Abstract
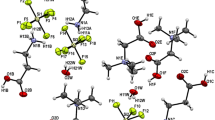
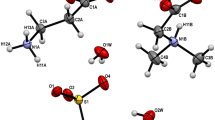
We report the use of anionic (I−), cationic (Ba2+, Cd2+) and ionic mixtures (I− plus Ba2+) for derivatizing liver fatty acid binding protein (LFABP) crystals. Use of cationic and anionic salts in phasing experiments revealed distinct non-overlapping sites for these ions, suggesting exclusive binding regions on LFABP. Interestingly, cations of identical charge and valency (like Ba2+ and Cd2+) bound to distinct pockets on the protein surface. Furthermore, a mixture of salts containing both I− and Ba2+ was very useful in phasing experiments as these oppositely charged ions bound to different regions of LFABP. Our data therefore suggest that cationic and anionic salt mixtures like BaCl2 with NH4I or salts like CdI, BaI where each ion has a significant anomalous signal for a given X-ray wavelength may be valuable reagents for phasing during structure determination.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- LFABP:
-
Liver fatty acid binding protein
- SAD:
-
Single wavelength anomalous dispersion
- MIR:
-
Mutiple isomorphous replacement
- S-SAD:
-
Sulphur-SAD
- I-SAD:
-
Iodide-SAD
- Ba-SAD:
-
Barium-SAD
- Cd-SAD:
-
Cadmium-SAD
- RMSD:
-
Root mean square deviation
References
Dauter Z (2005) Efficient use of synchrotron radiation for macromolecular diffraction data collection. Prog Biophys Mol Biol 89:153–172
Dauter Z, Dauter M, Rajashankar KR (2000) Novel approach to phasing proteins: derivatization by short cryo-soaking with halides. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr 56:232–237
Nagem RA, Dauter Z, Polikarpov I (2001) Protein crystal structure solution by fast incorporation of negatively and positively charged anomalous scatterers. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr 57:996–1002
Evans G, Bricogne G (2002) Triiodide derivatization and combinatorial counter-ion replacement: two methods for enhancing phasing signal using laboratory Cu Kα X-ray. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr 58:976–991
Moiseeva N, Allaire M (2007) Using barium ions for heavy-atom derivatization and phasing of xylanase II from Trichoderma longibrachiatum. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr 63:1025–1028
Wang BC (1985) Resolution of phase ambiguity in macromolecular crystallography. Methods Enzymol 115:90–112
Dauter Z, Dauter M, de La Fortelle E, Bricogne G, Sheldrick G (1999) Can anomalous signal of sulfur become a tool for solving protein crystal structures? J Mol Biol 289:83–92
Ramagopal UA, Dauter M, Dauter Z (2003) Phasing on anomalous signal of sulfurs: what is the limit? Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr 59:868–875
Debreczeni JE, Bunkoczi G, Ma Q, Blaser H, Sheldrick GM (2003) In-house phase determination of the lima bean trypsin inhibitor: a low-resolution sulfur-SAD case. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr 59:688–696
Sarma GN, Karplus PA (2005) In-house sulfur SAD phasing: a case study of the effects of data quality and resolution cutoffs. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr 62:707–716
Watanabe N, Kitago Y, Tanaka I, Wang J, Gu Y, Zeng C et al (2005) Comparison of phasing methods for sulfur-SAD using in-house chromium radiation: case studies for standard proteins and a 69 kDa protein. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr 62:1533–1540
Abbott RJ, Knott V, Rovesi P, Neudeck S, Lukacik P et al (2004) Crystallization and preliminary X-ray diffraction analysis of three EGF domains of EMR2, a 7TM immune-system molecule. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr 60:936–938
Kajander T, Cortajarena AL, Michrie S, Regan L (2007) Structure and stability of designed TPR protein superhelices: unusual crystal packing and implications for natural TPR proteins. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr 63:800–811
Xu Y, Feng L, Jeffery PD, Shi Y, Morel FMM (2008) Structure and metal exchange in the cadmium carbonic anhydrase of marine diatoms. Nature 452:56–61
Gangelhoff TA, Mungalachetty PS, Nix JC, Churchill MEA (2009) Structural analysis and DNA binding of the HMG domains of the human mitochondrial transcription factor A. Nucleic Acids Res 37:3153–3164
Stegmann CM, Lührmann R, Wahl MC (2010) The crystal structure of PPIL1 bound to cyclosporine A suggests a binding mode for a linear epitope of the SKIP protein. PLoS ONE 5:e10013
Yogavel M, Nithya N, Suzuki A, Sugiyama Y, Yamane T et al (2010) Structural analysis of actinidin and a comparison of cadmium and sulfur anomalous signals from actinidin crystals measured using in-house copper- and chromium-anode X-ray sources. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr 66:1323–1333
