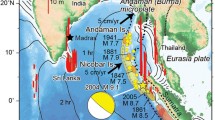
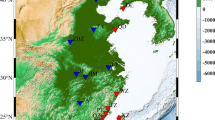
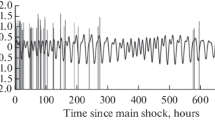
Abstract
There is a pressing need for a homogonous tsunami catalogue for the Indian Ocean as nearly 20% of tsunami events worldwide affect the region. Any study on tsunami hazard assessment necessitates a homogenous tsunamigenic earthquake catalogue. The existing records of strong tsunamigenic earthquakes have the magnitudes expressed in moment magnitude (MW), body wave magnitude (mb), local magnitude (ML), and surface wave magnitude (MS). This study deals with developing regional magnitude correlation equations for tsunamigenic earthquakes of the Indian Ocean. The present investigation estimates the threshold magnitude and focal depth for an earthquake to turn tsunamigenic. It is found that earthquakes above MW ≥ 5.9 and focal depth ≤ 80 km have the potential to generate a tsunami in the region. The moment magnitude is the most proper scale to characterize the size of large tsunamigenic earthquakes as it is more directly related to the released energy and does not suffer saturation. Hence, equations have been developed to convert surface wave magnitude (MS) to moment magnitude (MW) using three types of regression models viz. standard regression (SR), inverse standard regression (ISR), and orthogonal standard regression (OSR). The efficacy of these models has been compared in terms of R-squared and residual analysis. This study indicates that OSR is the best-suited regression model for developing magnitude correlation equations for the three zones of the Indian Ocean region under study. Also, a single unified conversion equation for the whole of the Indian Ocean has been derived with rational accuracy.










Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data used is freely available and can be downloaded from the address mentioned in the reference list.
References
Angove M, Arcas D, Bailey R, Carrasco P, Coetzee D, Fry B, Gledhill K, Harada S, von Hillebrandt-Andrade C, Kong L, McCreery C, McCurrach SJ, Miao Y, Sakya AE, Schindelé F (2019) Ocean observations required to minimize uncertainty in global tsunami forecasts, warnings, and emergency response. Front Mar Sci 6. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmars.2019.00350
Basili R, Brizuela B, Herrero A, Iqbal S, Lorito S, Maesano FE, Murphy S, Perfetti P, Romano F, Scala A, Selva J, Taroni M, Tiberti MM, Thio HK, Tonini R, Volpe M, Glimsdal S, Harbitz CB, Løvholt F, … Zaytsev A (2021) The making of the NEAM tsunami hazard model 2018 (NEAMTHM18). Front Mar Sci 8:1–29. https://doi.org/10.3389/feart.2020.616594
Carroll RJ, Ruppert D (1996) The use and misuse of orthogonal regression in linear errors-in-variables models. Am Stat 50(1):1–6. https://doi.org/10.1080/00031305.1996.10473533
Castellaro S, Bormann P (2007) Performance of different regression procedures on the magnitude conversion problem. Bull Seismol Soc Am 97(4):1167–1175. https://doi.org/10.1785/0120060102
Chicco D, Warrens MJ, Jurman G (2021) The coefficient of determination R-squared is more informative than SMAPE, MAE, MAPE, MSE and RMSE in regression analysis evaluation. PeerJ Computer Science 7:1–24. https://doi.org/10.7717/PEERJ-CS.623
Das R, Wason HR, Sharma ML (2011) Global regression relations for conversion of surface wave and body wave magnitudes to moment magnitude. Nat Hazards 59(2):801–810. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-011-9796-6
Das R, Wason HR, Sharma ML (2012) Magnitude conversion to unified moment magnitude using orthogonal regression relation. J Asian Earth Sci 50:44–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jseaes.2012.01.014
Davis JC (2002) Structural analysis and orthogonal regression. In: Gerber M, Berger B (eds) Statistics and data analysis in geology, 3rd edn. John Wiley and Sons, pp 218–220
Dziewonski AM, Chou T-A, Woodhouse JH (1981) Determination of earthquake source parameters from waveform data for studies of global and regional seismicity. J Geophys Res Solid Earth 86(B4):2825–2852. https://doi.org/10.1029/JB086iB04p02825
Ekström G, Nettles M, Dziewoński AM (2012) The global CMT project 2004–2010: centroid-moment tensors for 13,017 earthquakes. Phys Earth Planet Inter 200–201:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pepi.2012.04.002
Fuller WA (1987) Applied probability and statistics (Wiley Series). Measurement error models. John Wiley & Sons, pp 461–470. https://doi.org/10.1002/9780470316665
Gaba E (2015) Tectonic plates boundaries detailed-en.svg. In Wikimedia Commons. Wikimedia Commons. https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Tectonic_plates_boundaries_detailed-en.svg. Accessed 2 Apr 2022
Gardner JK, Knopoff L (1974) Is the sequence of earthquakes in Southern California, with aftershocks removed, Poissonian? Bull Seismol Soc Am 64(5):1363–1367. https://doi.org/10.1785/bssa0640051363
