Abstract
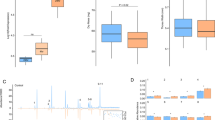
The analysis of expression of pheromone-carrying major urinary proteins (MUPs) from two subspecies of house mice (Mus m. musculus, Mus m. domesticus) was studied. It has been previously shown that commensal populations of the two subspecies can discriminate on the basis of urinary signals. MUPs are predominant urinary proteins that protect pheromones from rapid degradation in a hydrophilic environment, and individuals of M. m. musculus tend to rely on these urinary cues in the process of subspecies discrimination more than M. m. domesticus individuals. Although it is not precisely known what triggers phenotypic and epigenetic changes of MUP expression, our results show that in the subspecies M. m. musculus, sex is a significant factor influencing variations in the regulation of selected MUPs in the liver. Furthermore, male M. m. musculus individuals expressed all the studied MUPs’ mRNA significantly more than females or individuals of either sex in M. m. domesticus. Correspondingly, the pattern of mRNA abundance was corroborated with the level of total MUP concentration in the urine, such that the level of sexual dimorphism was also significant and species-specific. Our finding introduces a hypothesis that quantitative variation of these proteins may be an essential part of a subspecies recognition system that maintains homospecific mixing.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bacchini, A., Gaetani, E., and Cavaggioni, A. 1992. Pheromone binding proteins of the mouse. Mus musculus. Experientia 48:419–421.
Beynon, R. J., Veggerby, C., Payne, C. E., Roberstson, D. H. L., Gaskell, S. J., Humphries, R. E., and Hurst, J. L. 2002. Polymorphism in major urinary proteins: Molecular heterogeneity in a wild mouse population. J. Chem. Ecol. 28:1429–1446.
Bishop, J. O., Clark, A. J., Clissold, P. M., Hainey, S., and Francke, U. 1982. Two main groups of mouse major urinary protein genes, both largely located on chromosome 4. EMBO J. 1:615–620.
Boursot, P., Auffray, J. C., Britton-Davidian, J., and Bonhomme, F. 1993. The evolution of house mice. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 24:119–152.
Bustin, S. A. 2000. Absolute quantification of mRNA using real-time reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction assays. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 25:169–193.
Bustin, S. A. 2002. Quantification of mRNA using real-time reverse transcription PCR (RT-PCR): Trends and problems. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 29:23–39.
Cavaggioni, A., and Mucignat-Caretta, C. 2000. Major urinary proteins, α2U-globulins and aphrodisin. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Prot. Struct. Mol. Enzymol. 1482:218–228.
Christophe, N., and Baudoin, C. 1998. Olfactory preferences in two strains of wild mice, Mus musculus musculus and Mus musculus domesticus, and their hybrids. Anim. Behav. 56:365–369.
Finlayson, J. S., Asofsky, R., Potter, and M., Runner, C. C. 1965. Major urinary protein complex of normal mice: Origin. Science 149:981–982.
Giulietti, A., Overbergh, L., Valckx, D., Decallonne, B., Bouillon, R., and Matheu, C. 2001. An overview of real-time quantitative PCR: Applications to quantify cytokine gene expression. Methods 25:386–401.
Humphries, R. E., Robertson, D. H. L., Beynon, R. J., and Hurst, J. L. 1999.Unravelling the chemical basis of competitive scent marking in house mice. Anim. Behav. 58:1177–1190.
Hurst, J. L., Robertson, D. H. L., Tolladay, U., and Beynon, R. J. 1998. Proteins in urine scent marks of male house mice extend the longevity of olfactory signals. Anim. Behav. 55:1289–1297.
Hurst, J. L., Payne, C. E., Nevison, C. M., Marie, A. D., Humphries, R. E., Robertson, D. H. L., Cavaggioni, A., and Beynon, R. J. 2001. Individual recognition in mice mediated by major urinary proteins. Nature 414:631–634.
Knopf, J. L., Gallagher, J. F., and Held, W. A. 1983. Differential, multihormonal regulation of the mouse major urinary protein gene family in the liver. Mol. Cell. Biol. 3:2232–2240.
Laemmli, U. K. 1970. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227:680–685.
Linnaeus, C. 1758. Systema Naturae per regna tria naturae, secundum classis, ordines, genera species cum characteribus, differentiis, synonymis, locis. Tenth ed. Vol. 1. Laurentii Salvii, Stockholm, 824 pp.
Livak, K., and Schmittgen, T. 2001. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2-ΔΔCT method. Methods 25:402–408.
Marchlewska-Koj, A., Cavaggioni, A., Mucignat-Caretta, C., and Olejniczak, P. 2000. Stimulation of estrus in female mice by male urinary proteins. J. Chem. Ecol. 26:2355–2366.
