Abstract
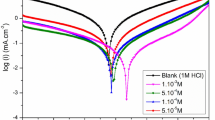
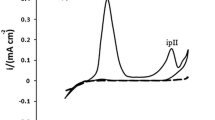
The thermal stability and the adsorption properties have been investigated for three benzothiazole compounds: 2-mercaptobenzothiazole (MBT), N-cyclohexyl-2-benzothiazole sulfenamide (NCBSA), and 2,2′-dibenzothiazole disulphide (BTD), reported in our early studies as corrosion inhibitors for carbon steel in different media. The electrochemical results were used to calculate the degree of surface coverage (θ). The adsorption mechanism of the three inhibitors was discussed according to the free energy of adsorption (\( \Delta G_{{\text{ads}}}^{\circ } \)) value obtained from Temkin adsorption isotherm, this being the best way to quantitatively express the adsorption process of their molecules on carbon steel surface. Thus, a mixed type mechanism involving the synergism between physisorption and chemisorption was proposed. The thermal analysis curves showed that, for the occurred events up to 470 °C, mass losses take place with endothermic effects followed by the total oxidation of the residue with an exothermic effect around 520 °C. Consequently, their effectiveness follows the order: BTD > NCBSA ≥ MBT, while the thermal stability ranges as follows: NCBSA < BTD ≤ MBT.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
El-Meligi AA. Corrosion preventive strategies as a crucial need for decreasing environmental pollution and saving economics. Recent Pat Corros Sci. 2010;2:22–33.
Larabi L, Harek Y, Traisnel M, Mansri A. Synergistic influence of poly(4-vynylpyridine) and potassium iodide on inhibition of corrosion of mild steel in 1 M HCl. J Appl Electrochem. 2004;34:833–9.
Samide A, Turcanu E, Bibicu I. Surface analysis of inhibitor films formed by N-(2-hydroxybenzilidene) thiosemicarbazide on carbon steel in acidic media. Chem Eng Commun. 2009;196:1008–17.
Ashassi-Sorkhabi H, Ghasemi Z, Seifzadeh D. The inhibition effect of some amino acids towards the corrosion of aluminum in 1 M HCl + 1 M H2SO4 solution. Appl Surf Sci. 2005;249:408–18.
Subramania A, Sundaram NTK, Priya RS, Saminathan K, Muralidharan VS, Vasudevan T. Aldimines: effective corrosion inhibitors for mild steel in hydrochloric acid solution. J Appl Electrochem. 2004;34:693–6.
El-Rehim SSA, Refaey SAM, Taha F, Saleh MB, Ahmed RA. Corrosion inhibition of mild steel in acidic medium using 2-amino thiophenol and 2-cyanomethyl benzothiazole. J Appl Electrochem. 2001;31:429–35.
Samide A, Bibicu I, Agiu M, Preda M. Mössbauer spectroscopy study on the corrosion inhibition of carbon steel in hydrochloric acid solution. Mater Lett. 2008;62(2):320–2.
Quraishi MA, Ansari FA, Jamal D. Thiourea derivatives as corrosion inhibitors for mild steel in formic acid. Mater Chem Phys. 2003;77:687–90.
Hassan N, Holze R. A comparative electrochemical study of electrosorbed 2- and 4-mercaptopyridines and their application as corrosion inhibitors at C60 steel. J Chem Sci. 2009;121(5):693–701.
Samide A, Tutunaru B, Negrila C, Trandafir I, Maxut A. Effect of sulfacetamide on the composition of corrosion products formed onto carbon steel surface in hydrochloric acid. Dig J Nanomater Bios. 2011;6:663–73.
Khaled KF, Hackerman N. Investigation of the inhibitive effect of ortho-substituted anilines on corrosion of iron in 1 M HCl solutions. Electrochim Acta. 2003;48:2715–23.
Forsal I, Lakhrissi L, Naji K, Abirou S, Touhami ME, Lakhrissi B, Addou M. The efficiency of corrosion inhibitor as given by electrochemical impedance spectroscopy Tafel polarization and weight-loss measurements. Spectrosc Lett. 2010;43:136–43.
