Abstract
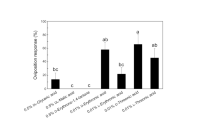
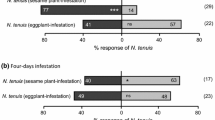
European corn borer larvae detect and avoid feeding in the presence of phytoecdysteroids (PEs) such as 20-hydroxyecdysone (20E). Therefore, we hypothesized that females would have taste receptors similar to larvae and avoid laying eggs in the presence of 20E. We found female-specific taste sensilla on the tarsi that respond to 20E at concentrations as low as 10−6 M, a threshold comparable to that of larvae. However, in choice tests, females laid a similar number of eggs on 20E-treated and on nontreated artificial substrates (filter paper, glass, and nylon), although they spent significantly more time in behavioral sequences related to substrate assessment when 20E was present. In contrast, when given a choice between maize plants (eight leaves) sprayed with 20E or only the solvent, females laid 70% fewer eggs on the treated than on control plants. These observations suggest that other chemical cues of plant origin must be present at the same time as 20E for females to modify their oviposition behavior.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akhtar, Y. and Isman, M. B. 2003. Larval exposure to oviposition deterrents alters subsequent oviposition behavior in generalist, Trichoplusia ni and specialist, Plutella xylostella moths. J. Chem. Ecol. 29:1853–1870.
Bethenod, M. T., Thomas, Y., Rousset, F., Frerot, B., Pelozuelo, L., Genestier, G., and Bourguet, D. 2005. Genetic isolation between two sympatric host plant races of the European corn borer, Ostrinia nubilalis Hübner. II. Assortative mating and host–plant preferences for oviposition. Heredity 94: 264–270.
Binder, B. F. and Robbins, J. C. 1996. Age- and density-related oviposition behavior of the European corn borer, Ostrinia nubilalis (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae). J. Insect Behav. 9:755–769.
Binder, B. F. and Robbins, J. C. 1997. Effect of terpenoids and related compounds on the oviposition behavior of the European corn borer, Ostrinia nubilalis (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae). J. Agric. Food Chem. 45:980–984.
Binder, B. F., Robbins, J. C., and Wilson, R. L. 1995. Chemically mediated ovipositional behaviors of the European corn borer, Ostrinia nubilalis (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae). J. Chem. Ecol. 21:1315–1327.
Bruce, T. J. A., Wadhams, L. J., and Woodcock, C. M. 2005. Insect host location: a volatile situation. Trends Plant Sci. 10:269–274.
Calas, D., Thiéry, D. and Marion-Poll, F. 2006. 20-Hydroxyecdysone deters oviposition and larval feeding in the European grapevine moth, Lobesia botrana. J. Chem. Ecol. 32:2443–2454.
Chapman, R. F. and Bernays, E. A. 1989. Insect behavior at the leaf surface and learning as aspects of host plant selection. Experientia 45:215–222.
Darazy-Choubaya, D. 2002. La perception gustative des phytoecdystéroides par les larves de la pyrale du mais, Ostrinia nubilalis Hübner. Ph.D. thesis, Ecole doctorale ABIES, INA-PG, Paris (106 pp.).
De Jong, R. and Städler, E. 1999. The influence of odour on the oviposition behaviour of the cabbage root fly. Chemoecology 9:151–154.
Derridj, S., Fiala, V., and Jolivet, E. 1986. Increase of European corn borer (Ostrinia nubilalis) oviposition induced by a treatment of maize plants with maleic hydrazide: role of leaf carbohydrate content. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 41:305–310.
Devarenne, T. P., Sen-Michael, B., and Adler, J. H. 1995. Biosynthesis of ecdysteroids in Zea mays. Phytochemistry 40:1125–1131.
Dinan, L. 1998. A strategy towards the elucidation of the contribution made by phytoecdysteroids to the deterrence of invertebrate predators on plants. Russ. J. Plant Physiol. 45:296–305.
