Abstract
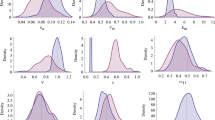
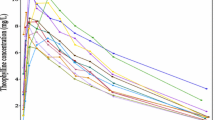
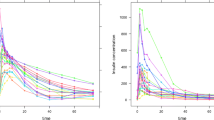
Motivated by the use of semiparametric nonlinear mixed-effects modeling on longitudinal data, we develop a new semiparametric modeling approach to address potential structural model misspecification for population pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic (PK/PD) analysis. Specifically, we use a set of ordinary differential equations (ODEs) with form dx/dt = A(t)x + B(t) where B(t) is a nonparametric function that is estimated using penalized splines. The inclusion of a nonparametric function in the ODEs makes identification of structural model misspecification feasible by quantifying the model uncertainty and provides flexibility for accommodating possible structural model deficiencies. The resulting model will be implemented in a nonlinear mixed-effects modeling setup for population analysis. We illustrate the method with an application to cefamandole data and evaluate its performance through simulations.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beal SL, Sheiner LB (1982) Estimating population kinetics. CRC Crit Rev Bioeng 8: 195–222
Lindstrom MJ, Bates DM (1990) Nonlinear mixed effects models for repeated measures data. Biometrics 46: 673–687 doi:10.2307/2532087
Linsey JK (1993) Models for repeated measurements. Oxford University Press, Oxford, UK
Davidian M, Giltinan DM (1995) Nonlinear models for repeated measurement data. Chapman and Hall, London
Vonesh EF, Chinchilli VM (1996) Linear and nonlinear models for the analysis of repeated measurements. Marcel Dekker, New York
Pinheiro JC, Bates DM (2000) Mixed-effects models in S and splus. Springer, New York
Diggle PJ, Heagerty P, Liang KY, Zeger SL (2002) Analysis of longitudinal data, 2nd edn. Oxford University Press, Oxford,UK
Demidenko E (2004) Mixed models: theory and applications. Wiley, Canada
Ruppert D, Wand MP, Carroll RJ (2003) Semiparametric regression. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Ke C, Wang Y (2001) Semiparametric nonlinear mixed models and their applications. J Am Stat Assoc 96: 1272–1298 doi:10.1198/016214501753381913
Li L, Brown MB, Lee KH, Gupta S (2002) Estimation and inference for a spline-enhanced population pharmacokinetic model. Biometrics 58: 601–611 doi:10.1111/j.0006-341X.2002.00601.x
Bates DM, Lindstrom MJ, Wahba G (2001) Comment to semiparametric nonlinear mixed models and their applications. J Am Stat Assoc 96: 1292–1293
Ladd WM, Lindstrom MJ (2000) Self-modeling for two dimensional response curves. Biometrics 56: 97–105 doi:10.1111/j.0006-341X.2000.00089.x
Bayard D, Jelliffe R (2004) A Bayesian approach to tracking patients having changing pharmacokinetic parameters. J Pharmacokinet Pharmacodyn 31: 75–107 doi:10.1023/B:JOPA.0000029490.76908.0c
Troconiz IF, Sheiner LB, Verotta D (1994) Semiparametric models for drug interactions. J Appl Physiol 76: 2224–2233
Tornoe CW, Overgaard RV, Agerso H, Nielsen HA, Madsen H, Jonsson EN (2005) Stochastic differential equations in NONMEM: implementation, application, and comparison with ordinary differential equations. Pharm Res 22: 1247–1258 doi:10.1007/s11095-005-5269-5
Ngo L, Wand MP (2004) Smoothing with mixed model software. J Stat Softw 9(1)
Tornoe CW, Agerso H, Jonsson EN, Madsen H, Nielsen HA (2004) Non-linear mixed-effects pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic modeling in NLME using differential equations. Comput Methods Programs Biomed 76: 31–40 doi:10.1016/j.cmpb.2004.01.001
Galecki AT, Wolfinger RD, Linares OA, Smith MJ, Halter JB (2004) Ordinary differential equation PK/PD models using the SAS macro NLINMIX. J Biopharm Stat 14: 483–503 doi:10.1081/BIP-120037194
Tornoe CW, Agerso H, Nielsen HA, Madsen H, Jonsson EN (2004) Pharmacokinetic/Pharmacodynamic modeling of GnRH antagonist degarelix: a comparison of the non-linear mixed-effects programs NONMEM and NLME. J Pharmacokinet Pharmacodyn 31: 441–461 doi:10.1007/s10928-005-5911-1
Aziz NS, Gambertoglio JG, Lin ET, Grausz H, Benet LZ (1977) Pharmacokinetics of cefamandole using a HPLC assay. J Pharmacokinet Biopharm 6: 153–164 doi:10.1007/BF01117449
Li L, Lin XH, Brown MB, Gupta S, Lee KH (2004) A population pharmacokinetic model with time-dependent covariates measured with error. Biometrics 60: 451–460 doi:10.1111/j.0006-341X.2004.00190.x
Bennett JE, Wakefield JC (1996) A comparison of a Bayesian population method with two methods as implemented in commercially available software. J Pharmacokinet Biopharm 24: 403–432 doi:10.1007/BF02353520
Wang Y, Eskridge K, Zhang S (2006) Bayesian and Non-Bayesian analysis of mixed-effects PK/PD models based on differential equations. In: Proceedings of the American Statistical Association, Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics Section [CD-ROM]. American Statistical Association, Alexandria, VA
Wang Y (2008) Semiparametric mixed-effects analysis on PK/PD models using differential equations, Ph.D. Dissertation. University of Nebraska, Lincoln
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Y., Eskridge, K.M. & Zhang, S. Semiparametric mixed-effects analysis of PK/PD models using differential equations. J Pharmacokinet Pharmacodyn 35, 443–463 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10928-008-9096-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10928-008-9096-2