Abstract
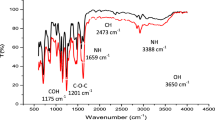
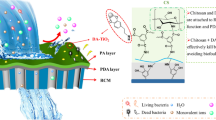
Biofouling is one of the major challenges of membrane technology in water and wastewater treatments. In this work, we investigated the potential of chitosan/chitosan powder activated carbon (PAC) composite to reduce biofouling of membrane. Polyethersulfone (PES) membrane was modified with chitosan/chitosan-PAC composite and the performance of the modified membrane in river water treatment was evaluated. The effect of different concentration of polymer [(chitosan: 2.0% (w/v), 1.0% (w/v), 0.5% (w/v), 0.1% (w/v), and chitosan-PAC composite: 1.5% (w/v) − 1.0 (w/v), 0.5% (w/v) − 0.2% (w/v)] on the membrane performance was examined. The properties of the modified membrane such as roughness, morphology, surface functional groups wettability, swelling ration and contact angle were analyzed. The membrane water flux increased with increasing chitosan concentration from 0.1% (w/v) (7.36 mL/cm2 m) to 1.0% (w/v) (9.46 mL/cm2 m), but decreased at (2.0 w/v) (5.30 mL/cm2 m). However, the water flux for chitosan-PAC-modified membrane was about 6.86 mL/cm2 m, which was slightly lower than unmodified membrane (7.36 mL/cm2 m). The chitosan-modified membrane resulted in 28% reduction in total coliform bacteria while the chitosan-PAC-modified membrane reduced 45% of the total coliform bacteria. These results indicated that chitosan and chitosan-PAC composite could enhance the anti-microbial properties of PES membrane, which would prevent biofilm formation during water treatment.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bick A, Gillerman L, Manor Y, Oron G (2012) Economic assessment of an integrated membrane system for secondary effluent polishing for unrestricted reuse. Water 4:219–236. https://doi.org/10.3390/w4010219
Ng YL, Mohammed AW, Leo CP, Hilal N (2013) Polymeric membranes incorporated with metal/metal oxide nanoparticles: a comprehensive review. Desalination 308:15–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2010.11.033
Zhao C, Liu X, Rikimaru S, Nomizu M, Nishi N (2003) Surface characterization of polysulfone membranes modified by DNA immobilization. J Membr Sci 214:179–189
Balta S, Sotto A, Luis P, Benea L, Van Der Bruggen B, Kim J (2012) A new outlook on membrane enhancement with nanoparticles: the alternative of ZnO. J Membr Sci 389:155–161. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2011.10.025
Ji H, Xu H, Jin L, Song X, He C, Liu X, Xiong L, Zhao W, Zhao C (2019) Surface engineering of low-fouling and hemocompatible polyethersulfone membranes via in situ ring-opening reaction. J Membr Sci 581:373–382. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2019.03.082
Zhao W, Huang J, Fang B, Nie S, Yi N, Su B, Li H, Zhao C (2011) Modification of polyethersulfone membrane by blending semi-interpenetrating network polymeric nanoparticles. J Membr Sci 369:258–266. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2010.11.065
Arthanareeswaran G, Mohan D, Raajenthiren M (2010) Preparation, characterization and performance studies of ultrafiltration membranes with polymeric additive. J Membr Sci 350:130–138. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2009.12.020
Mierzwa JC, Vecitis CD, Carvalho J, Arieta V, Verlage M (2012) Anion dopant effects on the structure and performance of polyethersulfone membranes. J Membr Sci 421–422:91–102. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2012.06.039
Ahn J, Chung W, Pinnau I, Guiver MD (2008) Polysulfone/silica nanoparticle mixed-matrix membranes for gas separation. J Membr Sci 314:123–133. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2008.01.031
Kim J, Van Der Bruggen B (2010) The use of nanoparticles in polymeric and ceramic membrane structures: review of manufacturing procedures and performance improvement for water treatment. Environ Pollut 158:2335–2349. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2010.03.024
Anadão P, Sato LF, Wiebeck H, Valenzuela-díaz FR (2010) Montmorillonite as a component of polysulfone nanocomposite membranes. Appl Clay Sci 48:127–132. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clay.2009.12.011