Dinan, L., Savchenko, T., and Whiting, P. 2001. On the distribution of phytoecdysteroids in plants. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 58:1121–1132.
Eigenbrode, S. D. 2004. The effects of plant epicuticular waxy blooms on attachment and effectiveness of predatory insects. Arthropod Struct. Develop. 33:91–102.
Eigenbrode, S. D. and Espelie, K. E. 1995. Effects of plant epicuticular lipids on insect herbivores. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 40:171–194.
Espelie, K. E., Bernays, E. A., and Brown, J. J. 1991. Plant and insect cuticular lipids serve as behavioral cues for insects. Arch. Insect Biochem. Physiol. 17:223–233.
Feeny, P., Städler, E., Ahman, I., and Carter, M. 1989. Effects of plant odor on oviposition by the black swallowtail butterfly, Papilio polyxenes (Lepidoptera: Papilionidae). J. Insect Behav. 2:803–827.
Garnier-Geoffroy, F., Robert, P., Hawlitzky, N., and Frerot, B. 1996. Oviposition behaviour in Ostrinia nubilalis (Lep: Pyralidae) and consequences on host location and oviposition in Trichogramma brassicae (Hym: Trichogrammatidae). Entomophaga 41:287–299.
Hodgson, B. E. 1928. The host plants of European corn borer in New England. USDA Tech. Bull. 77:1–63.
Kennedy, G. G. and Storer, N. P. 2000. Life systems of polyphagous arthropod pests in temporally unstable cropping systems. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 45:467–493.
Krishna, P. 2003. Brassinosteroid-mediated stress responses. J. Plant Growth Regul. 22:289–297.
Li, G. Q. and Ishikawa, Y. 2006. Leaf epicuticular wax chemicals of the Japanese knotweed Fallopia japonica as oviposition stimulants for Ostrinia latipennis. J. Chem. Ecol. 32:595–604.
Lombarkia, N. and Derridj, S. 2002. Incidence of apple fruit and leaf surface metabolites on Cydia pomonella oviposition. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 104:79–87.
Lupoli, R., Marion-Poll, F., Pham-Delegue, M. H., and Masson, C. 1990. Effect of maize leaf volatiles on the oviposition preferences of Ostrinia nubilalis (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae). C. R. Acad. Sci., Sér. 3 Sci. Vie 311:225–230.
Malausa, T., Bethenod, M. T., Bontemps, A., Bourguet, D., Cornuet, J. M., and Ponsard, S. 2005. Assortative mating in sympatric host races of the European corn borer. Science 308:258–260.
Marion-Poll, F. and Descoins, C. 2002. Taste detection of phytoecdysteroids in larvae of Bombyx mori, Spodoptera littoralis and Ostrinia nubilalis. J. Insect Physiol. 48:467–476.
Marion-Poll, F., Guillaumin, D., and Masson, C. 1992. Sexual dimorphism of tarsal receptors and sensory equipment of the ovipositor in the European corn borer, Ostrinia nubilalis. Cell Tissue Res. 267:507–518.
Marion-Poll, F., Dinan, L., and Lafont, R. 2005. The role of phytoecdysteroids in the control of phytophagous insects, in C. Regnault-Roger, B. J. Philogène, C. Vincent (eds.). Biopesticides of Plant Origin. Lavoisier, Paris, France.
Meunier, N., Marion-Poll, F., Lansky, P., and Rospars, J. P. 2003. Estimation of the individual firing frequencies of two neurons recorded with a single electrode. Chem. Senses 28:671–679.
Miles, C. I., Del Campo, M. L., and Renwick, J. A. 2005. Behavioral and chemosensory responses to a host recognition cue by larvae of Pieris rapae. J. Comp. Physiol., A. 191:147–155.
Müller, C. and Riederer, M. 2005. Plant surface properties in chemical ecology. J. Chem. Ecol. 31:2621–2651.
