Abstract
A novel reaction-based fluorescent probe 1 for Hg2+ was designed and synthesized. 1 was almost nonfluoresent due to inhibition of the ESIPT process between hydroxy group and imid carbonyl oxygen by diphenylphosphinothioate group. After reacting with Hg2+, the fluorescence intensity of 1 exhibited significant enhancement owing to recovery of the ESIPT process via Hg2+-promoted desulfurization-hydrolysis of the diphenylphosphinothioate moiety and cleavage of the P-O bond. 1 not only showed rapid response, high sensitivity, excellent selectivity for Hg2+ over other metal ions, but also could detect Hg2+ with large Stokes shift (165 nm), which was attributed to the ESIPT process. Moreover, the reaction mechanism was fully validated by absorption spectra, fluorescence spectra, fluorescence color as well as ESI–MS analysis.
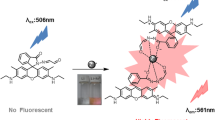
Graphical Abstract
1 is the reaction-based ESIPT fluorescent probe for the detection of Hg2+ with large Stokes shift, rapid response, high sensitivity and selectivity.









Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of Data and Material
The data generated and analyzed will be made available upon reasonable request from the corresponding author.
References
Yang L, Zhang Y, Wang F, Luo Z, Guo S, Strähle U (2020) Toxicity of mercury: Molecular evidence. Chemosphere 245:125586
Rice KM, Walker EM Jr, Wu M, Gillette C, Blough ER (2014) Environmental mercury and its toxic effects. J Prev Med Public Health 47:74–83
Bjørklund G, Dadar M, Mutter J, Aaseth J (2017) The toxicology of mercury: Current research and emerging trends. Environ Res 159:545–554
Clifton JC II (2007) Mercury exposure and public health. Pediatr Clin North Am 54(237):e1-237.e45
Bernhoft RA (2012) Mercury toxicity and treatment: A review of the literature. J Environ Public Health 2012:460508
Raj D, Maiti SK (2019) Sources, toxicity, and remediation of mercury: An essence review. Environ Monit Assess 191:566–588
Gibb H, O’Leary KG (2014) Mercury exposure and health impacts among individuals in the artisanal and small-scale gold mining community: A comprehensive review. Environ Health Perspect 122:667–672
Driscoll CT, Mason RP, Chan HM, Jacob DJ, Pirrone N (2013) Mercury as a global pollutant: Sources, pathways, and effects. Environ Sci Technol 47:4967–4983
Harris HH, Pickering IJ, George GN (2003) The chemical form of mercury in fish. Science 301:1203
Erdemir E, Suna G, Gunduz S, Şahin M, Eğlence-Bakır S, Karakuş E (2022) Rapid, ultrasensitive, highly selective detection of toxic Hg(II) ions in seabass, swordfish and water samples. Food Chem 371:131309
Ding C, Chen J, Zhu F, Chai L, Lin Z, Zhang K, Shi Y (2022) Biological toxicity of heavy metal(loid)s in natural environments: From microbes to humans. Front Environ Sci 10:920957
Li WC, Tse HF (2015) Health risk and significance of mercury in the environment. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:192–201
Bhan A, Sarkar NN (2005) Mercury in the environment: Effect on health and reproduction. Rev Environ Health 20:39–56
Peng S, Hajela RK, Atchison WD (2002) Effects of methylmercury on human neuronal L-type calcium channels transiently expressed in human embryonic kidney cells (HEK-293). J Pharmacol Exp Ther 302:424–432
Azevedo BF, Furieri LB, Peçanha FM, Wiggers GA, Vassallo PF, Simões MR, Fiorim J, de Batista PR, Fioresi M, Rossoni L, Stefanon I, Alonso MJ, Salaices M, Vassallo DV (2012) Toxic effects of mercury on the cardiovascular and central nervous systems. J Biomed Biotechnol 2012:949048
D’Itri FM (1991) Mercury contamination-what we have learned since Minamata. Environ Monit Assess 19:165–182
Fujimura M, Usuki F (2022) Cellular conditions responsible for methylmercury-mediated neurotoxicity. Int J Mol Sci 23:7218
Souza JP, Cerveira C, Miceli TM, Moraes DP, Mesko MF, Pereira JSF (2020) Evaluation of sample preparation methods for cereal digestion for subsequent As, Cd, Hg and Pb determination by AAS-based techniques. Food Chem 321:126715
Liu J-L, Han Q, Hu E-Y, Yang C, Yin M-M (2023) Determination of trace mercury in water samples by cloud point extraction coupled with atomic fluorescence spectrometry. J Anal Chem 78:303–309
Shih TT, Chen JY, Luo YT, Lin CH, Liu YH, Su YA, Chao PC, Sun YC (2019) Development of a titanium dioxide-assisted preconcentration/on-site vapor-generation chip hyphenated with inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry for online determination of mercuric ions in urine samples. Anal Chim Acta 1063:82–90