Toledo L, Rivas LB (2015) Quaternised chitosan in conjunction with ultrafiltration membranes to remove arsenate and chromate ions. Polym Bull 72:1341–1344. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-015-1341-4
Shao S, Liang H, Qu F, Li K, Chang H, Yu H, Li G (2016) Combined influence by humic acid (HA) and powdered activated carbon (PAC) particles on ultrafiltration membrane fouling. J Membr Sci 500:99–105. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2015.11.036
Wang Z, Dong B, Liu J, Zhao D, Tian J, Jia F (2017) Mechanism analysis of powdered activated carbon controlling microfiltration membrane fouling in surface water treatment. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 517:45–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2017.01.009
Oh H, Yu M, Takizawa S, Ohgaki S (2006) Evaluation of PAC behavior and fouling formation in an integrated PAC—UF membrane for surface water treatment. Desalination 192:54–62. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2005.07.034
Zhang M, Li C, Benjamin MM, Chang Y (2003) Fouling and natural organic matter removal in adsorbent/membrane systems for drinking water treatment. Environ Sci Technol 37:1663–1669. https://doi.org/10.1021/es0260418
Campinas M, Rosa MJ (2010) Assessing PAC contribution to the NOM fouling control in PAC/UF systems. Water Res 44:1636–1644. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2009.11.012
Cheng X, Li P, Zhou W, Wu D, Luo C (2019) Effect of peroxymonosulfate oxidation activated by powdered activated carbon for mitigating ultrafiltration membrane fouling caused by different natural organic matter fractions. Chemosphere 221:812–823. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.01.081
Salam MA, Makki MSI, Abdelaal MYA (2011) Preparation and characterization of multi-walled carbon nanotubes/chitosan nanocomposite and its application for the removal of heavy metals from aqueous solution. J Alloys Compd 509:2582–2587. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2010.11.094
Bakandritsos A, Kouvelos E, Steriotis T, Petridis D (2005) Aqueous and gaseous adsorption from montmorillonite—carbon composites and from derived carbons. Langmuir 21:2349–2355. https://doi.org/10.1021/la047495g
Yang L, Ma X, Guo N (2012) Sodium alginate/Na+-rectorite composite microspheres: preparation, characterization, and dye adsorption. Carbohydr Polym 90:853–858. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2012.06.011
Hou H, Zhou R, Wu P, Wu L (2012) Removal of Congo red dye from aqueous solution with hydroxyapatite/chitosan composite. Chem Eng J 211–212:336–342. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2012.09.100
Zhao S, Zhou F, Li L, Cao M, Zuo D, Liu H (2012) Removal of anionic dyes from aqueous solutions by adsorption of chitosan-based semi-IPN hydrogel composites. Compos Part B 43:1570–1578. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2012.01.015
Sheha RR (2012) Preparation and performance of a novel composite as a reactive resin for copper retention. Chem Eng J 213:163–174. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2012.09.113
Ma J, Jia Y, Jing Y, Yao Y, Sun J (2012) Dyes and pigments kinetics and thermodynamics of methylene blue adsorption by cobalt-hectorite composite. Dye Pigment 93:1441–1446. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dyepig.2011.08.010
Zhou C, Zhang D, Tong D, Wu L, Yu W, Ismadji S (2012) Paper-like composites of cellulose acetate–organo-montmorillonite for removal of hazardous anionic dye in water. Chem Eng J 209:223–234. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2012.07.107
Wang Q, Minh A, Cui Y, Delage P, Gatmiri B (2012) Experimental study on the swelling behaviour of bentonite/claystone mixture. Eng Geol 124:59–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2011.10.003
Hegab HM, Wimalasiri Y, Ginic-markovic M, Zou L (2015) Improving the fouling resistance of brackish water membranes via surface modification with graphene oxide functionalized chitosan. Desalination 365:99–107. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2015.02.029