Dauter Z, Li M, Wlodawer A (2001) Practical experience with the use of halides for phasing macromolecular structures: a powerful tool for structural genomics. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr 57:239–249
Abendroth J, Gardberg AS, Robinson JI, Christensen JS, Staker BL et al (2011) SAD phasing using iodide ions in a high-throughput structural genomics environment. J Struct Funct Genomics 12:83–95
Yogavel M, Gill J, Mishra PC, Sharma A (2007) SAD phasing of a structure based on cocrystallized iodides using an in-house Cu Kα X-ray source: effects of data redundancy and completeness on structure solution. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr 63:931–934
Yogavel M, Gill J, Sharma A (2009) Iodide-SAD, SIR and SIRAS phasing for structure solution of a nucleosome assembly protein. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr 65:618–622
Yogavel M, Khan S, Bhatt T, Sharma A (2010) Structure of D-tyrosyl-tRNATyr deacylase using home-source Cu Kα and moderate-quality iodide-SAD data: structural polymorphism and HEPES-bound enzyme states. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr 66:584–592
Sharma A, Yogavel M, Akhouri RR, Gill J, Sharma A (2008) Crystal structure of soluble domain of malaria sporozoite protein UIS3 in complex with lipid. J Biol Chem 283:24077–24088
Otwinowski Z, Monor W (1997) Processing of X-ray diffraction data collected in oscillation mode. Methods Enzymol 276:307–326
Sheldrick GM, Hauptman HA, Weeks CM, Miller R, Usón I (2001) International tables for macromolecular crystallography, vol F. In: Rossmann MG, Arnold E (eds) Kluwer, Dordrecht, Chap 16. pp 333–345
Schneider TR, Sheldrick GM (2002) Substructure solution with SHELXD. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr 50:760–763
Pape T, Schneider TR (2004) HKL2MAP: a graphical user interface for macromolecular phasing with SHELX programs. J Appl Crystallogr 37:843–844
Hendrickson WA, Teeter MM (1981) Crambin’s crystal structure, known to 0.945 Å resolution. Nature 290:107–113
Dauter Z, Dauter M, Dodson EJ (2002) Jolly SAD. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr 58:494–506
Sheldrick GM (2002) Macromolecular phasing with SHELXE. Z Kristallogr 217:1772–1779
Perrakis A, Morris RJ, Lamzin VS (1999) Automated protein model building combined with iterative structure refinement. Nat Struct Biol 6:458–463
Morris RJ, Zwart PH, Cohen S, Fernandez FJ, Kakaris M et al (2004) Breaking good resolutions with ARP/wARP. J Synchrotron Rad 11:56–59
Adams PD, Afonine PV, Bunkóczi G, Chen VB, Davis IW et al (2010) PHENIX: a comprehensive Python-based system for macromolecular structure solution. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr 66:213–221
Vagin A, Teplyakov A (1997) MOLREP: an automated program for molecular replacement. J Appl Crystallogr 30:1022–1025
Emsley P, Cowtan K (2004) Coot: model-building tools for molecular graphics. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr 60:2126–2132
Murshudov GN, Skubák P, Lebedev AA, Pannu NS, Steiner RA et al (2011) REFMAC5 for the refinement of macromolecular crystal structures. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr 67:355–367
Laskowski RA, MacArthur MW, Moss DS, Thronton JM (1993) J Appl Cryst 26:283–291
Chen VB, Arendal WB, Headd JJ, Keedy DA, Immormino RM et al (2010) MolProbity: all-atom structure validation for macromolecular crystallography. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr 66:12–21
Pettersen EF, Goddard TD, Huang CC, Couch GS, Greenbaltt DM et al (2004) UCSF Chimera—a visualization system for exploratory research and analysis. J Comput Chem 25:1605–1612
Panjikar S, Parthasarathy V, Lamzin VS, Weiss MS, Tucker PA (2005) Auto-rickshaw: an automated crystal structure determination platform as an efficient tool for the validation of an X-ray diffraction experiment. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr 61:449–457
Acknowledgments
The X-ray facility at ICGEB was funded by the Wellcome Trust. Ashwani Sharma is supported by University Grants Commission, Government of India. MY is supported by FP7 grants from the EU. Funding for research on “Exploration of salts combinations for fast phasing of protein crystals” is provided by a Department of Biotechnology, Government of India grant to the laboratory.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Ashwani Sharma and Manickam Yogavel contributed equally.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sharma, A., Yogavel, M. & Sharma, A. Utility of anion and cation combinations for phasing of protein structures. J Struct Funct Genomics 13, 135–143 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10969-012-9137-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10969-012-9137-3