Abstract
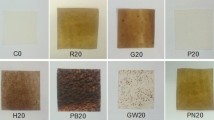
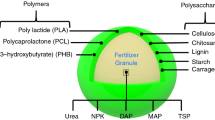
The composites consisting of poly(vinyl alcohol), horn meal, rapeseed cake, glycerol and phosphogypsum were proposed for the encapsulation of mineral fertilizers. Poly(vinyl alcohol) was used as a binder. The other components making ca. 70% of the mass of the composites were waste materials or by-products. They contain phosphorus, nitrogen, calcium, potassium and sulphur, which are useful nutrients for plants. The effect of the amount of glycerol and of the composition of the mixture of the fillers on the mechanical, sorption properties, water vapour permeability, solubility in water, dimensional stability of the composite films was studied. The addition of phosphogypsum and increase of the concentration of glycerol in the composites lead to the decrease of the tensile strength, water vapour permeability and to the increase of elongation at break and of the solubility of the composite films in water. The composites prepared were used for encapsulation of fertilizers. It was established that encapsulation resulted in the increase of the time of release of the fertilizers. In addition, encapsulation improved mechanical properties of the fertilizers. The fertilizer granules were coated with composite films and tested in the cultivation of tomato sprouts. They showed considerable positive effect on the development of the roots of the plants.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Savci S (2012) Int J Environ Sci Dev 3:77–80
Trenkel ME (2010) Slow- and controlled-release and stabilized fertilizers: an option for enhancing nutrient use efficiency in agriculture. IFA 160, Paris
Tomaszewska M, Jarosiewicz A, Karakulski K (2002) Desalination 146:319–323
Taran YuA, Pynkova TI, Taran AL (2012) Theor Found Chem Eng 48:524–553
Roshanravan B, Soltani SM, Mahdavi F, Rashid SA, Yusop MK (2015) Chem Speciat Bioavailab 26:249–256
Zhang M, Gao B, Chen J, Li Y, Creamer AE, Chen H (2014) Chem Eng J 255:107–113
Lum YH, Shaaban A, Dimin MF, Mohamad N, Hamid N, Se SM (2013) J Polym Environ 21:1083–1087
Rashidzadeh A, Olad A (2014) Carbohydr Polym 114:269–278
Zou H, Ling Y, Dang X, Yu N, Zhang Y, Zhang Y, Dong J (2015) Int J Photoenergy 2015:1–6
Rashidzadeh A, Olad A, Reyhanitabar A (2015) Polym Bull 72:2667–2684
Jacobs DF (2005) USDA Forest Service Proceedings RMRS-P-35:113–118
Azeem B, KuShaari K, Man ZB, Basit A, Thanh TH (2014) J Control Release 181:11–21
Meiczinger M, Marton GY (2010) Hung J Ind Chem Veszprem 38:175–179
Devassine M, Henry F, Guerin P, Briand X (2002) Int J Pharm 242:399–404
Yang Y, Tong Z, Geng Y, Li Y, Zhang M (2013) J Agric Food Chem 61:8166–8174
Ramaraj B, Poomalai P (2006) J Appl Polym Sci 102:3862–3867
Elizondo NJ, Sobral PJA, Menegalli FC (2009) Carbohydr Polym 75:592–598
Wu C-S (2012) Polym Degrad Stab 97:2388–2395
Babu RP, O‘Connor K, Seeram R (2013) Prog Biomater 2:1–16
Yeng CM, Husseinsyah S, Ting SS (2013) Polym Plast Technol Eng 52:1496–1502
Baek B-S, Park J-W, Lee B-H, Kim H-J (2013) J Polym Environ 21:702–709
Zulhaimi NZ, KuShaari K, Man Z (2011) World Acad Sci Eng Technol 58:395–399
Trinh TH, Shaari K, Zilati K, Basit A, Azeem B (2014) Int J Chem Eng Appl 5:58–63
Stoven AA, Mathers HM, Struge DK (2006) HortSci 41:1206–1212
Sadique Shaikh MD, Patil MA (2013) IJLPR 3:L1–5
McKittrick J, Chen P-Y, Bodde SG, Yang W, Novitskaya EE, Meyers MA (2012) JOM 64:449–468
Korniłłowicz-Kowalska T, Bohacz J (2011) Waste Manage 31:1689–1701
Vieira MGA, Silva MA, dos Santos LO, Beppu MM (2011) Eur Polym J 47:254–263
Bilck AP, Müller CMO, Olivato JB, Mali S, Grossmann MVE, Yamashita F (2015) Polímeros 25:331–335
Wang S, Ren J, Kong W, Gao C, Liu C, Peng F, Sun R (2014) Cellul 21:495–505
Saurabh CK, Gupta S, Variyar PS, Sharma A (2016) Ind Crops Prod 89:109–118
Chiellini E, Cinelli P, Imam SH, Mao L (2001) Biomacromol 2:1029–1037
Yu J-H, Wang J-L, Wu X, Zhu P-X (2008) Starch 60:257–262
De Campos A, Tonoli GHD, Marconcini JM, Mattoso LHC, Klamczynski A, Gregorski KS, Wood D, Williams T, Chiou BS, Imam SH (2013) J Polym Environ 21:1–7
Ramos ÓL, Reinas I, Silva SI, Fernandes JC, Cerqueira MA, Pereira RN, Vicente AA, Poças MF, Pintado ME, Malcata FX (2013) Food Hydrocolloids 30:110–122
Su J-F, Wang S-B, Lu X-Z, Zhang L-D, Zhang Y-Y (2010) In: Proceedings of the 17th IAPRI World conference on Packaging. China, October 12–15, Scientific Research Publishing, USA, pp 444–448
He Y, Wu Z, Tu L, Han Y, Zhang G, Li C (2015) Appl Clay Sci 109–110:68–75
Julkapli NM, Akil HM (2010) Polym Plast Technol Eng 49:944–951
Żywociński K, Gozdecka G, Korpal W (2011) Chemik 65:347–352
Mondini C, Sinicco T, Cayuela ML (2010) 19th World Congress of Soil Science, Soil Solutions for a Changing World 156–159
Santibáñez C, Varnero MT (2014) J Soil Sci Plant Nutr 14:129–138
Acknowledgements
Financial support of this research by the Research Council of Lithuania (project No MIP-066/2015) is gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Treinyte, J., Grazuleviciene, V., Paleckiene, R. et al. Biodegradable Polymer Composites as Coating Materials for Granular Fertilizers. J Polym Environ 26, 543–554 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10924-017-0973-x
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10924-017-0973-x