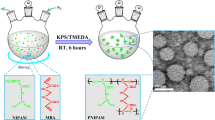
Abstract
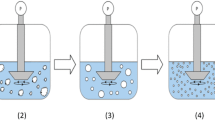
A novel method of synthesizing aqueous suspensions of monodisperse thermo-responsive poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) nanogel particles of varying sizes in the deci-micron range viz., controlled drop addition method (CDAM) by modifying the one-pot method has been developed. Unlike the conventional one-pot method which lacks control on the growth of the nuclei, this method controls the nuclei growth, thereby controlling the size polydispersity. The nuclei growth can be controlled by varying the drop rate as well as the ratio of pre-gel solution. The study showed that an optimum drop rate is desired for achieving narrow size distribution. The synthesized suspensions have been characterized for their particle size and size polydispersity using dynamic light scattering technique. The resultant particles fall well in the deci-micron regime with narrow size distribution. A plausible mechanism backed by atomic force microscopy images, governing the growth and size polydispersity is discussed. Implication of these monodisperse PNIPAM nanogel particles as carriers in drug delivery and as photonic crystals is briefed.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tata BVR., Brijitta J, Joshi RG. Thermo-responsive nanogel dispersions: dynamics and phase behavior. Int J Adv Eng Sci Appl Math. doi: 10.1007/s12572-010-0016-5
Brijitta J, Tata BVR, Kaliyappan T (2009) Phase behavior of poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) nanogel dispersions: Temperature dependent particle size and interactions. J Nanosci Nanotechnol 9:5323–5328
Senff H, Richtering W (1999) Temperature sensitive microgel suspensions: colloidal phase behavior and rheology of soft spheres. J Chem Phys 111:1705–1711
Mohanty PS, Richtering W (2008) Structural ordering and phase behavior of charged microgels. J Phys Chem B 112(47):14692–14697
Huang G, Hu Z (2007) Phase behavior and stabilization of microgel arrays. Macromolecules 40:3749–3756
Rzaev ZMO, Dincer S, Piskin E (2007) Functional copolymers of N-isopropylacrylamide for bioengineering applications. Prog Polym Sci 32:534–595
Ichikawa H, Fukumori Y (2000) A novel positively thermosensitive controlled-release microcapsule with membrane of nano-sized poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) gel dispersed in ethylcellulose matrix. J Control Release 63:107–119
Hu J, Shiheng Z, Xinglong X (2012) Dual stimuli responsive poly (N-isopropylacrylamide-co-acrylic acid) hydrogels based on a β-cyclodextrin crosslinker: synthesis, properties, and controlled protein releas. J Polym Res 19(11):1–9
Bucatariu S, Gheorghe F, Irina P, Mihaela B, Iuliana S, Valeria H, Marieta C (2014) Synthesis and characterization of thermosensitive poly (N-isopropylacrylamide-co-hydroxyethylacrylamide) microgels as potential carriers for drug delivery. J Polym Res 21(11):1–12
Debord JD, Lyon A (2000) Thermoresponsive photonic crystals. J Phys Chem B 104(27):6327–6331
Reese CE, Mikhonin AV, Kamenjicki M, Tikhonov A, Asher SA (2004) Nanogel nanosecond photonic crystal optical switching. J Am Chem Soc 126:1493–1496
Debord JD, Eustis S, Debord SB, Loyfe MT, Lyon LA (2002) Color-tunable colloidal crystals from soft hydrogel nanoparticles. Adv Mater 14:658–662
Su S, Ali MM, Filipe CDM, Li YF, Pelton R (2008) Microgel-based inks for paper-supported biosensing applications. Biomacromolecules 9:935–941
Hu Z, Chen Y, Wang C, Zheng Y, Li Y (1998) Polymer gels with engineered environmentally responsive surface patterns. Nature 393:149–152
Qiu Y, Park K (2001) Environment-sensitive hydrogels for drug delivery. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 53:321–339
Gao J, Hu Z (2002) Optical properties of N-isopropylacrylamide microgel spheres in water. Langmuir 18:1360–1367
Jones CD, Lyon LA (2000) Synthesis and characterization of multiresponsive core − shell microgels. Macromolecules 33:8301–8306
Jones CD, Lyon LA (2003) Shell-restricted swelling and core compression in poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) core − shell microgels. Macromolecules 36:1988–1993
Gan D, Lyon LA (2001) Tunable swelling kinetics in core − shell hydrogel nanoparticles. J Am Chem Soc 123:7511–7517
Naeem H, Zahoor HF, Luqman AS, Mohammad S (2012) Synthesis and characterization of p (NIPAM-AA-AAm) microgels for tuning of optical Properties of silver nanoparticles. J Polym Res 19(9):1–10
Saikia AK, Saroj A (2013) U. K. Mandal. Swelling dynamics of poly (NIPAM-co-AMPS) hydrogels synthesized using PEG as macroinitiator: effect of AMPS content. J Polym Res 20(1):1–9
Wang J, Weiqian Z, Xuelian L, Wuke L (2014) Fabrication and characterization of temperature-sensitive smart luminescent nanoparticles of poly (N-isopropylacrylamide)/lanthanide-polyoxometalates with core-shell structure. J Polym Res 21(7):1–8
Zhang Q, Zha L, Maa J, Liang B (2009) A novel route to prepare pH- and temperature-sensitive nanogels via a semibatch process. J Colloid Interface Sci 330:330–336
Tata BVR (2001) Colloidal dispersions and phase transitions in charged colloids. Curr Sci 80:948–958
Berne BJ, Pecora R (1975) In dynamic light scattering. Wiley, New York
Schneider CA, Rasband WS, Eliceiri KW (2012) NIH Image to ImageJ: 25 years of image analysis. Nat Methods 9:671–675
Osada Y, Hasebe M (1985) Chem Lett 9:1285–1288
Kajiwara K, Ross-Murphy SB (1992) Synthetic gels on the move. Nature 355:208–209
Langer R (1998) Drug delivery and targeting. Nature 392:5–10
Langer R (2001) Drugs on target. Science 293:58–59
Malmsten M (2006) Soft drug delivery systems. Soft Matter 2:760–769
Brijitta J, Tata BVR, Joshi RG, Kaliyappan T (2009) Random hcp and fcc structures in thermoresponsive microgel crystals. J Chem Phys 131:074904(1)–074904(8)
Acknowledgments
Authors acknowledge Shri. S. C. Chetal, Dr. C. S. Sundar and Dr. A. K. Arora for support and encouragement. First author acknowledges Dr. Jeppiaar and the Management, Sathyabama University for extending AFM measurements.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Brijitta, J., Tata, B.V.R. & Joshi, R.G. Controlled synthesis of monodisperse thermo-responsive nanogel particles. J Polym Res 22, 36 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-015-0674-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-015-0674-x