Abstract
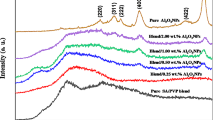
Copper dioxide (CuO) nanoparticles and Multiwall carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs) filled poly(vinyl alcohol) (PVA) and poly(vinyl pyrrolidone) (PVP) blend matrix (50/50 wt%) based polymer nanocomposites (PNCs) (i.e., PVA/PVP:(15-x)CuO(x)MWCNTs for x = 0,1,5,7.5, 10,14, and 15wt%) have been prepared employing the solution-cast method. The morphologies of these PNCs are semicrystalline, according to an X-ray diffraction investigation. The FTIR, SEM, and AFM measurements of PNCs were used to investigate the development of the miscible mix, polymer-polymer and polymer–nanoparticle interactions, and the influence of CuO and MWCNTs nanofillers on the morphology aspects on the main chain of PVA/PVP blend. The nanofiller dispersion signposting for x = 14 wt% nanoloading in the PVA–PVP blend matrix significantly enhances the crystalline phase, diminishing the optical energy gap to 2.31 eV. The DC conductivity values augment with the upsurge in nanofiller level for maximum x = 14 wt%. The dielectric and electrical characteristics of these PNCs are investigated for an applied frequency range from 1 kHz to 1 MHz. The enhancement in the nanofiller level upto x = 14 wt% in the PVA/PVP matrix leads to the development of percolating network through the PNCs. These factors boost the dielectric permittivity values substantially, owing to the decrease in the nano-confinement phenomenon. The rise in applied frequency reduces dielectric permittivity and impedance values and enhances ac electrical conductivity. These PNCs having good dielectric and electrical characteristics can be used as frequency tunable nanodielectric material in electronic devices.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
M.M. Demir, M. Memesa, P. Castignolles, G. Wegner, PMMA/zinc oxide nanocomposites prepared by in-situ bulk polymerization. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 27(10), 763–770 (2006)
E.M. Abdelrazek, I.S. Elashmawi, A. El-Khodary, A. Yassin, Structural, optical, thermal and electrical studies on PVA/PVP blends filled with lithium bromide. Curr. Appl. Phys. 10, 607–613 (2010)
M. Todd Alam, J.U. Otaigbe, D. Rhoades, G.P. Holland, B.R. Cherry, P.G. Kotula, Nanostructured polymer blends: synthesis and structure. Polymer 46(26), 12468–12479 (2005)
R. Baskaran, S. Selvasekarapandian, N. Kuwata, J. Kawamura, T. Hattori, Conductivity and thermal studies of blend polymer electrolytes based on PVAc–PMMA. Solid State Ionics 177, 2679–2682 (2006)
K.K. Kumar, M. Ravi, Y. Pavani, S. Bhavani, A.K. Sharma, V.V.R. Narasimha Rao, Investigations on PEO/PVP/NaBr complexed polymer blend electrolytes for electrochemical cell applications. J. Membr. Sci. 454, 200–211 (2014)
N.B. Rithin Kumar, S. Acharya, A. Alhadhrami, B.M. Prasanna, S.C. Gurumurthy, Role of TiO2/ZnO nanofillers in modifying the properties PMMA nanocomposites for optical device applications. Iran. J. Sci. Technol. Trans. Sci. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40995-021-01183-4
K. Phiwdang, S. Suphankij, W. Mekprasart, W. Pecharapa, Synthesis of CuO nanoparticles by precipitation method using different precursors. Energy Proc. 34, 740–745 (2013)
N. Rajeswari, S. Selvasekarapandian, C. Sanjeeviraja, J. Kawamura, S. Asath Bahadur, A study on polymer blend electrolyte based on PVA/PVP with proton salt. Polym. Bull. 71, 1061–1080 (2014)
C.V. Subba Reddy, A.K. Sharma, V.V.R. Narasimha Rao, Electrical and optical properties of a polyblend electrolyte. Polymer 47, 1318–1323 (2006)
Z.D. Dai, L. Ansaloni, D.L. Gin, R.D. Noble, L.Y. Deng, J. Membr. Sci. 523, 551–560 (2017)
B. Yalagala, S. Khandelwal, J. Deepika, S. Badhulika, Wirelessly destructible MgO-PVP-graphene composite based flexible transient memristor for security applications. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 104, 104673 (2019)
F.M. Ali, R.M. Kershi, M.A. Sayed, Y.M. AbouDeif, Evaluation of structural and optical properties of Ce3 + ions doped (PVA/PVP) composite films for new organic semiconductors. Physica B Condens. Matter 538, 160–166 (2018)
S. Mahendia, G. Kandhol, U.P. Deshpande, S. Kumar, Determination of glass transition temperature of reduced graphene oxide-poly(vinyl alcohol) composites using temperature-dependent Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy. J. Mol. Struct. 1111, 46–54 (2016)
R.F. Bhajantri, V. Ravindrachary, B. Poojary, A. Harisha, V. Crasta, Studies on fluorescent PVA + PVP + MPDMAPP composite films. Polym. Eng. Sci. 49(5), 903–909 (2009)
A. Azam, A.S. Ahmed, M. Oves, M.S. Khan, A. Memic, Size-dependent antimicrobial properties of CuO nanoparticles against gram-positive and -negative bacterial strains. Int. J. Nanomed. 7, 3527–3535 (2012)