Shoaee H, Roshdi M, Khanlarzadeh N, Beiraghi A (2012) Simultaneous preconcentration of copper and mercury in water samples by cloud point extraction and their determination by inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectrometry. Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc 98:70–75
Hellings J, Adeloju SB, Verheyen TV (2013) Rapid determination of ultra-trace concentrations of mercury in plants and soils by cold vapour inductively coupled plasma-optical emission spectrometry. Microchem J 111:62–66
Liu KX, Pan MF, Zhang ZW, Hong LP, Xie XQ, Yang JY, Wang S, Wang ZJ, Song Y, Wang S (2022) Electrochemical sensor applying ZrO2/nitrogen-doped three-dimensional porous carbon nanocomposite for efficient detection of ultra-trace Hg2+ ions. Anal Chim Acta 1231:340392
Hassan MM, Ahmad W, Zareef M, Rong Y, Xu Y, Jiao T, He P, Li H, Chen Q (2021) Rapid detection of mercury in food via rhodamine 6G signal using surface-enhanced Raman scattering coupled multivariate calibration. Food Chem 358:129844
George GN, Singh SP, Myers GJ, Watson GE, Pickering IJ (2010) The chemical forms of mercury in human hair: A study using X-ray absorption spectroscopy. J Biol Inorg Chem 15:709–715
Kim HN, Ren WX, Kim JS, Yoon J (2012) Fluorescent and colorimetric sensors for detection of lead, cadmium, and mercury ions. Chem Soc Rev 41:3210–3244
Yuan X, Leng T-H, Guo Z-Q, Wang C-Y, Li J-Z, Yang W-W, Zhu W-H (2019) A FRET-based dual-channel turn-on fluorescence probe for the detection of Hg2+ in living cells. Dyes Pigments 161:403–410
Sada PK, Bar A, Jassal AK, Singh AK, Singh L, Rai A (2023) A dual channel rhodamine appended smart probe for selective recognition of Cu2+ and Hg2+ via “turn on” optical readout. Anal Chim Acta 1263:341299
Duarte F, Dobrikov G, Kurutos A, Santos HM, Fernández-Lodeiro J, Capelo-Martinez JL, Oliveira E, Lodeiro C (2023) Enhancing water sensing via aggregation-induced emission (AIE) and solvatofluorochromic studies using two new dansyl derivatives containing a disulfide bound: Pollutant metal ions detection and preparation of water-soluble fluorescent polymeric particles. Dyes Pigments 218:111428
Loredo A, Wang L, Wang S, Xiao H (2021) Single-atom switching as a general approach to designing colorimetric and fluorogenic probes for mercury ions. Dyes Pigments 186:109014
Li M, Li R, Chen X, Liu J, Shao Y, Xu Z, Zhang W (2022) An activatable near-infrared hemicyanine-based probe for selective detection and imaging of Hg2+ in living cells and animals. Analyst 147:3065–3071
Gu J, Zhang F, Zheng Z, Li X, Deng R, Zhou Z, Ma L, Liu W, Wang Q (2021) Establishment of a new molecular model for mercury determination verified by single crystal X-ray diffraction, spectroscopic analysis and biological potentials. Chinese Chem Lett 32:87–91
Chen L, Park SJ, Wu D, Kim HM, Yoon J (2019) A two-photon fluorescent probe for colorimetric and ratiometric monitoring of mercury in live cells and tissues. Chem Commun 55:1766–1769
Gong J, Liu C, Jiao X, He S, Zhao L, Zeng X (2020) A novel near-infrared fluorescent probe with an improved Stokes shift for specific detection of Hg2+ in mitochondria. Org Biomol Chem 18:5238–5244
Chen Y, Zhang W, Cai Y, Kwok RTK, Hu Y, Lam JWY, Gu X, He Z, Zhao Z, Zheng X, Chen B, Gui C, Tang BZ (2017) AIEgens for dark through-bond energy transfer: Design, synthesis, theoretical study and application in ratiometric Hg2+ sensing. Chem Sci 8:2047–2055
Zhao J, Zhang J, Hu B, Gao C, Li Z, Sun Z, You J (2023) A FRET-based ratiometric fluorescent probe for Hg2+ detection in aqueous solution and bioimaging in multiple samples. Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc 286:121965
Liu L, Ma J, Pan J, Li D, Wang H, Yang H (2021) The preparation of novel triphenylamine-based AIE-effect fluorescent probe for selectively detecting mercury(II) ion in aqueous solution. New J Chem 45:5049–5059
Santra M, Roy B, Ahn KH (2011) A “reactive” ratiometric fluorescent probe for mercury species. Org Lett 13:3422–3425
Li L, Ouyang H, Long Z, Zhang Q, Jiang Y, Cai M, Xiong S, Peng S, Xu G, He Q (2023) A triphenylamine-based fluorescent probe with phenylboronic acid for highly selective detection of Hg2+ and CH3Hg+ in groundwater. Org Biomol Chem 21:5560–5566
Subedi S, Neupane LN, Mehta PK, Lee K-H (2021) Ratiometric fluorescent detection of Hg(II) by amino-acid based fluorescent chemodosimeter using irreversible reaction of phenylboronic acid with mercury species. Dyes Pigments 191:109374
