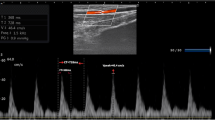
Abstract
Invasive arterial cannulation is a widely used method in intensive care units and operating rooms. However it has potential complications such as thrombosis, peripheral embolism, hematoma formation, and infection. The Masimo Root Radical-7 Pulse CO-Oximeter® (Masimo Corporation, Irvine, CA, USA) is a non-invasive hemodynamic monitoring device that measures perfusion index and pleth variability index, provides guidance to anaesthesiologists in the cases where hemodynamic fluctuations are expected. In this particular case, the perfusion index played a crucial role in the immediate diagnosis of radial artery embolism in a patient undergoing cytoreductive surgery and hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy procedure.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable.
References
Brown AE, Sweeney DB, Lumley J. Percutaneous radial artery cannulation. Anaesthesia. 1969;24:532–6. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2044.1969.tb02906.x.
Lima A, Bakker J. Noninvasive monitoring of peripheral perfusion. Intensive Care Med. 2005;31:1316–26. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00134-005-2790-2.
Cannesson M, Delannoy B, Morand A, Rosamel P, Attof Y, Bastien O, Lehot JJ. Does the pleth variability index indicate the respiratory-induced variation in the plethysmogram and arterial pressure waveforms? Anesth Analg. 2008;106:1189–94. https://doi.org/10.1213/ane.0b013e318167ab1f.
Wilkins RG. Radial artery cannulation and ischaemic damage: a review. Anaesthesia. 1985;40:896–9. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2044.1985.tb11055.x.
Mozersky DJ, Buckley CJ, Hagood CO Jr, Capps WF Jr, Dannemiller FJ Jr. Ultrasonic evaluation of the palmar circulation. A useful adjunct to radial artery cannulation. Am J Surg. 1973;126:810–2. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0002-9610(73)80077-7.
Barbeau GR, Arsenault F, Dugas L, Simard S, Lariviere MM. Evaluation of the ulnopalmar arterial arches with pulse oximetry and plethysmography: comparison with the Allen’s test in 1010 patients. Am Heart J. 2004;147:489–93. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ahj.2003.10.038.
Ginosar Y, Weiniger CF, Meroz Y, Kurz V, Bdolah-Abram T, Babchenko A, Nitzan M, Davidson EM. Pulse oximeter perfusion index as an early indicator of sympathectomy after epidural anesthesia. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 2009;53:1018–26. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1399-6576.2009.01968.x.
Cetgen N, Ener D, Dogukan M, Duran M, Uludag O. Perfusion index value in determining the success of axillary block. J Coll Physicians Surg Pak. 2022;32:1105–9. https://doi.org/10.29271/jcpsp.2022.09.1105.
Abdelhamid B, Yassin A, Ahmed A, Amin S, Abougabal A. Perfusion index-derived parameters as predictors of hypotension after induction of general anaesthesia: a prospective cohort study. Anaesthesiol Intensive Ther. 2022;54:34–41. https://doi.org/10.5114/ait.2022.113956.
Toyama S, Kakumoto M, Morioka M, Matsuoka K, Omatsu H, Tagaito Y, Numai T, Shimoyama M. Perfusion index derived from a pulse oximeter can predict the incidence of hypotension during spinal anaesthesia for caesarean delivery. Br J Anaesth. 2013;111:235–41. https://doi.org/10.1093/bja/aet058.
Al-Metwalli RR. Perfusion index as an objective alternative to the Allen test, with flow quantification and medico legal documentation. Anaesth Pain Intensive Care. 2014;18:245–9.
Funding
The authors declare that no funds, grants, or other support were received during the preparation of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the managing of the patient and the writing of this manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Informed consent was obtained from the patient.
Consent for publication
The patient has consented to the submission of the case report to the journal.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Eraslan, İ., Sarıoğlan, B.T., Ünsal, S. et al. Diagnostic utility of perfusion index in identifying radial artery embolism during hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy procedure: a case report. J Clin Monit Comput 38, 553–555 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10877-023-01102-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10877-023-01102-5