Abstract
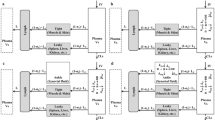
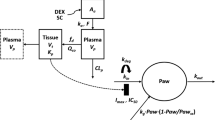
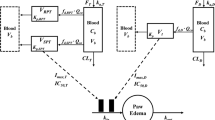
A population pharmacokinetic–pharmacodynamic–disease progression (PK/PD/DIS) model was developed to characterize the effects of anakinra in collagen-induced arthritic (CIA) rats and explore the role of interleukin-1β (IL-1β) in rheumatoid arthritis. The CIA rats received either vehicle, or anakinra at 100 mg/kg for about 33 h, 100 mg/kg for about 188 h, or 10 mg/kg for about 188 h by subcutaneous infusion. Plasma concentrations of anakinra were assayed by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Swelling of rat hind paws was measured. Population PK/PD/DIS parameters were computed for the various groups using non-linear mixed-effects modeling software (NONMEM® Version VI). The final model was assessed using visual predictive checks and nonparameter stratified bootstrapping. A two-compartment PK model with two sequential absorption processes and linear elimination was used to capture PK profiles of anakinra. A transduction-based feedback model incorporating logistic growth rate captured disease progression and indirect response model I captured drug effects. The PK and paw swelling versus time profiles in CIA rats were fitted well. Anakinra has modest effects (I max = 0.28) on paw edema in CIA rats. The profiles are well-described by our PK/PD/DIS model which provides a basis for future mechanism-based assessment of anakinra dynamics in rheumatoid arthritis.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Scott DL, Wolfe F, Huizinga TW (2010) Rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet 376:1094–1108
Klareskog L, Catrina AI, Paget S (2009) Rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet 373:659–672
Lipsky PE (2007) Why does rheumatoid arthritis involve the joints. N Engl J Med 356:2419–2420
Tracey D, Klareskog L, Sasso EH, Salfeld JG, Tak PP (2008) Tumor necrosis factor antagonist mechanisms of action: a comprehensive review. Pharmacol Ther 117:244–279
Smolen JS, Aletaha D, Koeller M, Weisman MH, Emery P (2007) New therapies for treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet 370:1861–1874
Choy EH, Panayi GS (2001) Cytokine pathways and joint inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis. N Engl J Med 344:907–916
Dinarello CA (2011) Interleukin-1 in the pathogenesis and treatment of inflammatory diseases. Blood 117:3720–3732
Jacques C, Gosset M, Berenbaum F, Gabay C (2006) The role of IL-1 and IL-1Ra in joint inflammation and cartilage degradation. Vitam Horm 74:371–403
Dinarello CA (2011) A clinical perspective of IL-1beta as the gatekeeper of inflammation. Eur J Immunol 41:1203–1217
Molto A, Olive A (2010) Anti-IL-1 molecules: new comers and new indications. Joint Bone Spine 77:102–107
Cohen SB, Moreland LW, Cush JJ, Greenwald MW, Block S, Shergy WJ, Hanrahan PS, Kraishi MM, Patel A, Sun G, Bear MB (2004) A multicentre, double blind, randomised, placebo controlled trial of anakinra (Kineret), a recombinant interleukin 1 receptor antagonist, in patients with rheumatoid arthritis treated with background methotrexate. Ann Rheum Dis 63:1062–1068
Wooley PH (2004) The usefulness and the limitations of animal models in identifying targets for therapy in arthritis. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol 18:47–58
Hegen M, Keith JC Jr, Collins M, Nickerson-Nutter CL (2008) Utility of animal models for identification of potential therapeutics for rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 67:1505–1515
Lalonde RL, Kowalski KG, Hutmacher MM, Ewy W, Nichols DJ, Milligan PA, Corrigan BW, Lockwood PA, Marshall SA, Benincosa LJ, Tensfeldt TG, Parivar K, Amantea M, Glue P, Koide H, Miller R (2007) Model-based drug development. Clin Pharmacol Ther 82:21–32