Choudhary NK, Mittapelli LL, Roy PK, Das G, Mandal M, Gore KR (2023) Vinyl substituted triphenylamine based turn-off fluorescent probe for selective and sensitive detection of mercury (II) in water and live cells. Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc 285:121887
Chen J, Tao J, Yu H-F, Ma C-P, Tan F, Wang X-C (2023) Highly selective chemosensor for the sensitive detection of Hg2+ in aqueous media and its cell imaging application. Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc 296:122648
He L, Li Q, Zhang Y, Huang K, Du B, Liang L (2023) A naphthalimide functionalized fluoran with AIE effect for ratiometric sensing Hg2+ and cell imaging application. Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc 296:122672
Tang B, Ding B, Xu K, Tong L (2009) Use of selenium to detect mercury in water and cells: An enhancement of the sensitivity and specificity of a seleno fluorescent probe. Chem Eur J 15:3147–3151
Nan X, Huyan Y, Li H, Sun S, Xu Y (2021) Reaction-based fluorescent probes for Hg2+, Cu2+ and Fe3+/Fe2+. Coord Chem Rev 426:213580
Yang X, Yuan Z, Lu W, Yang C, Wang M, Tripathi R, Fultz Z, Tan C, Wang B (2023) De novo construction of fluorophores via CO insertion-initiated lactamization: A chemical strategy toward highly sensitive and highly selective turn-on fluorescent probes for carbon monoxide. J Am Chem Soc 145:78–88
Li Z, Jia X, Zhang P, Guo Z, Zhao H, Li X, Wei C (2021) A hepatocyte-specific fluorescent probe for imaging endogenous carbon monoxide release in vitro and in vivo. Sens Actuators B Chem 344:130177
Shao S, Chen B, Cheng J, Wang C, Zhang Y, Shao L, Hu Y, Han Y, Han F, Li X (2017) A fluorogenic probe for imaging protein S-nitrosylation in live cells. Biosens Bioelectron 94:162–168
Shen Y, Zhang X, Wu Y, Zhang Y, Liu X, Chen Y, Li H, Zhong Y (2018) A lysosome targetable fluorescent probe for palladium species detection base on an ESIPT phthalimide derivative. Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc 205:66–71
Liu X, Liu X, Shen Y, Gu B (2020) A simple water-soluble ESIPT fluorescent probe for fluoride ion with large stokes shift in living cells. ACS Omega 5:21684–21688
Jain N, Sonawane PM, Liu H, Roychaudhury A, Lee Y, An J, Kim D, Kim D, Kim Y, Kim Y-C, Cho K-B, Park H-S, Kim C-H, Churchill DG (2023) “Lighting up” fluoride: Cellular imaging and zebrafish model interrogations using a simple ESIPT-based mycophenolic acid precursor-based probe. Analyst 148:2609–2615
Wu Y, Li Z, Shen Y (2019) A novel ESIPT phthalimide-based fluorescent probe for quantitative detection of H2O2. ACS Omega 4:16242–16246
Wu L, Tian X, Lee DJ, Yoon J, Lim CS, Kim HM, James TD (2021) Two-photon ESIPT-based fluorescent probe using 4-hydroxyisoindoline-1,3-dione for the detection of peroxynitrite. Chem Commun 57:11084–11087
Xia X, Liu S, Liu W, Xu Q, Xu X, Liu F, Deng T (2022) Probe and dye design through copper-mediated reactions of N-arylhydroxylamines. Org Biomol Chem 20:9234–9240
Wang T, Douglass EF Jr, Fitzgerald KJ, Spiegel DA (2013) A “turn-on” fluorescent sensor for methylglyoxal. J Am Chem Soc 135:12429–12433
Ren A, Zhu D, Luo Y (2020) A novel Boranil-based turn-on fluorescent probe for imaging of biothiols in living cells. J Mol Struct 1209:127914
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Guangxi.
Funding
The work was supported by funding from the Natural Science Foundation of Guangxi (2021GXNSFBA220038, 2019GXNSFDA185003).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
D.Z. designed the experiments and wrote the manuscript. W.Y. synthesized and purified the compounds as well as performed the characterization experiments. A.R. created the figures, carried out the theoretical calculations and characterization experiments.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical Approval
This article does not contain any studies involving human participants conducted by any of the authors.
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Highlights
• A reaction-based ESIPT fluorescent probe 1 for Hg2+ was developed.
• 1 exhibited rapid response, high sensitivity, excellent selectivity.
• 1 could detect Hg2+ with large Stokes shift.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu, D., Yao, W. & Ren, A. A Reaction-Based ESIPT Fluorescent Probe for the Detection of Hg2+ with Large Stokes Shift. J Fluoresc (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10895-023-03508-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10895-023-03508-5