Abstract
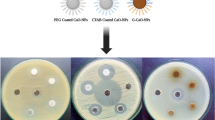
β-cyclodextrin (β-CD) is biocompatible and biodegradable polymer having inherent hydrophobic cavities, thus is widely used as a drug nanocarrier for less water soluble drugs. Naringin is a pharmacologically active important compound however, its therapeutic efficacy is limited due to its unique physicochemical properties including lower aqueous solubility. This study reports improvement in bactericidal potentials of naringin through construction of its nano-formulation using biocompatible β-CD. Naringin loaded β-CD NPs were prepared via solvent evaporation method and characterized using various techniques such as FTIR, UV–visible spectroscopy, AFM, DSC and TGA analysis. Tetrazolium Microplate and AFM assays were used for investigating the bactericidal potential of naringin loaded β-CD NPs. Monodispersed NPs with spherical morphology of 70.00 ± 15.06 nm mean diameter were obtained that possessed net negative surface charge of − 18.20 ± 3.24 mV and were highly stable and did not change the chemical nature of the drug in various media. Antibacterial activity of naringin in β-CD NPs significantly enhanced that was authenticated by AFM, showing prominent destructive changes in the bacterial cell’s morphology through destabilization of outer membrane of bacterial cells by drug loaded NPs. Results of this study suggest that the β-CD NPs of naringin could be used as a successful formulation for developing more efficacious form of the drug against various bacterial infections.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
J. J. Peterson, G. R. Beecher, S. A. Bhagwat, J. T. Dwyer, S. E. Gebhardt, D. B. Haytowitz, and J. M. Holden (2006). J. Food Compos. Anal. 19, S74–S80.
J. A. Manthey, N. Guthrie, and K. J. Grohmann (2001). Curr. Med. Chem. 8, (2), 135–153.
R. A. Dixon and C. L. Steele (1999). Trends Plant Sci. 4, (10), 394–400.
M. Yu, D. You, J. Zhuang, S. Lin, L. Dong, S. Weng, B. Zhang, K. Cheng, W. Weng, and H. Wang (2017). ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 9, (23), 19698–19705.
F. Sansone, R. Aquino, P. Del Gaudio, P. Colombo, and P. J. E. J. O. P. Russo (2009). Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 72, (1), 206–213.
K. Rao, M. Imran, T. Jabri, I. Ali, S. Perveen, S. Ahmed, and M. R. Shah (2017). Carbohydr. Polym. 174, 243–252.
J. Panyam and V. J. Labhasetwar (2012). Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 64, 61–71.
H. S. Yoo, J. E. Oh, K. H. Lee, and T. G. Park (1999). Pharm. Res. 16, (7), 1114–1118.
Z. Liu, Y. Jiao, Y. Wang, C. Zhou, and Z. J. Zhang (2008). Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 60, (15), 1650–1662.
R. Mejia-Ariza, L. Graña-Suárez, W. Verboom, and J. Huskens (2017). J. Mater. Chem. B 5, (1), 36–52.
E. Bilensoy Cyclodextrins in Pharmaceutics, Cosmetics, and Biomedicine: Current and Future Industrial Applications (Wiley, New York, 2011).
Y. Çirpanli, E. Bilensoy, A. L. Doğan, and S. Çaliş (2009). Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 73, (1), 82–89.
P. Karande and S. Mitragotri (2009). Biochim Biophys Acta (BBA) Biomembr 1788, (11), 2362–2373.
T. Loftsson and D. Duchene (2007). Int. J. Pharm. 329, (1–2), 1–11.
Y. Yang, J. Gao, X. Ma, and G. Huang (2017). Asian J. Pharm. Sci. 12, (2), 187–192.
H. Rachmawati, C. A. Edityaningrum, and R. Mauludin (2013). AAPS PharmSciTech 14, (4), 1303–1312.
T. Van Hees, G. Piel, S. H. de Hassonville, B. Evrard, and L. J. Delattre (2002). Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 15, (4), 347–353.
K. A. Owoseni-Fagbenro, S. Saifullah, M. Imran, S. Perveen, K. Rao, T. M. Fasina, I. A. Olasupo, L. A. Adams, I. Ali, and M. R. Shah (2019). J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 50, 347–354.
S. M. Habib, R. Maharjan, T. Kanwal, I. I. Althagafi, S. Saifullah, S. Ullah, S. U. Simjee, and M. R. Shah (2020). Int. J. Pharm. 590, 119897.
S. P. Piaru, R. Mahmud, and S. Perumal (2012). Int J Pharmacol. 8, (6), 572–576.
S. D. Sarker, L. Nahar, and Y. Kumarasamy (2007). Methods 42, (4), 321–324.
I. Ghaffar, M. Imran, S. Perveen, T. Kanwal, S. Saifullah, M. F. Bertino, C. J. Ehrhardt, V. K. Yadavalli, and M. R. Shah (2019). Mater. Sci. Eng. C 105, 110111.
M. Imran, M. R. Shah, F. Ullah, S. Ullah, A. M. Elhissi, W. Nawaz, F. Ahmad, A. Sadiq, and I. Ali (2016). Int. J. Pharm. 505, (1–2), 122–132.
A. A. Kassem, A. M. Mohsen, R. S. Ahmed, and T. M. Essam (2016). J. Mol. Liq. 218, 219–232.
J. Jingou, H. Shilei, L. Weiqi, W. Danjun, W. Tengfei, and X. Yi (2011). Colloids Surf. B: Biointerfaces 83, (1), 103–107.
A. Calderini and F. Pessine (2008). J. Incl. Phenom. Macrocycl. Chem. 60, (3–4), 369–377.
Z. Hadian, M. Maleki, K. Abdi, F. Atyabi, A. Mohammadi, and R. J. Khaksar (2018). Iran. J. Pharm. Res. 17, (1), 39.
K. I. Matshetshe, S. Parani, S. M. Manki, and O. S. Oluwafemi (2018). Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 118, 676–682.
G. Athanassiou, S. Michaleas, E. Lada-Chitiroglou, T. Tsitsa, and E. Antoniadou-Vyza (2003). J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 55, (3), 291–300.
G. Celiz, M. Daz, and M. C. J. J. O. A. M. Audisio (2011). J. Appl. Microbiol. 111, (3), 731–738.
N. Sahu, D. Soni, B. Chandrashekhar, D. Satpute, S. Saravanadevi, B. Sarangi, and R. A. Pandey (2016). Int. Nano Lett. 6, (3), 173–181.
Acknowledgements
All the authors acknowledge International Center for Chemical and Biological Sciences (ICCBS), University of Karachi, Pakistan, for providing lab facilities.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
All authors declare they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hussain, K., Ali, I., Ullah, S. et al. Enhanced Antibacterial Potential of Naringin Loaded β Cyclodextrin Nanoparticles. J Clust Sci 33, 339–348 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10876-020-01972-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10876-020-01972-8