Abstract
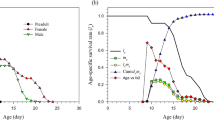
Sublethal concentrations of chemical insecticides may cause changes in some behavioral characteristics of natural enemies such as functional responses. The residual effect of three synthetic insecticides including deltamethrin, fenvalerate and azadirachtin were studied on functional response of Habrobracon hebetor Say to Ephestia kuehniella Zeller larvae. Seven host densities (2, 4, 8, 16, 32, 64 and 96) were used during a 24 h period. The resulting data were appropriately fit to Type II functional response models in all treatments: (1) control (0.0916 h−1; and T h = 0.2011 h); (2) deltamethrin (a = 0.0839 h−1; and T h = 0.3560 h); (3) fenvalerate (a = 0.0808 h−1 and T h = 0.3623 h); and (4) azadirachtin (a = 0.0900 h−1 and T h = 0.2042 h). Maximum theoretical parasitism rate (T/T h ) was 119.34 estimated for control wasps. There was no significant difference between the values of attack rates (a and a + D a ) in all treatments while the handling time was statistically affected in female wasps treated with fenvalerate. Our findings will be useful in safe application of these insecticides in pest management programmes.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abedi Z, Saber M, Gharekhani G, Mehrvar A, Mahdavi V (2012) Effects of azadirachtin, cypermethrin, methoxyfenozide and pyridalil on functional response of Habrobracon hebetor Say (Hym.: Braconidae. J Plant Prot Res 52:353–358. doi:10.2478/v10045-012-0058-8
Allahyari H, Fard PA, Nozari J (2004) Effects of host on functional response of offspring in two populations of Trissolcus grandis on the sunn pest. J Appl Entomol 128:39–43. doi:10.1046/j.1439-0418.2003.00804.x
Chen WL, Leopold RA, Harris MO (2006) Parasitism of the glassy-winged sharpshooter, Homalodisca coagulata (Homoptera: Cicadellidae): functional response and superparasitism by Gonatocerus ashmeadi (Hymenoptera: Mymaridae. Biol Control 37:119–129. doi:10.1016/j.biocontrol.2005.10.011
Chen H, Zhang H, Zhu KY, Throne JE (2012) Induction of reproductive diapause in Habrobracon hebetor (Hymenoptera: Braconidae) when reared at different photoperiods at low temperatures. Environ Entomol 41(3):697–705. doi:10.1603/EN11311
Faal-Mohammad-Ali H, Allahyari H, Saber M (2015) Sublethal effect of chlorpyriphos and fenpropathrin on functional response of Habrobracon hebetor (Hym.: Braconidae). Arch Phytopathol Plant Protect 48:288–296. doi:10.1080/03235408.2014.886411
Farrokhi S, Ashouri A, Shirazi J, Allahyari H, Huigens ME (2010) A comparative study on the functional response of Wolbachia-infected and uninfected forms of the parasitoid wasp Trichogramma brassicae. J Insect Sci 10:167. doi:10.1673/031.010.14127
Ghimire MN, Phillips TW (2010) Mass rearing of Habrobracon hebetor Say (hymenoptera: Braconidae) on larvae of the Indian meal moth, Plodia interpunctella (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae): effects of host density, parasitoid density, and rearing containers. J Stored Prod Res 46:214–220. doi:10.1016/j.jspr.2010.05.003
Holling CS (1959) The components of predation as revealed by a study of small-mammal predation of the european pine sawfly. Can Entomol 91:293–320. doi:10.4039/Ent91385-7
Jarrahi A, Safavi SA (2016) Effects of pupal treatment with Proteus® and Metarhizium anisopliae sensu lato on functional response of Habrobracon hebetor parasitizing Helicoverpa armigera in an enclosed experiment system. Biocontrol Sci Tech 26:206–216. doi:10.1080/09583157.2015.1088933
Juliano SA (2001) Non-linear curve fitting: predation and functional response curves. In: Cheiner SM, Gurven J (eds) Design and analysis of ecological experiments. Oxford University Press, New York, pp. 178–196
Luck RF (1985) Principles of arthropod predation. In: Huffaker CB, Rabb RL (eds) Ecological entomology. Wiley, New York, pp. 497–530
Luo S, Li H, Lu Y, Zhang F, Haye T, Kuhlmann U, Wu K (2014) Functional response and mutual interference of Peristenus spretus (Hymenoptera: Braconidae), a parasitoid of Apolygus lucorum (Heteroptera: Miridae). Biocontrol Sci Tech 24:247–256. doi:10.1080/09583157.2013.855703