Wang Y, Bhattaram AV, Jadhav PR, Lesko LJ, Madabushi R, Powell JR, Qiu W, Sun H, Yim DS, Zheng JJ, Gobburu JV (2008) Leveraging prior quantitative knowledge to guide drug development decisions and regulatory science recommendations: impact of FDA pharmacometrics during 2004–2006. J Clin Pharmacol 48:146–156
Atkinson AJ Jr, Lalonde RL (2007) Introduction of quantitative methods in pharmacology and clinical pharmacology: a historical overview. Clin Pharmacol Ther 82:3–6
Earp JC, Dubois DC, Molano DS, Pyszczynski NA, Almon RR, Jusko WJ (2008) Modeling corticosteroid effects in a rat model of rheumatoid arthritis II: mechanistic pharmacodynamic model for dexamethasone effects in Lewis rats with collagen-induced arthritis. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 326:546–554
Earp JC, Dubois DC, Molano DS, Pyszczynski NA, Keller CE, Almon RR, Jusko WJ (2008) Modeling corticosteroid effects in a rat model of rheumatoid arthritis I: mechanistic disease progression model for the time course of collagen-induced arthritis in Lewis rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 326:532–545
R&D Systems, Inc. Human IL-1ra/IL-1F3 Immunoassay. www.rndsystems.com/pdf/DRA00B.pdf
Yang BB, Baughman S, Sullivan JT (2003) Pharmacokinetics of anakinra in subjects with different levels of renal function. Clin Pharmacol Ther 74:85–94
Chang DM, Chang SY, Yeh MK, Lai JH (2004) The pharmacokinetics of interleukin-1 receptor antagonist in Chinese subjects with rheumatoid arthritis. Pharmacol Res 50:371–376
Center for Drug Evaluation and Research, Food and Drug Administration (2001) Pharmacology review, application number: 103950/0. http://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/nda/2001/103950-0_Kineret_Pharmr.PDF
Earp JC, Dubois DC, Almon RR, Jusko WJ (2009) Quantitative dynamic models of arthritis progression in the rat. Pharm Res 26:196–203
Lon HK, Liu D, Zhang Q, Dubois DC, Almon RR, Jusko WJ (2011) Pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic disease progression model for effect of etanercept in lewis rats with collagen-induced arthritis. Pharm Res 28:1622–1630
Holford N (2005) The visual predictive check—superiority to standard diagnostic (Rorschach) plots. www.page-meeting.org/?abstract=738
Shi J, Ludden TM, Melikian AP, Gastonguay MR, Hinderling PH (2001) Population pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of sotalol in pediatric patients with supraventricular or ventricular tachyarrhythmia. J Pharmacokinet Pharmacodyn 28:555–575
Efron B (1979) Bootstrap methods: another look at the jackknife. Ann Statisit 7:1–26
Lindbom L, Ribbing J, Jonsson EN (2004) Perl-speaks-NONMEM (PsN)–a Perl module for NONMEM related programming. Comput Methods Programs Biomed 75:85–94
Jain L, Woo S, Gardner ER, Dahut WL, Kohn EC, Kummar S, Mould DR, Giaccone G, Yarchoan R, Venitz J, Figg WD (2011) Population pharmacokinetic analysis of sorafenib in patients with solid tumors. Br J Clin Pharmacol 72:294–305
Nam JL, Winthrop KL, Van VRF, Pavelka K, Valesini G, Hensor EM, Worthy G, Landewe R, Smolen JS, Emery P, Buch MH (2010) Current evidence for the management of rheumatoid arthritis with biological disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs: a systematic literature review informing the EULAR recommendations for the management of RA. Ann Rheum Dis 69:976–986
Mertens M, Singh JA (2009) Anakinra for rheumatoid arthritis: a systematic review. J Rheumatol 36:1118–1125
Gueorguieva I, Clark SR, McMahon CJ, Scarth S, Rothwell NJ, Tyrrell PJ, Hopkins S, Rowland M (2008) Pharmacokinetic modelling of interleukin-1 receptor antagonist in plasma and cerebrospinal fluid of patients following subarachnoid haemorrhage. Br J Clin Pharmacol 65:317–325
Kim DC, Reitz B, Carmichael DF, Bloedow DC (1995) Kidney as a major clearance organ for recombinant human interleukin-1 receptor antagonist. J Pharm Sci 84:575–580
Granowitz EV, Porat R, Mier JW, Pribble JP, Stiles DM, Bloedow DC, Catalano MA, Wolff SM, Dinarello CA (1992) Pharmacokinetics, safety and immunomodulatory effects of human recombinant interleukin-1 receptor antagonist in healthy humans. Cytokine 4:353–360
