Abstract
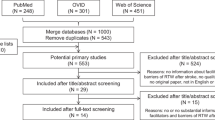
Purpose Addressing return to work early after neurological impairment from stroke or moderate and severe traumatic brain injury may improve likelihood of returning to employment, yet little is known about how best to organize work interventions for delivery in the inpatient hospital setting. The purpose of this scoping review was to identify knowledge gaps and inform program development in hospital-based work interventions. Method We searched MEDLINE, CINAHL, OTSeeker and Embase for English-language articles published from database inception until March 2018. Citations were then manually searched using reference lists of included papers and Google Scholar. Articles were included if they described programs providing return to work intervention within a hospital to adults with newly acquired neurological conditions, such as traumatic brain injury or stroke. After identifying and selecting relevant studies, we charted the data and then synthesized the results. Results Twenty-eight articles explored work intervention in an inpatient hospital setting. Interventions targeted a diagnostically heterogeneous population, mostly including adults who had suffered either a traumatic brain injury or stroke. Most interventions included a structured process for assessment, highlighted the importance of collaboration, and aimed to improve performance of work skills that could be facilitated within a hospital setting only (as opposed to all work skills). Thematic analysis of included studies resulted in four themes: structure, collaboration, clinician training, and belief in future work capacity. Conclusion Return to work intervention appears to be an important component of neurological rehabilitation. While studies to date have identified enablers for the integration of work interventions into the inpatient hospital setting, there is limited description of specific components of programs, and a lack of studies evaluating program effectiveness.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Thurman DJ, Alverson C, Dunn KA, Guerrero J, Sniezek JE. Traumatic brain injury in the United States: a public health perspective. J Head Trauma Rehabil. 1999;14(6):602–615.
van Velzen JM, van Bennekom CA, Edelaar MJ, Sluiter JK, Frings-Dresen MH. How many people return to work after acquired brain injury?: A systematic review. Brain Inj. 2009;23(6):473–488.
Cifu DX, Stewart DG. Factors affecting functional outcome after stroke: a critical review of rehabilitation interventions. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 1999;80(5):9–35.
Eames P, Cotterill G, Kneale T, Storrar A, Yeomans P. Outcome of intensive rehabilitation after severe brain injury: a long-term follow-up study. Brain Inj. 1996;10:631–650.
Cifu DX, Keyser-Marcus L, Lopez E, Wehman P, Kreutzer JS, Englander J, et al. Acute predictors of successful return to work 1 year after traumatic brain injury: a multicenter analysis. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 1997;78(2):125–131.
Keyser-Marcus LA, Bricout JC, Wehman P, Campbell LR, Cifu DX, Englander J, et al. Acute predictors of return to employment after traumatic brain injury: a longitudinal follow-up. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2002;83(5):635–641.
Wolf TJ, Baum C, Conner LT. Changing face of stroke: implications for occupational therapy practice. Am J Occup Ther. 2009;63(5):621–625.
Medin J, Barajas J, Ekberg K. Stroke patients’ experiences of return to work. Disabil Rehabil. 2006;28(17):1051–1060.
Kerschke S, Witas M. Brain injury rehabilitation for the real world. Rehab Manag. 2013;26(5):34–39.
Soeker MS, Van Rensburg V, Travill A. Are rehabilitation programmes enabling clients to return to work? Return to work perspectives of individuals with mild to moderate brain injury in South Africa. Work 2012;43(2):171–182.
Johansson J, Bernspang B. Life satisfaction related to work re-entry after brain injury: a longitudinal study. Brain Inj. 2003;17(11):991–1002.
Bryson-Campbell M, Shaw L, O’Brien J, Holmes J, Magalhaes L. A scoping review on occupational and self identity after a brain injury. Work 2013;44(1):57–67.
O’neill J, Hibbard MR, Broivn M, Jaffe M, Sliwinski M, Vandergoot D, et al. The effect of employment on quality of life and community integration after traumatic brain injury. J Head Trauma Rehabil. 1998;13:468–479.
Soeker MS, Van Rensburg V, Travill A. Individuals with traumatic brain injuries perceptions and experiences of returning to work in South Africa. Work. 2012;42(4):589–600.
Hart T, Dijkers M, Whyte J, Braden C, Trott CT, Fraser R. Vocational interventions and supports following job placement for persons with traumatic brain injury. J Vocat Rehabil. 2010;32(3):135–150.
