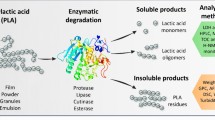
Abstract
Degradation of post-consumer PLA to lactic acid was analysed in order to assess the economic feasibility of the PLA chemical recycling process. Hydrolysis of PLA, in batch reactor, was analysed in the temperature range of 443–473 K, under autogenous pressure and a constant PLA to water ratio (equal to approximately 0.11 by weight), without the use of a catalyst. The experimental results suggest that the complete degradation of PLA can be obtained using relatively low reaction-times with the production of a mixture containing the monomer and traces of the dimer of lactic acid. The overall process was modelled using a two-step process: bulk degradation of PLA (in the solid or molten phase) with the solubilisation of low molecular weight oligomers, and their subsequent hydrolysis in water (stabilization). The model describes the trend of oligomer concentrations in the aqueous phase and PLA conversion as a function of time with both high accuracy and agreement with experimental results.






Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles and news from researchers in related subjects, suggested using machine learning.References
Holten C (1971) Lactic acid—properties and chemistry of lactic acid and derivatives. VerlagChemie, Weinheim
Crank M, Patel M, Marscheider-Weidemann F, Schleich J, Hüsing B, Angerer G (2005) Techno-economic feasibility of large-scale production of bio-based polymers in Europe. Institute for Prospective Technological Studies, Technical Report Series
Chen G, Kim H, Kim E, Yoon J (2006) Synthesis of high-molecular-weight poly(L-lactic acid) through the direct condensation polymerization of L-lactic acid in bulk state. Eur Polym J 42:468–472
Gruber P, Hall E, Kolstad J, Iwen M, Benson R, Borchardt R (1992) Patent No. US Patent 5142023
Piemonte V, Gironi F (2013) Lactic acid production by hydrolysis of poly(L-lactic acid) in the solid state in aqueous solutions: an experimental and kinetic study. J Polym Environ 21:275–279
Piemonte V, Gironi F (2013) Kinetics of hydrolytic degradation of PLA. J Polym Environ 21(2):313–318
Piemonte V, Sabatini S, Gironi F (2013) Chemical recycling of PLA: a great opportunity towards the sustainable development? J Polym Environ 21(3):640–647
Gironi F, Frattari S, Piemonte V, Chemical Recycling PLA (2016) Process optimization: PLA solubilization in organic solvents. J Polym Environ 24:328–333
Davies S, Kolstad J, Vink E (2010) The eco-profile for current Ingeo polylactide production. Ind Biotechnol 6:212–224
Brake L (1993) Patent No. US Patent 5264614
Brake L, Subramanian N (1993) Patent No. US Patent 5229528
Coszach P, Bogaert J, Willocq J (2010) Patent No. WO Patent 118954
Xiuyan S, Hui W, Xuequn Y, Fusheng L, Shitao Y, Shiwei L (2014) Hydrolysis of poly(lactic acid) into calcium lactate using ionic liquid [Bmim][OAc] for chemical recycling. Polym Degrad Stab 110:65–70
Plichta A, Lisowska P, Kundys A, Zychewicz A, Debowski M, Florjanczyk Z (2014) Chemical recycling of poly(lactic acid) via controlled degradation with protic(macro)molecules. Polym Degrad Stab 108:288–296
Tsuji H, Daimon H, Fujie K (2003) New strategy for recycling and preparation of poly(L-lactic acid): hydrolysis in the melt. Biomacromolecules 4:835–840
Mohd-Adnan A, Nishida A, Shirai Y (2008) Evaluation of kinetics parameters for poly(L-lactic acid) hydrolysis under high-pressure steam. Polym Degrad Stab 93:1053–1058
Tsuji H, Saekia T, Tsukegia T, Daimona H, Fujie K (2008) Comparative study on hydrolytic degradation and monomer recovery of poly(L-lactic acid) in the solid and in the melt. Polym Degrad Stab 93:1956–1963
Proikakis C, Mamouzelos N, Tarantili P, Andreopoulos A (2006) Swelling and hydrolytic degradation of poly(D,L-lactic acid) in aqueous solutions. Polym Degrad Stab 91:614–619
Lee S, Kim H, Han Y, Kim Y (2001) Synthesis and degradation of end-group functionalized polylactide. J Polym Sci A 39:973–985
Yagihashi M, Funazukuri T (2010) Recovery of L-lactic acid from poly(L-lactic acid) under hydrothermal conditions of dilute aqueous sodium hydroxide solution. Ind Eng Chem Res 49:1247–1251
Tisserat B, Finkenstadt V (2011) Degradation of poly(L-lactic acid) and biocomposites by alkaline medium under various temperatures. J Polym Environ 19:766–775
Henton D, Gruber P, Lunt J, Randall J (2005) Polylactic acid technology. Natural fibers, biopolymers, and biocomposites. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Gopferich A (1996) Mechanisms of polymer degradation and erosion. Biomaterials 17:103–114
Gopferich A (1997) Polymer bulk erosion. Macromolecules 30:2598–2604
Burkersrodaa F, Schedlb L, Göpferich A (2002) Why degradable polymers undergo surface or bulk erosion. Biomaterials 23:4221–4231
Codari F, Lazzari S, Soos M, Storti G, Morbidelli M, Moscatelli D (2012) Kinetics of the hydrolytic degradation of poly(lactic acid). Polym Degrad Stab 97:2460–2466
Frattari S, Gironi F, Sabia R, Villani C (2016) Equilibrium condition and stabilization kinetics of lactic acid oligomers in aqueous solutions. Can J Chem Eng. https://doi.org/10.1002/cjce.22737
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Claudio Capparucci who helped perform the experimental runs and the students who performed some experimental runs during their master thesis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cristina, A.M., Sara, F., Fausto, G. et al. Degradation of Post-consumer PLA: Hydrolysis of Polymeric Matrix and Oligomers Stabilization in Aqueous Phase. J Polym Environ 26, 4396–4404 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10924-018-1312-6
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10924-018-1312-6