Obot IB, Obi Egbedi NO. Adsorption properties and inhibition of mild steel corrosion in sulphuric acid solution by ketoconazole: experimental and theoretical investigation. Corros Sci. 2010;52:198–204.
Ahamad I, Prasad R, Quraishi MA. Inhibition of mild steel corrosion in acid solution by pheniramine drug: experimental and theoretical study. Corros Sci. 2010;52:3033–41.
Obot IB, Obi-Egbedi NO. 2,3-Diphenylbenzoquinoxaline: a new corrosion inhibitor for mild steel in sulphuric acid. Corros Sci. 2010;52:282–5.
Shukla SK, Singh AK, Ahamad I, Quraishi MA. Streptomycin: a commercially available drug as corrosion inhibitor for carbon steel in hydrochloric acid solution. Mater Lett. 2009;63:819–22.
El-Naggar MM. Corrosion inhibition of mild steel in acidic medium by some sulfa drugs compounds. Corros Sci. 2007;49:2226–36.
Abdallah M. Antibacterial drugs as corrosion inhibitors for corrosion of aluminium in hydrochloric solution. Corros Sci. 2004;46:1981–96.
Ebenso EE, Arslan T, Kandemirli F, Love I, Ödretır C, Saracoğlu M, Umoren SA. Theoretical studies of some sulphonamides as corrosion inhibitors for mild steel in acidic medium. Int J Quantum Chem. 2010;110:2614–36.
Podobaev NI, Avdeev YG. Temperature and time effects on the acid corrosion of steel in the presence of acetylenic inhibitors. Met Protect. 2001;37:529–33.
Gece G. Drugs: a review of promising novel corrosion inhibitors. Corros Sci. 2011;53:3873–98.
Kumar H, Karthikeyan S. Inhibition of mild steel in hydrochloric acid solution by cloxacillin drug. J Mater Environ Sci. 2012;3:925–34.
Vaszilcsin N, Ordodi V, Borza A. Corrosion inhibitors from expired drugs. Int J Pharm. 2012;431:241–4.
Samide A, Tutunaru B, Dobritescu A, Negrila C. Study of the corrosion products formed on carbon steel surface in hydrochloric acid solution. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2012;110:145–52.
Tutunaru B, Samide A, Negrila C. Thermal analysis of corrosion products formed on carbon steel in ammonium chloride solution. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2013;111:1149–54.
Thickett D, Odlyha M. Application of thermomagnetometry to corrosion studies of archaeological iron. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2005;80:565–71.
Rusu I, Sutiman D, Lisa G, Mareci D, Melniciuc Puica N. On the correlation between thermal analysis results and corrosion behaviour of some metallic religious artefacts. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2011;104:423–30.
Moanţă A, Ionescu C, Rotaru P, Socaciu M, Hărăbor A. Structural characterization, thermal investigation and liquid crystalline behavior of 4-[(4-chlorobenzyl)oxy]-3,4′-dichloroazobenzene. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2010;102:1079–86.
Rotaru A, Moanţă A, Popa G, Rotaru P, Segal E. Thermal decomposition kinetics of some aromatic azomonoethers. Part IV. Non-isothermal kinetics of 2-allyl-4-((4-(4-methylbenzyloxy)phenyl)diazenyl) phenol in dynamic air atmosphere. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2009;97:485–91.
Rotaru A, Moanţă A, Rotaru P, Segal E. Thermal decomposition kinetics of some aromatic azomonoethers. Part III. Non-isothermal study of 4-[(4-chlorobenzyl)oxy]-4′-chloro-azobenzene in dynamic air atmosphere. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2009;95:161–6.
Rotaru A, Kropidłowska A, Moanţă A, Rotaru P, Segal E. Thermal decomposition kinetics of some aromatic azomonoethers. Part II. Non-isothermal study of three liquid crystals in dynamic air atmosphere. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2008;92:233–8.
Rotaru A, Moanţă A, Sălăgeanu I, Budrugeac P, Segal E. Thermal decomposition kinetics of some aromatic azomonoethers. Part I. Decomposition of 4-[(4-chlorobenzyl)oxy]-4′-nitro-azobenzene. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2007;87:395–400.