X. Peng, S.S. Wong, Functional Covalent Chemistry of Carbon Nanotube Surfaces. Adv. Mater. 21(6), 625–642 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.200801464
R. Jeyaraman, J. Kadarkaraithangam, M. Arumugam, R. Govindasamy, A. Abdul.Synthesis and antimicrobial activity of copper nanoparticles. Mater. Lett. 71, 114–116 (2011)
Z. Liu, L. Jiao, Y. Yao, X. Xian, J. Zhang, Aligned, ultralong single-walled carbon nanotubes: from synthesis, sorting, to electronic devices. Adv. Mater. 22(21), 2285–2310 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.200904167
S.H. Park, W.J. Lee, Hierarchically mesoporous CuO/carbon nanofiber coaxial shell-core nanowires for lithium ion batteries. Sci. Rep. 5, 9754 (2015)
M. Sahooli, S. Sabbaghi, R. Saboori, Synthesis and characterization of mono sized CuO nanoparticles. Mater. Lett. 81, 169–172 (2012)
H.M. Zidan, J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 88, 1115–1120 (2003)
N.B. Rithin Kumar, B.M. Vincent Crasta, Enhancement of optical, mechanical and micro structural properties in nanocomposite films of PVA doped with WO3 nanoparticles. Int. J. Struct. Integr. 6(3), 338–354 (2015)
G.N. Hemanth Kumar, J. Lakshmana Rao, N.O. Gopal, K.V.C. Narasimhulu, R.P.S. Chakradhar, A. Varada Rajulu, Spectroscopic investigation Mn+2 ions doped polyvinyl alcohol films. Polymer 45, 5407–5415 (2004)
E.M. Abdelrazek, A.M. Abdelghany, A.H. Oraby, G.M. Asnag, Investigation of mixed filler effect on optical and structural properties of PEMA films. Int. J. Eng. Technol. 12, 98–102 (2012)
I. Saini, J. Rozra, N. Chandak, S. Aggarwal, P.K. Sharma, A. Sharma, Tailoring of electrical, optical and structural properties of PVA by adding Ag nanoparticles. Mater. Chem. Phys. 139, 802–810 (2013)
E.A. Davis, N.F. Mott, Conduction in non-crystalline systems. V. Conductivity, optical absorption and photoconductivity in amorphous semiconductors. Philos. Mag. 22, 0903–0922 (1970)
N.F. Mott, Conduction in non-crystalline systems: IV. Anderson localization in a disordered lattice. Philos. Mag. 22, 7–29 (1970)
B.A. Collins, J.E. Cochran, H. Yan, E. Gann, C. Hub, R. Fink, C. Wang, T. Schuettfort, C.R. McNeill, M.L. Chabinyc, H. Ade, Polarized X-ray scattering reveals non-crystalline orientational ordering in organic films. Nat. Mater. 11, 536–543 (2012)
R. Noriega, J. Rivnay, K. Vandewal, F.P. Koch, N. Stingelin, P. Smith, M.F. Toney, A. Salleo, A general relationship between disorder, aggregation and charge transport in conjugated polymers. Nat. Mater. 12, 1038–1044 (2013)
S.D. Kang, G.J. Snyder, Charge-transport model for conducting polymers. Nat. Mater. 16, 252–257 (2017)
S.N. Patel, A.M. Glaudell, K.A. Peterson, E.M. Thomas, K.A. O’Hara, E. Lim, M.L. Chabinyc, Morphology controls the thermoelectric power factor of a doped semiconducting polymer. Sci. Adv. 3, e1700434 (2017)
H.-S. Kim, H.-S. Yang, H.-J. Kim, H.-J. Park, J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 76, 395–404 (2004)
G. Zuo, X. Liu, M. Fahlman, M. Kemerink, High seebeck coefficient in mixtures of conjugated polymers. Adv. Funct. Mater. 28, 1703280 (2018)
A.W. Coats, J.P. Redfern, Nature 201, 68–69 (1964)
A. Broido, J. Polym. Sci. A 2(7), 1761–1773 (1969)
B.G. Shetty, N.B.V. Crasta, R. Kumar, K. Rajesh, R. Bairy, P.S. Patil, Promising PVA/TiO2, CuO filled nanocomposites for electrical and third order nonlinear optical applications. Opt. Mater. 95, 109218 (2019)
E.S. Mora, E.G. Barojas, E.R. Rojas, R.S. Gonzalez, Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 91, 1412–1415 (2007)
M. Mazzera, M. Zha, D. Calestani, A. Zappettini, L. Lazzarini, G. Salviati, L. Zanotti, Nanotechnology 18, 355707 (2007)
N.B. Rithin Kumar, V. Crasta, B.M. Praveen, Dielectric and electric conductivity studies of PVA (Mowiol 10-98) doped with MWCNTs and WO3 nanocomposites films. Mater. Res. Express 3(5), 055012 (2016)
D. Mardare, G.I. Rusu, Ccomparison of the dielectric properties for doped and undoped TiO2 thin films. J. Optoelectron. Adv. Mater. 6, 333–336 (2004)
V. Rao, P.V. Ashokan, M.H. Shridhar, Studies of dielectric relaxation and a.c. conductivity in cellulose acetate hydrogen phthalate-poly (methyl methacrylate) blends. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 281, 213–220 (2000)
Acknowledgements
The author is thankful to University of Jeddah, Saudi Arabia.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The author declares no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Alzahrani, H.A.H. CuO and MWCNTs Nanoparticles Filled PVA–PVP Nanocomposites: Morphological, Optical, Thermal, Dielectric, and Electrical Characteristics. J Inorg Organomet Polym 32, 1913–1923 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-022-02233-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-022-02233-z