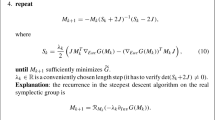Abstract
Optimization problems over compact Lie groups have been studied extensively due to their broad applications in linear programming and optimal control. This paper analyzes an optimization problem over a noncompact symplectic Lie group Sp(2N,ℝ), i.e., minimizing the Frobenius distance from a target symplectic transformation, which can be used to assess the fidelity function over dynamical transformations in classical mechanics and quantum optics. The topology of the set of critical points is proven to have a unique local minimum and a number of saddlepoint submanifolds, exhibiting the absence of local suboptima that may hinder the search for ultimate optimal solutions. Compared with those of previously studied problems on compact Lie groups, such as the orthogonal and unitary groups, the topology is more complicated due to the significant nonlinearity brought by the incompatibility of the Frobenius norm with the pseudo-Riemannian structure on the symplectic group.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Helmke, U., Moore, J.B.: Optimization and Dynamical Systems. Springer, London (1994)
Rabitz, H., Hsieh, H., Rosenthal, C.: Quantum optimally controlled transition landscapes. Science 303, 1998–2001 (2004)
Frankel, T.: Critical submanifolds of the classical groups and Stiefel manifolds. In: Cairns, S.S. (ed.) Differential and Combinatorial Topology: A Symposium in Honor of Marston Morse, vol. 1, pp. 37–53. Princeton University Press, Princeton (1962)
Dynnikov, I., Veselov, A.: Integrable gradient flows and Morse theory. St. Petersb. Math. J. 8, 429–446 (1997)
Brockett, R.: Least squares matching problems. Linear Algebra Appl. 123–124, 761–777 (1989)
Glaser, S.J., Schulte-Herbruggen, T., Sieveking, M., Scheletzky, O., Nielsen, N.C., Sorensen, O.W., Griesinger, C.: Unitary control in quantum ensembles: maximizing signal intensity in coherent spectroscopy. Science 280, 421–424 (1998)
Khaneja, N., Brockett, R.W., Glaser, S.J.: Time optimal control in spin systems. Phys. Rev. A 63, 032308 (2001)
Khaneja, N., Glaser, S.J., Brockett, R.W.: Sub-Riemannian geometry and time optimal control in three spin systems: quantum gates and coherence transfer. Phys. Rev. A 65, 032301 (2002)
Rabitz, H., Hsieh, M., Rosenthal, C.: The landscape for optimal control of quantum-mechanical unitary transformations. Phys. Rev. A 72, 52337 (2005)
Mahony, R., Manton, J.: The geometry of the Newton method on noncompact Lie groups. J. Glob. Optim. 23, 309–327 (2002)
Wu, R.-B., Chakrabarti, R., Rabitz, H.: Optimal control theory for continuous-variable quantum gates. Phys. Rev. A 77, 052303 (2008)
Dragt, A., Neri, F., Rangarajan, G.: Lie algebraic treatment of linear and nonlinear beam dynamics. Ann. Rev. Nucl. Part. Sci. 38, 455–496 (1988)
Han, Y., Park, F.: Least squares tracking, on the Euclidean group. IEEE Trans. Automat. Control 46, 1127–1131 (2001)
Cardoso, J., Silva-Leite, F.: Extending results from orthogonal to P-orthogonal matrices. http://www2.isec.pt/~jocar/Ficheiros/Pmatrizes.pdf (2007)
Bartlett, S.D., Sanders, B., Braunstein, S., Nemoto, K.: Efficient classical simulation of continuous variable quantum information processes. Phys. Rev. Lett. 88, 097904 (2002)
Gottesman, D., Kitaev, A., Preskill, J.: Encoding a qubit in an oscillator. Phys. Rev. A 64, 012310 (2001)
Chakrabarti, R., Rabitz, H.: Quantum control landscapes. Int. Rev. Phys. Chem. 26, 671–735 (2007)
Wu, R.-B., Rabitz, H., Hsieh, M.: Characterization of the critical submanifolds in quantum ensemble control landscapes. J. Phys. A 41, 015006 (2008)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by Q.C. Zhao.
The authors acknowledge support from NSF. R.B. Wu would also like to acknowledge support from NSFC (Grant No. 60904034 and 60635040).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, RB., Chakrabarti, R. & Rabitz, H. Critical Landscape Topology for Optimization on the Symplectic Group. J Optim Theory Appl 145, 387–406 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10957-009-9641-1
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10957-009-9641-1