Ownsworth T, McKenna K. Investigation of factors related to employment outcome following traumatic brain injury: a critical review and conceptual model. Disabil Rehabil. 2004;26(13):765–783.
O’Brien L. Achieving a successful and sustainable return to the workforce after ABI: a client-centred approach. Brain Inj. 2007;21(5):465–478.
Murphy L, Chamberlain E, Weir J, Berry A, Nathaniel-James D, Agnew R. Effectiveness of vocational rehabilitation following acquired brain injury: preliminary evaluation of a UK specialist rehabilitation programme. Brain Inj. 2006;20(11):1119–1129.
Geurtsen GJ, van Heugten CM, Martina JD, Geurts AC. Comprehensive rehabilitation programmes in the chronic phase after severe brain injury: a systematic review. J Rehabil Med. 2010;42(2):97–110.
Arksey H, O'Malley L. Scoping studies: towards a methodological framework. Int J Soc Methodol. 2005;8(1):19–32.
Moher D, Chan AW. SPIRIT (Standard Protocol Items: Recommendations for Interventional Trials). Guidelines for reporting health research: a user’s manual. Chichester: Wiley Blackwell; 2014. pp. 56–67.
Stemler S. An overview of content analysis. Pract Assess Res Eval. 2001;7(17):137–146.
Braverman SE, Spector J, Warden DL, Wilson BC, Ellis TE, Bamdad MJ, et al. A multidisciplinary TBI inpatient rehabilitation programme for active duty service members as part of a randomized clinical trial. Brain Inj. 1999;13(6):405–415.
Hayden ME, Moreault A, LeBlanc J, Plenger PM. Reducing level of handicap in traumatic brain injury: an environmentally based model of treatment. J Head Trauma Rehabil. 2000;15(4):1000–1021.
Man DW, Poon WS, Lam C. The effectiveness of artificial intelligent 3-D virtual reality vocational problem-solving training in enhancing employment opportunities for people with traumatic brain injury. Brain Inj. 2013;27(9):1016–1025.
Thomas DF, Menz F. Validation of the vocational assessment protocol. J Head Trauma Rehabil. 1997;12(5):72–87.
Watanabe S. Vocational rehabilitation for clients with cognitive and behavioral disorders associated with traumatic brain injury. Work. 2013;45(2):273–277.
Salazar AD, Warden DL, Schwab K, Spector J, Braverman S, Walter J, Cole R, Rosner MM, Martin EM, Ecklund J, Ellenbogen RG. Cognitive rehabilitation for traumatic brain injury. JAMA. 2000;283(23):3075–3081.
Sarajuuri JM, Kaipio ML, Koskinen SK, Niemela MR, Servo AR, Vilkki JS. Outcome of a comprehensive neurorehabilitation progrm for patients with traumatic brain injury. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2005;86(12):2296–2302.
Buffington ALH, Malec JF. The vocational rehabilitation continuum: maximizing outcomes through bridging the gap from hospital to community-based services. J Head Trauma Rehabil. 1997;12(5):1–13.
Mateer CA, Sira CS. Cognitive and emotional consequences of TBI: intervention strategies for vocational rehabilitation. Neurorehabilitation 2006;21(4):315–326.
Roth EJ, Lovell L. Employment after stroke: report of a state of the science symposium. Top Stroke Rehabil. 2014;21(Suppl 1):S75–S86.
Sinclair E, Radford K, Grant M, Terry J. Developing stroke-specific vocational rehabilitation: a soft systems analysis of current service provision. Disabil Rehabil. 2014;36(5):409–417.
Soeker MS. Occupational adaptation: a return to work perspective of persons with mild to moderate brain injury in South Africa. J Occup Sci. 2011;18(1):81–91.
Soeker MS. The development of the model of occupational self efficacy: an occupational therapy practice model to facilitate returning to work after a brain injury. Work. 2012;43(3):313–322.
van Velzen JM, van Bennekom CAM, van Dormolen M, Sluiter JK, Frings-Dresen MHW. Factors influencing return to work experienced by people with acquired brain injury: a qualitative research study. Disabil Rehabil. 2011;33(23):2237–2246.
van Velzen JM, van Bennekom CAM, Sluiter JK, Frings-Dresen MHW. Early vocational rehabilitation after acquired brain injury: a structured and interdisciplinary approach. J Vocat Rehabil. 2015;42(1):31–40.
