Abstract
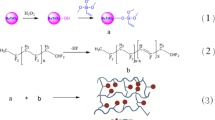
Hybrid materials from poly(vinyl chloride) (PVC) and silica have been prepared using different conditions by the sol–gel technique. In situ generation of silica network in the PVC matrix was carried out by hydrolysis/condensation of tetraethoxysilane (TEOS) in the matrix. Morphology of the silica particles produced in hybrid films was studied by scattering electron microscopy. The shape of silica particle produced in the matrix was modified by carrying out the sol–gel process under steam on the hybrid films using TEOS. The films were subjected to strain conditions during this process, which produced lamellar shaped particles in the matrix. It was possible to produce platelet type of structure with different aspect ratio by changing the composition and the stress conditions on the films during the steaming process. Addition of a very small amount of γ-glycidoxypropyltrimethoxysilane as compatibilizer drastically reduced the silica particles size in the matrix to nano-level. Thermal–mechanical properties of some of these hybrids were studied and related to the composition, structure and inter-phase interaction between the silica and the matrix.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Braun D (2004) J Polym Sci Part A Polym Chem 42:578–586
Wilkes Charles E, Summers J, Anthony C, Berard Mark T (2005) Handbook. Hanser Verlag, Munich
Titow WV (1986) PVC techanology. Elsevier Applied Science Publisher, London
Narkis M, Shach-Caplan M, Haba Y, Silverstein S (2005) J Vinyl Addit Tech 10:109–120
Ateia E (2005) J Appl Polym Sci 95(4):916–921
Pielichowski K (1999) Eur Polym J 35:27–34
Park IH, Jang J, Chujo Y (1995) Die Ange Makromol Chem 226:1–12
Xu WB, Zhou ZF, Ge ML, Pan WP (2004) Therm Anal Calorim 78:91–99
Gong F, Feng M, Hao C, Shang S, Yang M (2004) Polm Degrad Stab 84:289–294
Ogoshi T, Chujo Y (2003) Bull Chem Soc Japan 76:1865–1871
Cao YM, Sun J, Yu DH (2002) J Appl Polym Sci 83:70–77
Xie XL, Liu QX, Li RKY, Zhou XP, Zhang QX, Yu ZZ (2004) Polymer 45:6665–6673
Hsiue GH, Kuo WH, Huang YP, Jeng RG (2000) Polymer 41:2813–2825
Bialk M, Prucker O, Ruhe J (2002) Colloids Surf A Phsicochem Eng Asp 198–2:543–549
Yoshinaga K, Shimada J, Nishida H, Komatsu M (1999) J Colloid Interf Sci 214(2):180–188
Werne TV, Patten TE (2001) J Am Chem Soc 123:7497–7505
Brinker CJ, Scherer GW (1990) Sol gel science’ the physics and chemistry of sol gel processing. Academic Press, Boston
Al-Sagheer F, Ahmad Z, Muslim S (2008) Int J Polym Mater 57:1–16
Pukanszky B (1990) Composites 21:255–262
Zhu A, Cai A, Zhou W, Shi Z (2008) Appl Surf Sci 254:3745–3752
Zhu A, Cai A, Zhang J, Wang J (2008) J Appl Polym Sci 108:2189–2196
Wu D, Wang X, Song Y, Jin R (2004) J Appl Polym Sci 92:2714–2723
Kelnar I, Schatz M (1993) J Appl Polym Sci 48:669–676
Kelnar I, Schatz M (1993) J Appl Polym Sci 48:657–668
Jorn S, Bard S, Steinar P (1998) J Appl Polym Sci 67:849–853
Gilbert M, Haghighat S, Chua SK, Ng SY (2006) Macromol Symp 233(1):198–202
Gilbert M, Rodriguez-Fernandez OS (1997) J Appl Polym Sci 66:2111–2119
Khan MK, Sarwar MI, Rafiq S, Ahmad Z (1998) Polym Bull 40:583–590
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to acknowledge the financial support provided by the Kuwait University under the project SC03/05. They would also like to appreciate the technical support from the E. M unit and the general facilities projects GS01/01, GS01/05 under the SAF program.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Al-Sagheer, F.A., Ahmad, Z. PVC-silica hybrids: effect of sol–gel conditions on the morphology of silica particles and thermal mechanical properties of the hybrids. J Sol-Gel Sci Technol 61, 229–235 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-011-2618-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-011-2618-1