Mahdavi V, Saber M (2013) Functional response of Habrobracon hebetor Say (Hym.: Braconidae) to mediterranean flour moth (Anagasta kuehniella Zeller),response to pesticides. J Plant Prot Res 53:399–403. doi:10.2478/jppr-2013-0059
Mahdavi V, Saber M, Rafiee-Dastjerdi H, Mehrvar A, Hassanpour M (2013) Efficacy of pesticides on the functional response on larval ectoparasitoid, Habrobracon hebetor Say (hymenoptera: Braconidae. Arch Phytopathol Plant Protect 46:841–848. doi:10.1080/03235408.2012.753182
Moezipour M, Kafil M, Allahyari H (2008) Functional response of Trichogramma brassicae at different temperatures and relative humidities. Bull Insectology 61:245–250. doi:01/2008
Pervez A, Omkar (2005) Functional responses of coccinellid predators: an illustration of a logistic approach. J Insect Sci 5:1–6. doi:10.1093/jis/5.1.5
Rafiee-Dastjerdi H, Hejazi MJ, Nouri-Ganbalani GH, Saber M (2009) Effects of some insecticides on functional response of ectoparasitoid, Habrobracon hebetor Say (Hym.: Braconidae. J Entomol 6:161–166. doi:10.3923/je.2009.161.166
Rogers D (1972) Random search and insect population models. J Anim Ecol 41:369–383. doi:10.2307/3474
Ruberson JR, Nemoto H, Hirose Y (1998) Pesticides and conservation of natural enemies in pest management. In: Barbosa P (ed) Conservation biological control Academic Press, New York, pp 207–220
Sabelis MW (1992) Predatory arthropods. In: Crawly MJ (ed) Natural enemies: the population biology of predators, parasites and diseases. Blackwell Scientific Publications, Oxford, pp. 225–264
Sakaki S, Sahragard A (2011) A new method to study the functional response of Scymnus syriacus (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae) to different densities of Aphis gossypii. J Asia Pac Entomol 14:459–462. doi:10.1016/j.aspen.2011.07.003
SAS (2003) A guide to statistical and data analysis, version 9.1. SAS Institute, Cary
Skovgård H, Nachman G (2015) Temperature-dependent functional response of Spalangia cameroni (hymenoptera: Pteromalidae), a parasitoid of Stomoxys calcitrans (Diptera: Muscidae. Environ Entomol 44(1):90–99. doi:10.1093/ee/nvu014
Stark JD, Banks JE, Acheampong S (2004) Estimating susceptibility of biological control agents to pesticides: influence of life history strategies and population structure. Biol Control 29:392–398. doi:10.1016/j.biocontrol.2003.07.003
Talebi KH, Hosseininaveh V, Ghadamyari M (2011) Ecological impacts of pesticides in agricultural ecosystem. In: Stoytcheva M (ed) Pesticides in the modern world–risks and benefits. InTech, Rijeka, pp. 143–168
Torres JB, Ruberson JR (2004) Toxicity of thiamethoxam and imidacloprid to Podisus nigrispinus (Dallas) (Heteroptera: Pentatomidae) nymphs associated to aphid and whitefly control in cotton. Neotrop Entomol 33(1):99–106. doi:10.1590/S1519-566X2004000100017
Umbanhowar J, Maron J, Harrison S (2003) Density-dependent foraging behaviors in a parasitoid lead to density-dependent parasitism of its host. Oecologia 137:123–130. doi:10.1007/s00442-003-1313-5
Yu SH, Ryoo MI, Na JH, Choi WI (2003) Effect of host density on egg dispersion and the sex ratio of progeny of Bracon hebetor (Hymenoptera: Braconidae. J Stored Prod Res 39:385–393. doi:10.1016/S0022-474X(02)00032-2
Zhong BZ, ZF X, Qin WQ (2009) Influence of temperature on functional response of Habrobracon hebetor (Say) (Hymenoptera: Braconidae) attacking larvae of Plodia interpunctella (Hubner) (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae). Acta. Entomol Sinica 52:395–400
Acknowledgments
This study received financial support from Urmia University, Urmia, Iran, which is greatly appreciated.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jarrahi, A., Safavi, S.A. Parasitism Rate of Habrobracon hebetor to Ephestia kuehniella Larvae: Residual Effect of Deltamethrin, Fenvalerate and Azadirachtin. J Insect Behav 29, 548–556 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10905-016-9583-z
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10905-016-9583-z