Nakashita, H., Yasuda, M., Nitta, T., Asami, T., Fujioka, S., Arai, Y., Sekimata, K., Takatsuto, S., Yamaguchi, I., and Yoshida, S. 2003. Brassinosteroid functions in a broad range of disease resistance in tobacco and rice. Plant J. 33:887–898.
Qiu, Y. T., Van Loon, J. J. A., and Roessingh, P. 1998. Chemoreception of oviposition inhibiting terpenoids in the diamondback moth Plutella xylostella. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 87:143–155.
Renwick, J. A. A. 2002. The chemical world of crucivores: lures, treats and traps. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 104:35–42.
Roessingh, P., Hora, K. H., Fung, S. Y., Peltenburg, A., and Menken, S. B. J. 2000. Host acceptance behaviour of the small ermine moth Yponomeuta cagnagellus: larvae and adults use different stimuli. Chemoecology 10:41–47.
Schmelz, E. A., Grebenok, R. J., Galbraith, D. W., and Bowers, W. S. 1999. Insect-induced synthesis of phytoecdysteroids in spinach, Spinacia oleracea. J. Chem. Ecol. 25:1739–1757.
Schmelz, E. A., Grebenok, R. J., Ohnmeiss, T. E., and Bowers, W. S. 2000. Phytoecdysteroid turnover in spinach: long-term stability supports a plant defense hypothesis. J. Chem. Ecol. 26:2883–2896.
Schurr, K. and Holdaway, F. G. 1970. Olfactory responses of female Ostrinia nubilalis (Lepidoptera: Pyraustinae). Entomol. Exp. Appl. 13:455–461.
Spangler, S. M. and Calvin, D. D. 2000. Influence of sweet corn growth stages on European corn borer (Lepidoptera: Crambidae) oviposition. Environ. Entomol. 29:1226–1235.
Spangler, S. M. and Calvin, D. D. 2001. Vertical distribution of European corn borer (Lepidoptera: Crambidae) egg masses on sweet corn. Environ. Entomol. 30:274–279.
Spencer, J. L. 1996. Waxes enhance Plutella xylostella oviposition in response to sinigrin and cabbage homogenates. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 81:165–173.
Spencer, J. L., Pillai, S., and Bernays, E. A. 1999. Synergism in the oviposition behavior of Plutella xylostella: sinigrin and wax compounds. J. Insect Behav. 12:483–500.
Tallamy, D. W., Stull, J., Ehresman, N. P., Gorski, P. M., and Mason, C. E. 1997. Cucurbitacins as feeding and oviposition deterrents to insects. Environ. Entomol. 26:678–683.
Thompson, J. N. and Pellmyr, O. 1991. Evolution of oviposition behavior and host preference in Lepidoptera. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 36:65–89.
Udayagiri, S. and Mason, C. E. 1995. Host plant constituents as oviposition stimulants for a generalist herbivore: European corn borer. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 76:59–65.
Udayagiri, S. and Mason, C. E. 1997. Epicuticular wax chemicals in Zea mays influence oviposition in Ostrinia nubilalis. J. Chem. Ecol. 23:1675–1687.
Vrieling, K. and Derridj, S. 2003. Pyrrolizidine alkaloids in and on the leaf surface of Senecio jacobaea L. Phytochemistry 64:1223–1228.
Wang, Z. Y. and He, J. X. 2004. Brassinosteroid signal transduction—choices of signals and receptors. Trends Plant Sci. 9:91–96.
Acknowledgments
We thank René Lafont (University Paris VI) for his gift of 20E used in this study and numerous discussions. We thank Alan Cork for reviewing the manuscript as well as two anonymous referees and the editor for their useful suggestions. This work was supported by an INCO-DEV program SUSVEG-ASIA.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Calas, D., Berthier, A. & Marion-Poll, F. Do European Corn Borer Females Detect and Avoid Laying Eggs in the Presence of 20-Hydroxyecdysone?. J Chem Ecol 33, 1393–1404 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10886-007-9302-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10886-007-9302-5