioresour Technol. 2012;120:273–84.
Ibbett R, Gaddipati S, Davies S, Hill S, Tucker G. The mechanisms of hydrothermal deconstruction of lignocellulose: new insights from thermal-analytical and complementary studies. Bioresour Technol. 2011;102(19):9272–8.
Wu W, Cai J, Liu R. Isoconversional kinetic analysis of distributed activation energy model processes for pyrolysis of solid fuels. Ind Eng Chem Res. 2013;52(40):14376–83.
White JE, Catallo WJ, Legendre BL. Biomass pyrolysis kinetics: a comparative critical review with relevant agricultural residue case studies. J Anal Appl Pyrolysis. 2011;91(1):1–33.
Koufopanos CA, Papayannakos N, Maschio G, Lucchesi A. Modelling of the pyrolysis of biomass particles. Studies on kinetics, thermal and heat transfer effects. Can J Chem Eng. 1991;69(4):907–15.
Srivastava VK, Jalan RK. Prediction of concentration in the pyrolysis of biomass material—II. Energy Convers Manag. 1996;37(4):473–83.
Babu BV, Chaurasia AS. Modeling, simulation and estimation of optimum parameters in pyrolysis of biomass. Energy Convers Manag. 2003;44(13):2135–58.
Kim S-S, Agblevor FA. Thermogravimetric analysis and fast pyrolysis of Milkweed. Bioresour Technol. 2014;169:367–73.
Borges FC, Du Z, Xie Q, Trierweiler JO, Cheng Y, Wan Y, et al. Fast microwave assisted pyrolysis of biomass using microwave absorbent. Bioresour Technol. 2014;156:267–74.
Yu F, Steele PH, Ruan R. Microwave pyrolysis of corn cob and characteristics of the pyrolytic chars. Energy Sour Part A Recovery Util Environ Effects. 2009;32(5):475–84.
Gauthier G, Melkior T, Salvador S, Corbetta M, Frassoldati A, Pierucci S, et al. Pyrolysis of thick biomass particles: experimental and kinetic modelling. Chem Eng Trans. 2013;32:601–6.
Yin R, Liu R, Wu J, Wu X, Sun C, Wu C. Influence of particle size on performance of a pilot-scale fixed-bed gasification system. Bioresour Technol. 2012;119:15–21.
ASTM E1721-01. Standard test method for determination of carbohydrates in biomass by high performance liquid chromatograph. 2007.
Van de Velden M, Baeyens J, Brems A, Janssens B, Dewil R. Fundamentals, kinetics and endothermicity of the biomass pyrolysis reaction. Renew Energy. 2010;35(1):232–42.
Koufopanos CA, Lucchesi A, Maschio G. Kinetic modelling of the pyrolysis of biomass and biomass components. Can J Chem Eng. 1989;67(1):75–84.
Roberts C. Ordinary differential equations: applications, models, and computing. London: Taylor & Francis; 2011.
Attaway S. Matlab: A practical introduction to programming and problem solving. Amsterdam: Elsevier Science; 2013.
Nan Z, Yang M, Han W, Liu C, Huang F. Fast pyrolysis oil crops straw and characteristics of bio-oil (in Chinese with English abstract). Chin J Oil Crop Sci. 2008;30(4):501–5.
Ateş F, Pütün E, Pütün AE. Fast pyrolysis of sesame stalk: yields and structural analysis of bio-oil. J Anal Appl Pyrolysis. 2004;71(2):779–90.
Carpenter D, Westover TL, Czernik S, Jablonski W. Biomass feedstocks for renewable fuel production: a review of the impacts of feedstock and pretreatment on the yield and product distribution of fast pyrolysis bio-oils and vapors. Green Chem. 2014;16(2):384–406.
Cai J, Wu W, Liu R, Huber GW. A distributed activation energy model for the pyrolysis of lignocellulosic biomass. Green Chem. 2013;15(5):1331–40.
Várhegyi G, Bobály B, Jakab E, Chen H. Thermogravimetric study of biomass pyrolysis kinetics. A distributed activation energy model with prediction tests. Energy Fuels. 2010;25(1):24–32.
Park J, Lee Y, Ryu C, Park Y-K. Slow pyrolysis of rice straw: analysis of products properties, carbon and energy yields. Bioresour Technol. 2014;155:63–70.
Zhang J, Chen T, Wu J, Wu J. Multi-Gaussian-DAEM-reaction model for thermal decompositions of cellulose, hemicellulose and lignin: comparison of N2 and CO2 atmosphere. Bioresour Technol. 2014;166:87–95.
Pasangulapati V, Ramachandriya KD, Kumar A, Wilkins MR, Jones CL, Huhnke RL. Effects of cellulose, hemicellulose and lignin on thermochemical conversion characteristics of the selected biomass. Bioresour Technol. 2012;114:663–9.
Acknowledgements
Financial support from School of Agriculture and Biology, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, China (Grant No. NRC201101), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 51176121), and the Ministry of Agriculture, China (Special Fund for Agro-scientific Research in the Public Interest: No. 201003063-09) are acknowledged. The authors would like to appreciate Dr. Xiaojuan Yu from School of Environmental Science & Engineering, Shanghai Jiao Tong University for her help in the chemical analysis of lignocellulosic materials.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Li Huang and Tao Ding have contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, L., Ding, T., Liu, R. et al. Prediction of concentration profiles and theoretical yields in lignocellulosic biomass pyrolysis. J Therm Anal Calorim 120, 1473–1482 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-014-4383-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-014-4383-1