Gusiakov VK (2005) Historical tsunami database for the pacific, 47 B.C to present. In Novosibirsk Tsunami Laboratory (NTL). http://tsun.sscc.ru/htdbpac/. Accessed 28 Jan 2022
Gusiakov V (2001) Basic pacific tsunami catalog and database, 47 BC – 2000 AD : Results of the first stage of the project. In: Proceedings of the International Tsunami Symposium 2001 (ITS 2001), Session-1, Number 1-2, Seattle, WA, pp 263–272
Gutenberg B, Richter CF (1945) Frequency of earthquakes in California. Nature 156(3960):371. https://doi.org/10.1038/156371a0
Hanks TC, Kanamori H (1979) A moment magnitude scale. J Geophys Res 84(B5):2348–2350
Ingale VV, Bazin S, Royer JY (2021) Hydroacoustic observations of two contrasted seismic swarms along the Southwest Indian ridge in 2018. Geosciences (Switzerland) 11(6). https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences11060225
Kanamori H (1977) The energy release in great earthquakes. J Geophys Res 82(20):2981–2987
Munschy M, Schlich R (1989) The Rodriguez Triple junction (Indian Ocean): structure and evolution for the past one million years. Mar Geophys Res 11(1):1–14. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00286244
Kendall MG, Stuart A (1961) Inference and relationship. In: The advanced theory of statistics, 3rd ed, vol 2, issue 1. Hafner Publishing Company. https://doi.org/10.2307/3006935
National Geophysical Data Center / World Data Service (NGDC/WDS) (2015) Global historical tsunami database. In National Geophysical Data Center, NOAA (p. Boulder, CO, USA). https://doi.org/10.7289/V5PN93H7
NOAA (2017) Natural hazards viewer. In national centers for environmental information. https://maps.ngdc.noaa.gov/viewers/hazards/?layers=0. Accessed 3 Mar 2022
Orfanogiannaki K, Papadopoulos GA (2007) Conditional probability approach of the assessment of tsunami potential: application in three tsunamigenic Regions of the Pacific Ocean. Pure Appl Geophys 164(2–3):593–603. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00024-006-0170-7
Petricca P, Babeyko AY (2019) Tsunamigenic potential of crustal faults and subduction zones in the Mediterranean. Sci Rep 9(1):1–12. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-40740-1
Sabah N, Sil A (2020) Probabilistic forecasting of tsunami occurrences across various tsunamigenic zones of the earth. Pure Appl Geophys. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00024-020-02469-1
Scordilis EM (2006) Empirical global relations converting MS and mb to moment magnitude. J Seismolog 10(2):225–236. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10950-006-9012-4
Selva J, Lorito S, Volpe M, Romano F, Tonini R, Perfetti P, Bernardi F, Taroni M, Scala A, Babeyko A, Løvholt F, Gibbons SJ, Macías J, Castro MJ, González-Vida JM, Sánchez-Linares C, Bayraktar HB, Basili R, Maesano FE, … Amato A (2021). Probabilistic tsunami forecasting for early warning. Nat Commun 12(1). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-021-25815-w
Shukla J, Choudhury D (2012) Estimation of seismic ground motions using deterministic approach for major cities of Gujarat. Nat Hazards Earth Syst Sci 12(6):2019–2037. https://doi.org/10.5194/nhess-12-2019-2012
Sitharam TG, Sil A (2014) Comprehensive seismic hazard assessment of Tripura and Mizoram states. J Earth Syst Sci 123(4):837–857. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12040-014-0438-8
Stefanski LA (2000) Measurement Error Models. J Am Stat Assoc 95(452):1353–1358. https://doi.org/10.1080/01621459.2000.10474347
Suppasri A, Imamura F, Koshimura S (2012) Tsunamigenic ratio of the Pacific Ocean earthquakes and a proposal for a Tsunami Index. Nat Hazard 12(1):175–185. https://doi.org/10.5194/nhess-12-175-2012
Tinti S, Mulargia F (1985) An improved method for the analysis of the completeness of a seismic catalogue. Lett Nuovo Cimento Series 2 42(1):21–27. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02739471
Uhrhammer RA (1986) Characteristics of northern and southern California seismicity (abs.). In Earthquake Notes 21st edn, Vol. 57, Issue 1, p. 21First Page
Van Stiphout T, Zhuang J, Marsan D (2012) Seismicity declustering. Community online resource for statistical seismicity analysis. https://doi.org/10.5078/corssa-52382934. Available at http://www.corssa.org
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to sincerely thank the Department of Earthquake Engineering, Indian Institute of Technology Roorkee, India, for providing the computational facilities for carrying out this work. The authors are highly obliged to the anonymous reviewers for critically examining the manuscript and for providing constructive scientific comments that enhanced the quality of the paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
This manuscript is a part of a PhD research work by Nazeel Sabah under the supervision of Daya Shanker who supported and reviewed the initial draft of the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Highlights
• Identifying magnitude and focal depth ranges for an earthquake to turn potentially tsunamigenic.