Zuurmond AM, Koudijs A, Van EB, Doornbos RP, Van MBC, Bastiaans JH, Penninks AH, Van BJH, Cnubben NH, Degroot J (2011) Integration of efficacy, pharmacokinetic and safety assessment of interleukin-1 receptor antagonist in a preclinical model of arthritis. Regul Toxicol Pharmacol 59:461–470
Wang W, Wang EQ, Balthasar JP (2008) Monoclonal antibody pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics. Clin Pharmacol Ther 84:548–558
Lin JH (2009) Pharmacokinetics of biotech drugs: peptides, proteins and monoclonal antibodies. Curr Drug Metab 10:661–691
Dirks NL, Meibohm B (2010) Population pharmacokinetics of therapeutic monoclonal antibodies. Clin Pharmacokinet 49:633–659
Davies B, Morris T (1993) Physiological parameters in laboratory animals and humans. Pharm Res 10:1093–1095
Giraudel JM, Diquelou A, Laroute V, Lees P, Toutain PL (2005) Pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic modelling of NSAIDs in a model of reversible inflammation in the cat. Br J Pharmacol 146:642–653
Jeunesse EC, Bargues IA, Toutain CE, Lacroix MZ, Letellier IM, Giraudel JM, Toutain PL (2011) Paw inflammation model in dogs for preclinical PK/PD investigations of non steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 338:548–558
Sun YN, Jusko WJ (1998) Transit compartments versus gamma distribution function to model signal transduction processes in pharmacodynamics. J Pharm Sci 87:732–737
Mager DE, Jusko WJ (2001) Pharmacodynamic modeling of time-dependent transduction systems. Clin Pharmacol Ther 70:210–216
Liu L, Paolo JD, Barbosa J, Rong H, Reif K, Wong H (2011) Anti-arthritis effect of a novel bruton’s tyrosine kinase (BTK) inhibitor in rat collagen-induced arthritis and mechanism-based pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic modeling: relationships between inhibition of BTK phosphorylation and efficacy. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 338:154–163
Jusko WJ, Ko HC (1994) Physiologic indirect response models characterize diverse types of pharmacodynamic effects. Clin Pharmacol Ther 56:406–419
Dayneka NL, Garg V, Jusko WJ (1993) Comparison of four basic models of indirect pharmacodynamic responses. J Pharmacokinet Biopharm 21:457–478
Bendele A, McAbee T, Sennello G, Frazier J, Chlipala E, McCabe D (1999) Efficacy of sustained blood levels of interleukin-1 receptor antagonist in animal models of arthritis: comparison of efficacy in animal models with human clinical data. Arthritis Rheum 42:498–506
Schett G, Middleton S, Bolon B, Stolina M, Brown H, Zhu L, Pretorius J, Zack DJ, Kostenuik P, Feige U (2005) Additive bone-protective effects of anabolic treatment when used in conjunction with RANKL and tumor necrosis factor inhibition in two rat arthritis models. Arthritis Rheum 52:1604–1611
D’Argenio DZ, Schumitzky A (1979) A program package for simulation and parameter estimation in pharmacokinetic systems. Comput Programs Biomed 9:115–134
Zhang L, Beal SL, Sheiner LB (2003) Simultaneous vs. sequential analysis for population PK/PD data I: best-case performance. J Pharmacokinet Pharmacodyn 30:387–404
Zhang L, Beal SL, Sheiner LB (2003) Simultaneous vs. sequential analysis for population PK/PD data II: robustness of methods. J Pharmacokinet Pharmacodyn 30:405–416
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the UB Center for Protein Therapeutics, fellowship support for Dr. Liu from Hoffman-La Roche Inc., fellowship support for Ms. Lon from Amgen, Inc., and NIH Grant GM24211.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, D., Lon, HK., DuBois, D.C. et al. Population pharmacokinetic–pharmacodynamic–disease progression model for effects of anakinra in Lewis rats with collagen-induced arthritis. J Pharmacokinet Pharmacodyn 38, 769–786 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10928-011-9219-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10928-011-9219-z