Holmes J, Phillips J, Morris R, Bedekar Y, Tyerman R, Radford K. Development and evaluation of an early specialised traumatic brain injury vocational rehabilitation training package. Br J Occup Ther. 2016;79(11):693–702.
Gilworth G, Phil M, Cert A, Sansam KA, Kent RM. Personal experiences of returning to work following stroke: an exploratory study. Work 2009;34(1):95–103.
Scott SL, Bondoc S. Occupational therapy’s distinct value for stroke survivors: facilitating return to work across the continuum of care. Phys Disabil Spec Interest Sect Q. 2015;38(3):1–4.
Hellman T, Bergström A, Eriksson G, Hansen Falkdal A, Johansson U. Return to work after stroke: important aspects shared and contrasted by five stakeholder groups. Work 2016;55(4):901–911.
Bush EJ, Hux K, Guetterman TC, McKelvey M. The diverse vocational experiences of five individuals returning to work after severe brain injury: a qualitative inquiry. Brain Inj. 2016;30(4):422–436.
Donker-Cools BH, Schouten MJ, Wind H, Frings-Dresen MH. Return to work following acquired brain injury: the views of patients and employers. Disabil Rehabil. 2018;4(2):185–191.
Stergiou-Kita M, Rappolt S, Dawson D. Towards developing a guideline for vocational evaluation following traumatic brain injury: the qualitative synthesis of clients’ perspectives. Disabil Rehabil. 2012;34(3):179–188.
Thomas DF, Menz FE. Employment-related services for persons with brain injury. J Head Trauma Rehabil. 1997;12(5):9–11.
Chappell I, Higham J, McLean AM. An occupational therapy work skills assessment for individuals with head injury. Can J Occup Ther. 2003;70(3):163–169.
MacDonald S, Johnson CJ. Utility of a verbal reasoning test in indicating vocational readiness following traumatic brain injury. Brain Inj. 1996;10(7):531–542.
van Velzen JM, van Bennekom CAM, van Dormolen M, Sluiter JK, Frings-Dresen MHW. Evaluation of the implementation of the protocol of an early vocational rehabilitation intervention for people with acquired brain injury. Disabil Rehabil. 2016;38(1):62–70.
Grant M, Radford K, Sinclair E, Walker M. Return to work after stroke: recording, measuring, and describing occupational therapy intervention. Br J Occup Ther. 2014;77(9):457–465.
Stergiou-Kita M, Dawson D, Rappolt S. Inter-professional clinical practice guideline for vocational evaluation following traumatic brain injury: a systematic and evidence-based approach. J Occup Rehabil. 2012;22(2):166–181.
Smith RK. Prevocational programming in the rehabilitation of the head-injured patient. A summary. Phys Ther. 1983;63(12):2026–2029.
Kirsch NL, Levine SP, Lajiness-O’Neill R, Schnyder M. Computer-assisted interactive task guidance: facilitating the performance of a simulated vocational task. J Head Trauma Rehabil. 1992;7(3):13–25.
van Velzen JM, van Bennekom CA, van Dormolen M, Sluiter JK, Frings-Dresen MH. Factors influencing return to work experienced by people with acquired brain injury: a qualitative research study. Disabil Rehabil. 2011;33(23–24):2237–2246.
Doucet T, Muller F, Verdun-Esquer C, Debelleix X, Brochard P. Returning to work after a stroke: a retrospective study at the Physical and Rehabilitation Medicine Center La Tour de Gassies. Ann Phys Rehabil Med. 2012;55(2):112–127.
Grant MI, Sinclair EJ, Walker MF, Radford KA. Vocational rehabilitation following stroke: describing intervention. Int J Stroke. 2012;7:20.
Bush EJ, Hux K, Guetterman TC, McKelvey M. The diverse vocational experiences of five individuals returning to work after severe brain injury: a Qualitative inquiry. Brain Inj. 2016;30(4):422–436.
Donker-Cools BH, Daams JG, Wind H, Frings-Dresen MH. Effective return-to-work interventions after acquired brain injury: a systematic review. Brain Inj. 2016;30(2):113–131.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
O’Keefe, S., Stanley, M., Adam, K. et al. A Systematic Scoping Review of Work Interventions for Hospitalised Adults with an Acquired Neurological Impairment. J Occup Rehabil 29, 569–584 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10926-018-9820-8
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10926-018-9820-8