Abstract
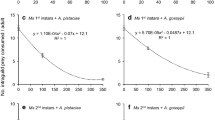
Cannibalism is an important factor influencing both immature survival and adult reproductive success in aphidophagous lady beetles. This study employed three series of laboratory experiments to characterize life stage-specific cannibalism responses of Coccinella undecimpunctata L. and Cydonia vicina nilotica Mulsant to 1) different conspecific densities, with and without prey, 2) other life stages, and 3) various densities of prey, Myzus persicae Sulzer. All larval instars of both species cannibalized more in the absence of prey than in its presence at all conspecific densities, but in general, cannibalism increased with conspecific density only in the absence of prey, and more strongly for third and fourth instar C. undecimpunctata than for their C. vicina nilotica counterparts. Adults contributed the most cannibalism of any life stage, and eggs were the most vulnerable. In addition to cannibalizing their own and earlier instars, second and third instar C. undecimpunctata sometimes cannibalized third and fourth instars, respectively, and fourth instars occasionally ate pupae. Larvae of C. vicina nilotica were only preyed upon by the same or later stages and pupae, by adults, not fourth instars. A relative vulnerability index was calculated for each life stage based on its net vulnerability to cannibalism by all life stages and plotting these indices revealed species-specific patterns of diminishing vulnerability to cannibalism as a function of life stage. Relative species vulnerability to cannibalism, considering all life stages, was higher for C. undecimpunctata (0.55) than for C. vicina nilotica (0.45). Finally, linear regression was used to characterize the change in propensity for cannibalism between same-instar larval pairs as a function of prey density, which enabled determination of a theoretical upper prey threshold for each larval instar, i.e., the prey density beyond which no cannibalism would be expected. In both species, regressions for third and fourth instars did not intercept the X-axis, suggesting that some cannibalism by these stages was inevitable within the range of prey densities tested.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agarwala BK, Dixon AFG (1992) Laboratory study of cannibalism and interspecific predation in ladybirds. Ecol Entomol 17:303–309
Agarwala BK, Dixon AG (1993) Kin recognition: egg and larval cannibalism in Adalia bipunctata (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae). Eur J Entomol 90:45–50
Alabi T, Michaud JP, Arnaud L, Haubruge E (2008) A comparative study of cannibalism and predation in seven species of flour beetle. Ecol Entomol 33:716–726
Al-Zubaidi FS, Capinera JL (1983) Application of different nitrogen levels to the host plant and cannibalistic behaviour of beet armyworm, Spodoptera exigua (Hubner) (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). Environ Entomol 12:1687–1689
Brown HD (1972) The behaviour of newly hatched coccinellid larvae (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae). J Entomol Soc South Afr 35:149–157
Claessen D, de Roos AM, Persson L (2003) Population dynamic theory of size dependent cannibalism. Proc R Soc Lond 271:333–340
Cottrell TE (2004) Suitability of exotic and native lady beetle eggs (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae) for development of lady beetle larvae. Biol Control 31:362–371
Cottrell TE (2005) Predation and cannibalism of lady beetle eggs by adult lady beetles. Biol Control 34:159–164
Cottrell TE, Yeargan KV (1998a) Effect of pollen on Coleomegilla maculata (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae) population density, predation, and cannibalism in sweet corn. Environ Entomol 27:1402–1410
Cottrell TE, Yeargan KV (1998b) Intraguild predation between an introduced lady beetle, Harmonia axyridis (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae), and a native lady beetle, Coleomegilla maculata (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae). J Kansas Entomol Soc 71:159–163
Dickinson JL (1992) Egg cannibalism by larvae and adults of the milkweed leaf beetle (Labidomera clivicollis, Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae). Ecol Entomol 17:209–218
Dixon AFG (2000) Insect predator-prey dynamics: ladybird beetles and biological control. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Doumbia M, Hemptinne JL, Dixon AFG (1998) Assessment of patch quality by ladybirds: role of larval tracks. Oecologia 113:197–202