Zinadini S, Zinatizadeh AA, Rahimi M, Vatanpour V, Zangeneh H, Beygzadeh M (2014) Novel high flux antifouling nanofiltration membranes for dye removal containing carboxymethyl chitosan coated Fe3O4 nanoparticles. Desalination 349:145–154. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2014.07.007
Fini MN, Soroush S, Montazer-Rahmati MM (2018) Synthesis and optimization of chitosan ceramic-supported membranes in pervaporation ethanol dehydration. Membranes (Basel) 8:119. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes8040119
Zodrow K, Brunet L, Mahendra S, Li D, Zhang A, Li Q, Alvarez PJJ (2009) Polysulfone ultrafiltration membranes impregnated with silver nanoparticles show improved biofouling resistance and virus removal. Water Res 43:715–723. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2008.11.014
Mnasri N, Moussaoui Y, Elaloui E, Salem R, Lagerge S, Douillard JM, de Menorval LC (2012) Study of interaction between chitosan and active carbon in view of optimising composite gels devoted to heal injuries Study of interaction between chitosan and active carbon in view of optimising composite gels devoted to heal injuries. In: EPJ Web of Conference. 29:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1051/epjconf/20122900028
Elizalde CNB, Al-Gharabli S, Kujawa J, Mavukkandy M, Hasan SW, Arafat HA (2018) Fabrication of blend polyvinylidene fluoride/chitosan membranes for enhanced flux and fouling resistance. Sep Purif Technol 190:68–76. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2017.08.053
Çay A, Miraftab M, Akçakoca EP (2014) Characterization and swelling performance of physically stabilized electrospun poly (vinyl alcohol)/chitosan nanofibres. Eur Polym J 61:253–262. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eurpolymj.2014.10.017
Kyriakopoulos G, Doulia D (2007) Morphology of polymeric resins in adsorption of organic pesticides. Fresenius Environ Bull 16:731–734
Kyriakopoulos G, Doulia D, Hourdakis A (2006) Effect of ionic strength and pH on the adsorption of selected herbicides on Amberlite. Int J Environ Anal Chem 86:207–214. https://doi.org/10.1080/03067310500247678
Kyriakopoulos G, Doulia D, Anagnostopoulos E (2005) Adsorption of pesticides on porous polymeric adsorbents. Chem Eng Sci 60:1177–1186. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ces.2004.09.080
Ghaee A, Shariaty-Niassar M, Barzin J, Ismail AF (2013) Chitosan/polyethersulfone composite nanofiltration membrane for industrial wastewater treatment. Int J Nanosci Nanotechnol 9:213–220
Cui L, Gao S, Song X, Huang L, Dong H, Liu J, Chen F, Yu S (2018) Preparation and characterization of chitosan membranes. RSC Adv 8:28433–28439. https://doi.org/10.1039/c8ra05526b
Van Der Mei HC, Bos R, Busscher HJ (1998) A reference guide to microbial cell surface hydrophobicity based on contact angles. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces 11:213–221
Rivas LA, Parro V, Moreno-paz M, Mellado RP (2000) The Bacillus subtilis 168 csn gene encodes a chitosanase with similar properties to a streptomyces enzyme. Microbiology 146:2929–2936
Wieczorek AS, Hetz SA, Kolb S (2014) Microbial responses to chitin and chitosan in oxic and anoxic agricultural soil slurries. Biogeoscience 11:3339–3352. https://doi.org/10.5194/bg-11-3339-2014
Nakashima T, Nakano Y (2005) Biodegradation characteristics of chitin and chitosan films. J Home Econ Jpn 56:889–897
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge financial supports from the Institut Pengurusan dan Pemantauan Penyelidikan, University of Malaya, Malaysia under Government Agency [PPP Grant Number, PG345-2016A].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gafri, H.F., Zuki, F.M., Aroua, M.K. et al. Enhancing the Anti-biofouling Properties of Polyethersulfone Membrane Using Chitosan-Powder Activated Carbon Composite. J Polym Environ 27, 2156–2166 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10924-019-01505-z
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10924-019-01505-z