Abstract
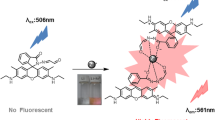
In pH 1.99 sodium acetate-HCl buffer solutions at 60 °C, Rhodamine B exhibited a strong fluorescence peak at 584 nm using an excitation wavelength of 548 nm. The fluorescence quenching occurred when Fe3O4 nanoparticles catalyzed H2O2 oxidation of Rhodamine B. Under the chosen conditions, the fluorescence intensity at 584 nm decreased when the concentration of H2O2 increased. The fluorescence quenching intensity is linear with the concentration of H2O2 in the range of 10–200 nmol/L. Thus, a new and simple and sensitive nanocatalytic fluorescence method was proposed for the determination of H2O2 in synthetic sample, with satisfactory results.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhang YT, Bai SJ, Zhang W (2006) An improved method for determination of trace hydrogen peroxide in water. J Environ Health 23:258–261
The Minister of Health of the People’s Republic of China (2007) Health standards for the use of food additives (GB 2760-2007). Standards Press of China, Beijing
The Minister of Health of the People’s Republic of China (2009) Disinfection technical guidelines. Peoples Medical Publishing House, Beijing, p 12
Chen YH, Liu Y, Zhou JL, Zhu HW, Xiang LX (2009) Determination of peroxides in food samples by high performance liquid chromatography with variable wavelength detector. Chin J Spec Lab 26:414–417
Xu JR, Chen ZM (2005) Determination of peroxides in environmental samples by high performance liquid chromatography with fluorescence detection. Chin J Chromatograph 23:366–369
Toniolo R, Geatt P, Bontempelli G (2001) Amperometric monitoring of hydrogen peroxide in work place atmospheres by electrodes supported on ion-exchangemembranes. J Electroanal Chem 514:123–128
Campanella LI, Rovers R, Sammartino MP (1998) Hydrogen peroxide determination in pharmaceutical for mulations and cosmetics using a new catalase biosensor. J Pharm Biom Anal 18:105–106
Lin MJ, Arakawa H, Yamada M (1998) Flow injection chemiluminescent determination of trace amounts of hydrogen peroxide in snow-water using KIO4-K2CO3 system. Anal Chim Acta 37:171–176
Li YZ, Townshend A (1998) Evaluation of the adsorptive immobilization of horseradish peroxidase on PTFE tubing in flow systems for hydrogen peroxide determination using fluorescence detection. Anal Chim Acta 359:149–156
Wu ZS, Zhang SB, Guo MM (2007) Homogeneous, unmodified gold nanoparticel-based colorimetric assay of hydrogen peroxide. Anal Chim Acta 584:122–128
Jiang ZL, Tang YF, Liang AH, Gong Q (2009) Flame atomic absorption spectrometric determination of H2O2 using (Au)core(Ag)shell nanoparticles. Spectrosc Spect Anal 29:1990–1992
Liang AH, Jiang ZL, Tao HL (2007) A new and sensitive resonance scattering spectral method for the determination of H2O2 using acridine red. Spectrosc Spect Anal 27:120–122
Li ZZ, Jiang ZL, Yang G, Lu D, Liu SP (2005) Resonance-scattering spectral determination of H2O2 using rhodamine 6 G association particles. Spectrosc Spect Anal 125:1286–1288
Gao L, Zhuang J, Nie L (2007) Intrinsic peroxidase-like activity of ferromagnetic nanoparticles. Nature Nanotechnology 2:577–583
Zamocky M, Furtmuller PG (2008) Evolution of catalases from bacteria to humans. Antioxidants Redox Signal 10:1527–1548
Chang Q, Deng KJ, Zhu LH, Jiang GD, Yu C, Tang HQ (2009) Determination of hydrogen peroxide with the aid of peroxidase-like Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles as the catalyst. Microchim Acta 165:299–305
Wu Q, Rong J, Shan Z, Chen H, Yang WS (2009) Effects of aqueous-organic solvents on peroxidase mimetic activity of Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles. Chin J Biotechnol 25:1976–1982
Li DJ, Hu SY, Zou GL (2003) Progress of the mimetic enzyme of horseradish peroxidase. Amino Biotic Resources 25:43–47
Tournebize J, Sapin-Minet A, Schneider R, Boudier A, Maincent P, Leroy P (2011) Simple spectrophotocolorimetric method for quantitative determination of gold in nanoparticles. Talanta 83:1780–1783
Jiang ZL, Zhou SM, Liang AH, Kang CY, He XC (2006) Resonance scattering effect of rhodamine dye association nanoparticles and its application to respective determination of trace ClO2 and Cl2. Environ Sci Technol 40:4286–4291
Cui Z, Han C, Li H (2011) Dual-signal fenamithion probe by combining fluorescence with colorimetry based on Rhodamine B modified silver nanoparticles. Analyst 136:1351–1356
Vangala K, Yanney M, Hsiao CT, Wu WW, Shen RF, Zou S, Sygula A, Zhang D (2010) Sensitive carbohydrate detection using surface enhanced Raman tagging. Anal Chem 82:10164–10171
Liu HJ, Peng TY, Peng ZH, Dai K (2007) Photocatalytic degradation mechanism of RB over dye-doped WO3 photocatalysts. J. Wuhan Univ. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 53: pp 127–132
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 20865002, 20965002, 21075023), Natural Science Foundation of Guangxi (No.0991021Z) and the Research Funds of Guangxi Key Laboratory of Environmental Engineering, Protection and Assessment (No. 0701Z022).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jiang, Z., Kun, L., Ouyang, H. et al. A Simple and Sensitive Fluorescence Quenching Method for the Determination of H2O2 Using Rhodamine B and Fe3O4 Nanocatalyst. J Fluoresc 21, 2015–2020 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10895-011-0902-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10895-011-0902-7