Mucignat-Caretta, C., Cavaggioni, A., and Caretta, A. 2004. Male urinary chemosignals differentially affect aggressive behavior in male mice. J. Chem. Ecol. 30:777–791.
Munclinger, P., and Frynta, D. 1997. Relations between distant populations of Mus musculus sensu lato: is there any odour-based discrimination? Folia Zool. 46:193–199.
Munclinger, P., Božíková, E., Šugerková, M., Piálek, J., and Macholán, M. 2002. Genetic variation in house mice (Mus, Muridae, Rodentia) from the Czech and Slovak republics. Folia Zool. 51:81–92.
Novotny, M. V. 2003. Pheromones, binding proteins and receptor responses in rodents. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 31:117–122.
Novotny, M. V., Ma, W., Žídek, L., and Daev, E. 1999. Recent biochemical insights into puberty acceleration, estrus induction, and puberty delay in the house mouse, pp. 99–116, in R. E. Johnston, D. Müller-Schwarze, and P. Sorensen (eds.). Advances in Chemical Communication in Vertebrates. Plenum Press, New York.
Pes, D., Robertson, D. H. L., Hurst, J. L., Gaskell, S., and Beynon, R. J. 1999. How many major urinary proteins are produced by the house mouse Mus domesticus, pp. 149–162, in R. E. Johnston, D. Müller-Schwarze, and P. Sorensen (eds.). Advances in Chemical Communication in Vertebrates. Plenum Press, New York.
Pfaffl, M. W. 2003. Quantification strategies in real-time PCR, in S. Bustin (ed.). A–Z of Quantitative PCR. IUL, La Jolla.
Robertson, D. H. L., Beynon, R. J., and Evershed, R. P. 1993. Extraction, characterization, and binding analysis of two pheromonally active ligands associated with Major Urinary Protein of house mouse (Mus musculus). J. Chem. Ecol. 19:1405–1417.
Robertson, D. H. L., Cox, K. A., Gaskell, S. J., Evershed, R. P., and Beynon, R. J. 1996. Molecular heterogeneity in the Major Urinary Proteins of the house mouse Mus musculus. Biochem. J. 316:265–272.
Robertson, D. H. L., Hurst, J. L., Bolgar, M. S., Gaskell, S. J., and Beynon, R. J. 1997. Molecular heterogeneity of urinary proteins in wild house mouse populations. Rapid. Commun. Mass Sp. 11:786–790.
Sampsell, B. M., and Held, W. A. 1985. Variation in the major urinary protein multigene family in wild-derived mice. Genetics 109:549–568.
Schwarz, E., and Schwarz, H.K. 1943. The wild and commensal stocks of the house mouse, Mus musculus Linneaus. J. Mammal. 24:59–72.
Shahan, K., Denaro, M., Gilmartin, M., Shi, Y., and Derman, E. 1987. Expression of six mouse major urinary protein genes in the mammary, parotid, sublingual, submaxillary, and lachrymal glands and in the liver. Mol. Cell. Biol. 7:1947–1954.
Smadja, C., and Ganem, G. 2002. Subspecies recognition in the house mouse: a study of two populations from the border of a hybrid zone. Behav. Ecol. 13:312–320.
Vandesompele, J., De Paepe, A., and Spelman, F. 2002. Elimination of primer-dimer artifacts and genomic coamplification using a two-step SYBR Green I Real-Time RT-PCR. Anal. Biochem. 303:95–98.
Whitten, W. K. 1966. Pheromones and mammalian reproduction. Adv. Reprod. Physiol. 1:155–177.
Wicks, L. F. 1941. Sex and proteinuria of mice. Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. 48:395–400.
Žídek, L., Stone, M. J., Lato, S. M., Pagel, M. D., Miao, Z., Ellington, A. D., and Novotny, M. V. 1999. NMR mapping of the recombinant mouse major urinary protein I binding site occupied by the pheromone 2-sec-butyl-4,5-dihydrothiazole. Biochemistry 38:9850–9861.
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to Timothy Hort for language correction, Jaroslav Pialek, Milos Macholan, and Pavel Munclinger for helpful discussions. The work was funded by the Grant Agency of the Czech Republic (206-04/0493), whereas grant MSMT VZ 0021620828 from the Ministry of Education, Youth and Sport of the Czech Republic formed a framework for this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stopková, R., Stopka, P., Janotová, K. et al. Species-specific Expression of Major Urinary Proteins in the House Mice (Mus musculus musculus and Mus musculus domesticus). J Chem Ecol 33, 861–869 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10886-007-9262-9
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10886-007-9262-9