Elgar MA, Crespi BJ (1992) Cannibalism: ecology and evolution among diverse taxa. Oxford University Press, Oxford
Faria LDB, Trinca LA, Godoy WAC (2004) Cannibalistic behavior and functional response in Chrysomya albiceps (Diptera: Calliphoridae). J Insect Behav 17:251–261
Félix S, Soares AO (2004) Intraguild predation between the aphidophagous ladybird beetles Harmonia axyridis and Coccinella undecimpunctata (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae): the role of body weight. Eur J Entomol 101:237–242
Ferrer A, Corbani AC, Dixon AFG, Hemptinne JL (2011) Egg dumping by predatory insects. Physiol Entomol 36:290–293
Fox LR (1975) Cannibalism in natural populations. Annu Rev Ecol Syst 6:87–106
Hart DD (1987) Processes and patterns of competition in larval black flies. In: Kim KC, Merritt RW (eds) Black flies – ecology, population management, and annotated world list. Pennsylvania State University, pp 108–129
Hatchett JH, Daugherty DM, Robbins JC, Barry RM, Houser EC (1975) Biology in Missouri of Dectes texanus, a new pest of soybean. Ann Entomol Soc Am 68:209–213
Hemptinne JL, Lognay G, Gauthier C, Dixon AFG (2000) Role of surface chemical signals in egg cannibalism and intraguild predation in ladybirds (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae). Chemoecology 10:123–128
Ho FK, Dawson PS (1966) Egg cannibalism by Tribolium larvae. Ecology 45:318–322
Hodek I, Evans EW (2012) Food relationships. In: Hodek I, Honěk A (eds) Ecology and Behaviour of the Ladybird Beetles (Coccinellidae). Blackwell Publishing Ltd, UK, pp 141–274
Hofmann A, Kia-Hofmann T (2012) Cannibalism of unhatched siblings by larvae of burnet moths (Zygaena Fabricius, 1775), with notes on oophagy and the behaviour of newly hatched larvae (Lepidoptera: Zygaenidae). Entomol Gaz 63:3–36
Joseph SB, Snyder WE, Moore AJ (1999) Larvae of the ladybug Harmonia axyridis use endogenous cues to avoid cannibalizing relatives. J Evol Biol 12:792–797
Martini X, Haccou P, Olivieri I, Hemptinne JL (2009) Evolution of cannibalism and female’s response to oviposition-deterring pheromone in aphidophagous predators. J Anim Ecol 78:964–972
Michaud JP (2002) Invasion of the Florida citrus ecosystem by Harmonia axyridis (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae) and asymmetric competition with a native ladybeetle, Cycloneda sanguinea. Environ Entomol 31:827–835
Michaud JP (2003) A comparative study of larval cannibalism in three species of ladybird. Ecol Entomol 28:92–101
Michaud JP, Belliure B (2000) Consequences of foundress aggregation in the brown citrus aphid, Toxoptera citricida. Ecol Entomol 25:307–314
Michaud JP, Grant AK (2003) Intraguild predation among ladybeetles and a green lacewing: do the larval spines of Curinus coeruleus (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae) serve a defensive function? Bull Entomol Res 93:499–505
Michaud JP, Grant AK (2004) Adaptive significance of sibling egg cannibalism in Coccinellidae: comparative evidence from three species. Ann Entomol Soc Am 97:710–719
Michaud JP, Jyoti JL (2007) Repellency of conspecific and heterospecific larval residues to ovipositing Hippodamia convergens Guerin (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae) foraging for greenbugs on sorghum plants. Eur J Entomol 104:399–405
Mills MJ (1982) Voracity, cannibalism and coccinellid predation. Ann Appl Biol 101:144–148
Nakakita H (1982) Effect of larval density on pupation of Tribolium freemani Hinton (Coleoptera: Tenebrionidae). Appl Entomol Zool 17:269–276
Nakamura K, Ohgushi T (1981) Studies on the population dynamics of a thistle-feeding lady beetle, Henosepilachna pustulosa (Kono) in a cool temperate climax forest II. Life tables, key-factor analysis, and detection of regulatory mechanisms. Res Popul Biol 23:210–231
Nishimura K, Isoda Y (2004) Evolution of cannibalism: referring to costs of cannibalism. J Theor Biol 226:291–300
Omkar, Pervez A, Gupta AK (2004) Role of surface chemicals in egg cannibalism and intraguild predation by neonates of two aphidophagous ladybirds, Propylea dissecta and Coccinella transversalis. J Appl Entomol 128:691–695
Osawa N (1989) Sibling and non-sibling cannibalism by larvae of a lady beetle Harmonia axyridis Pallas (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae) in the field. Res Popul Ecol 31:153–160
Osawa N (1992) Sibling cannibalism in the lady beetle Harmonia axyridis: fitness consequences for mother and offspring. Res Popul Ecol 34:45–55