Rotaru A, Brătulescu G, Rotaru P. Thermal analysis of azoic dyes. Part I. Non-isothermal decomposition kinetics of [4-(4-chlorobenzyloxy)-3-methylphenyl](p-tolyl)diazene in dynamic air atmosphere. Thermochim Acta. 2009;489:63–9.
Moanţă A, Tutunaru B, Rotaru P. Spectral and thermal studies of 4-(phenyldiazenyl)phenyl 2-furoate as corrosion inhibitor for carbon steel. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2013;111:1273–9.
Samide A, Bibicu I, Rogalski MS, Preda M. A study of the corrosion inhibition of carbon steel in diluted ammonia media using 2-mercapto benzothiazole (MBT). Acta Chim Slov. 2004;51:127–36.
Samide A, Bibicu I, Rogalski MS, Preda M. Study of the corrosion inhibition of carbon steel in dilute ammoniacal media using N-cyclohexyl benzothiazole sulfenamide. Corros Sci. 2005;47(5):1119–27.
Samide A, Bibicu I. Kinetics corrosion process of carbon steel in hydrochloric acid in absence and presence of 2-(cyclohexylaminomercapto)benzothiazole. Surf Interface Anal. 2008;40:944–52.
Samide A, Bibicu I. A new inhibitor for corrosion of carbon steel in hydrochloric acid solution. Rev Roum Chim. 2009;54:33–43.
Zerga B, Attayibat A, Sfaira M, Taleb M, Hammouti B, Touhami ME, Radi S, Rais Z. Effect of some tripodal bipyrazolic compounds on C38 steel corrosion in hydrochloric acid solution. J Appl Electrochem. 2010;40:1575–82.
Samide A, Tutunaru B. Corrosion inhibition of carbon steel in hydrochloric acid solution using a sulfa drug. Chem Biochem Eng Q. 2011;25:299–308.
Fouda AS, Mostafa HA, El-Abbasy HM. Antibacterial drugs as inhibitors for the corrosion of stainless steel type 304 in HCl solution. J Appl Electrochem. 2010;40:163–73.
Samide A. A pharmaceutical product as corrosion inhibitor for carbon steel in acidic environments. J Environ Sci Health A Tox Hazard Subst Environ Eng. 2013;48:159–65.
Zerga B, Hammouti B, Ebn Touhami M, Touir R, Taleb M, Sfaira M, Bennajeh M, Forssal I. Comparative inhibition study of new synthesised pyridazine derivatives towards mild steel corrosion in hydrochloric acid. Part-II: thermodynamic proprieties. Int J Electrochem Sci. 2012;7:471–83.
Samide A, Tutunaru B, Negrila C, Prunaru I. Surface analysis of inhibitor film formed by 4-amino-N-(1,3-thiazol-2-yl) benzene sulfonamide on carbon steel surface in acidic media. Spectrosc Lett. 2012;45:55–64.
Zarrok H, Al-Deyab SS, Zarrouk A, Salghi R, Hammouti B, Oudda H, Bouachrine M, Bentiss F. Thermodynamic characterisation and density functional theory investigation of 1,1′,5,5′-tetramethyl-1H,1′H-3,3′-bipyrazole as corrosion inhibitor of C38 steel corrosion in HCl. Int J Electrochem Sci. 2012;7:4047.
Wolkenstein Th. Physico-chimie de la surface des semi-conducteurs. Moscou: Editions Mir; 1977.
http://www.gequisa.es/media/productos/Aceler%20y%20antiox%20ING/MSDS/Ing_MBT_2_0.pdf.
http://www.gequisa.es/media/productos/Aceler%20y%20antiox%20ING/MSDS/Ing_MBTS_2_0.pdf.
http://www.gequisa.es/media/productos/Aceler%20y%20antiox%20ING/MSDS/Ing_CBS_2_0.pdf.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Samide, A., Rotaru, P., Ionescu, C. et al. Thermal behaviour and adsorption properties of some benzothiazole derivatives. J Therm Anal Calorim 118, 651–659 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-014-3644-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-014-3644-3