• Magnitude conversion equations for the Indian Ocean Region.
• Orthogonal standard regression as the best fitting regression model.
Appendices
Appendix 1 Python code for web-scrapping

Appendix 2 Tables explaining the calculation of cumulative wave height vs depth and moment magnitude
(a) The calculation for cumulative wave height in increasing order of focal depth.
Dep | Hmax | Cum H |
|---|---|---|
8 | 0.8 | 0.8 |
10 | 1 | 1.8 |
10 | 1.5 | 3.3 |
12 | 10.6 | 13.9 |
13 | 0.24 | 14.14 |
14 | 0.15 | 14.29 |
14 | 2.5 | 16.79 |
15 | 0.1 | 16.89 |
15 | 0.26 | 17.15 |
15 | 0.3 | 17.45 |
15 | 0.5 | 17.95 |
15 | 0.57 | 18.52 |
15 | 3 | 21.52 |
15 | 3.7 | 25.22 |
15 | 4 | 29.22 |
15 | 15 | 44.22 |
15 | 17 | 61.22 |
16 | 0.22 | 61.44 |
18 | 2 | 63.44 |
18 | 13.9 | 77.34 |
20 | 1.5 | 78.84 |
20 | 10 | 88.84 |
21 | 16.86 | 105.7 |
23 | 1.08 | 106.78 |
25 | 15 | 121.78 |
25 | 20.9 | 142.68 |
29 | 0.24 | 142.92 |
29 | 0.4 | 143.32 |
30 | 0.01 | 143.33 |
30 | 4.2 | 147.53 |
30 | 50.9 | 198.43 |
31 | 0.44 | 198.87 |
33 | 0.1 | 198.97 |
33 | 0.7 | 199.67 |
33 | 2 | 201.67 |
33 | 3.43 | 205.1 |
34 | 5 | 210.1 |
35 | 0.03 | 210.13 |
35 | 1 | 211.13 |
35 | 1 | 212.13 |
35 | 1.5 | 213.63 |
35 | 3 | 216.63 |
35 | 5 | 221.63 |
37 | 0.21 | 221.84 |
40 | 0.18 | 222.02 |
46 | 0.4 | 222.42 |
50 | 3.4 | 225.82 |
70 | 7 | 232.82 |
80 | 25 | 257.82 |
83 | 2 | 259.82 |
90 | 0.27 | 260.09 |
100 | 0.1 | 260.19 |
130 | 1.4 | 261.59 |
150 | 0.3 | 261.89 |
179 | 0.5 | 262.39 |
600 | 3.5 | 265.89 |
(b) The calculation for cumulative wave height in increasing order of moment magnitude.
Mw | Hmax | Cum. H |
|---|---|---|
5.2 | 0.15 | 0.15 |
5.9 | 2 | 2.15 |
6.1 | 3 | 5.15 |
6.2 | 1.5 | 6.65 |
6.4 | 2.5 | 9.15 |
6.5 | 0.4 | 9.55 |
6.52 | 1 | 10.55 |
6.6 | 3.7 | 14.25 |
6.7 | 0.18 | 14.43 |
6.9 | 2 | 16.43 |
7 | 0.4 | 16.83 |
7 | 4 | 20.83 |
7.2 | 0.24 | 21.07 |
7.2 | 10 | 31.07 |
7.4 | 1 | 32.07 |
7.5 | 0.01 | 32.08 |
7.5 | 0.03 | 32.11 |
7.5 | 0.5 | 32.61 |
7.6 | 0.1 | 32.71 |
7.6 | 0.27 | 32.98 |
7.6 | 10.6 | 43.58 |
7.7 | 0.57 | 44.15 |
7.7 | 3 | 47.15 |
7.7 | 16.86 | 64.01 |
7.72 | 20.9 | 84.91 |
7.76 | 13.9 | 98.81 |
7.8 | 0.21 | 99.02 |
7.8 | 0.26 | 99.28 |
7.8 | 0.44 | 99.72 |
7.8 | 15 | 114.72 |
7.9 | 0.3 | 115.02 |
7.9 | 1.22 | 116.24 |
7.9 | 3.43 | 119.67 |
7.9 | 5 | 124.67 |
8 | 1.5 | 126.17 |
8.1 | 17 | 143.17 |
8.2 | 0.22 | 143.39 |
8.3 | 15 | 158.39 |
8.5 | 5 | 163.39 |
8.6 | 1.08 | 164.47 |
8.6 | 4.2 | 168.67 |
9 | 50.9 | 219.57 |
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Sabah, N., Shanker, D. Development of magnitude correlation equations for the tsunamigenic zones of the Indian Ocean. J Seismol 27, 473–492 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10950-023-10151-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10950-023-10151-x