Osawa N (2002) Sex-dependent effects of sibling cannibalism on life history traits of the ladybird beetle Harmonia axyridis (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae). Biol J Linn Soc 76:349–360
Osawa N (2011) Ecology of Harmonia axyridis in natural habitats within its native range. BioControl 56:613–621
Parajulee MN, Philips TW (1995) Survivorship and cannibalism in Lyctocoris campestris (Hemiptera: Anthocoridae): effects of density, prey availability, and temperature. J Entomol Sci 30:1–8
Perry JC, Roitberg BD (2005) Ladybird mothers mitigate offspring starvation risk by laying trophic eggs. Behav Ecol Sociobiol 58:578–586
Persson L, De Roos AM, Claessen D, Byström P, Lövgren J, Sjögren S (2003) Gigantic cannibals driving whole lake trophic cascades. Proc Natl Acad Sci 100:4035–4039
Pervez A, Gupta AK, Omkar (2006) Larval cannibalism in aphidophagous ladybirds: influencing factors, benefits and costs. Biol Control 38:307–313
Pfennig DW, Ho SG, Hoffman EA (1998) Pathogen transmission as a selective force against cannibalism. Anim Behav 55:1255–1261
Pienkowski RL (1965) The incidence and effect of egg cannibalism in first-instar Coleomegilla maculata lengi (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae). Ann Entomol Soc Am 58:150–153
Polis GA (1981) The evolution and dynamics of intraspecific predation. Annu Rev Ecol Syst 12:225–251
Ponsonby DJ, Copland MJW (1998) Environmental influences on fecundity, egg viability and egg cannibalism in the scale insect predator, Chilocorus nigritus. BioControl 43:39–52
Rudolf VHW (2008) The impact of cannibalism in the prey on predator prey dynamics. Ecology 89:3116–3127
Ruzicka Z (2003) Perception of oviposition-deterring larval tracks in aphidophagous coccinellids Cycloneda limbifer and Ceratomegilla undecimnotata (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae). Eur J Entomol 100:345–350
Santi F, Maini S (2007) Ladybird mothers eating their eggs: is it cannibalism? Bull Insect 60:89–91
Sato S, Yasuda H, Evans EW, Dixon AFG (2009) Vulnerability of larvae of two species of aphidophagous ladybirds, Adalia bipunctata Linnaeus and Harmonia axyridis Pallas, to cannibalism and intraguild predation. Entomol Sci 12:111–115
Schellhorn NA, Andow D (1999) Mortality of coccinellid (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae) larvae and pupae when prey become scarce. Environ Entomol 28:1092–1100
SigmaPlot (2009) SigmaPlot version 11 from Systat Software, Inc., San Jose California USA, www.sigmaplot.com
Sloggett JJ, Splichal LK, Kajita Y, Haynes KF, Lorenz MW (2013) Ladybird egg cannibalism and intraguild predation by Harmonia axyridis: the effects of egg age. IOBC/WPRS Bull 94:33–40
Sonleitner FJ, Guthrie PJ (1991) Factors affecting oviposition rate in the flour beetle Tribolium castaneum and the origin of the population regulation mechanism. Res Popul Ecol 33:1–11
Story RN, Robinson WH (1979) Biological control potential of Taphrocerus schaefferi (Coleoptera: Buprestidae), a leaf miner of yellow nut sedge, Cyperus esculentus. Environ Entomol 8:1088–1091
Takizawa T, Snyder WE (2011) Cannibalism and intraguild predation of eggs within a diverse predator assemblage. Environ Entomol 40:8–14
Tarpley MD, Breden F, Chippendale GM (1993) Genetic control of geographical variation for cannibalism in the southwestern corn borer, Diatraea grandiosella. Entomol Exp Appl 66:145–152
Ware RL, Ramon-Portugal F, Magro A, Ducamp C, Hemptinne JL, Majerus MEN (2008) Chemical protection of Calvia quatuordecimguttata eggs against intraguild predation by the invasive ladybird Harmonia axyridis. BioControl 53:189–200
Yasuda H, Kikuchi T, Kindlmann P, Sato S (2001) Relationships between attack and escape rates, cannibalism, and intraguild predation in larvae of two predatory ladybirds. J Insect Behav 14:373–383
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to thank A.A. Abdel-Hady for rearing the aphids. This is contribution no. 15-207J of the Kansas Agricultural Experiment Station.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bayoumy, M.H., Michaud, J.P. Cannibalism in Two Subtropical Lady Beetles (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae) as a Function of Density, Life Stage, and Food Supply. J Insect Behav 28, 387–402 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10905-015-9510-8
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10905-015-9510-8