Abstract
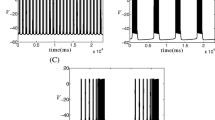
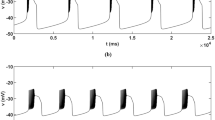
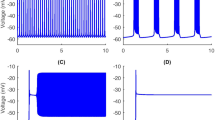
This paper illustrates an informatic technique for inferring and quantifying the dynamic role of a single intrinsic current in a mechanism of neural bursting activity. We analyze the patterns of the most dominant currents in a model of half-center oscillation in the leech heartbeat central pattern generator. We find that the patterns of dominance change substantially over a cycle, allowing different local reductions to be applied to the model. The result is a hybrid dynamical systems model, which is a piecewise representation of the mechanism combining multiple vector fields and discrete state changes. The simulation of such a model tests explicit hypotheses about the mechanism and is a novel way to retain both mathematical clarity and scientific detail in answering mechanistic questions about a complex model. Several insights into the central mechanism of “escape-release” in the model are elucidated by this analysis and compared with previous studies. The broader application and extension of this technique is also discussed.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Coombes, S., Bressloff, P.C. (eds.): Bursting: The Genesis of Rhythm in the Nervous System. World Scientific, London (2005).
Grillner, S.: Control of locomotion in bipeds, tetrapods and fish. In: V. Brooks (ed.) Handbook of physiology. Sec 1: the nervous system, vol. II: motor control, pp. 1179–1236. American Physiological Society (1981)
Marder, E., Calabrese, R.L.: Principles of rhythmic motor pattern generation. Physiol. Rev. 76, 687–717 (1996)
Cymbalyuk, G., Gaudry, Q., Masino, M.A., Calabrese, R.L.: Bursting in leech heart interneurons: cell-autonomous and network-based mechanisms. J. Neurosci. 22, 10,580–10,592 (2002)
Hill, A.A.V., Lu, J., Masino, M.A., Olsen, Ø.H., Calabrese, R.L.: A model of a segmental oscillator in the leech heartbeat neuronal network. J. Comput. Neurosci. 10, 281–302 (2001)
Ermentrout, G.B., Terman, D.H.: Mathematical Foundations of Neuroscience. Springer, Berlin (2010)
Izhikevich, E.M., Edelman, G.M.: Large-scale model of mammalian thalamocortical systems. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 105, 3593–3598 (2008)
Markram, H.: The Blue Brain project. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 7, 153–160 (2006)
Clewley, R., Rotstein, H.G., Kopell, N.: A computational tool for the reduction of nonlinear ODE systems possessing multiple scales. Multiscale Modeling and Simulation 4(3), 732–759 (2005)
Van Der Schaft, A., Schumacher, J.M.: An Introduction to Hybrid Systems. Springer, London (2000)
Clewley, R., Soto-Treviño, C., Nadim, F.: Dominant ionic mechanisms explored in the transition between spiking and bursting using local low-dimensional reductions of a biophysically realistic model neuron. J. Comput. Neurosci. 26(1), 75–90 (2009)
Bongard, J., Lipson, H.: Automated reverse engineering of nonlinear dynamical systems. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 104(24), 9943–9948 (2007)
Nadim, F., Olsen, Ø.H., de Schutter, E., Calabrese, R.L.: Modeling the leech heartbeat elemental oscillator I. interactions of intrinsic and synaptic currents. J. Comput. Neurosci. 2, 215–235 (1995)
Olypher, A., Cymbalyuk, G., Calabrese, R.L.: Hybrid systems analysis of the control of burst duration by low-voltage-activated calcium current in leech heart interneurons. J. Neurophysiol. 96, 2857–286 (2006)
Olypher, A.V., Calabrese, R.L.: How does maintenance of network activity depend on endogenous dynamics of isolated neurons? Neural Comput. 21, 1665–1682 (2009)
Sorensen, M., DeWeerth, S., Cymbalyuk, G., Calabrese, R.L.: Using a hybrid neural system to reveal regulation of neuronal network activity by an intrinsic current. J. Neurosci. 24, 5427–5438 (2004)
Tobin, A.E., Calabrese, R.L.: Endogenous and half-center bursting in morphologically inspired models of leech heart interneurons. J. Neurophysiol. 96, 2089–2106 (2006)
Shelley, M., McLaughlin, D., Shapley, R., Wielaard, J.: States of high conductance in a large-scale model of the visual cortex. J. Comput. Neurosci. 13, 93–109 (2002)
Clewley, R.: Encoding the fine-structured mechanism of action potential dynamics with qualitative motifs. J. Comput. Neurosci. (e-pub ahead of print 18 August 2010) (2010)
Hairer, E., Wanner, G.: Solving Ordinary Differential Equations II: Stiff and Differential-Algebraic Equations, 2nd edn. Springer, Berlin (1996)
Clewley, R.H., Sherwood, W.E., LaMar, M.D., Guckenheimer, J.M.: PyDSTool, a software environment for dynamical systems modeling (2007). Available at: http://pydstool.sourceforge.net
Govaerts, W., Sautois, B.: Computation of the phase response curve: a direct numerical approach. Neural Comput. 18, 817–847 (2006)
Sherwood, W.E., Guckenheimer, J.: Dissecting the phase response of a model bursting neuron. SIAM J. Appl. Dyn. Syst. 9(3), 659–703 (2010)
Daun, S., Rubin, J.E., Rybak, I.A.: Control of oscillation periods and phase durations in half-center central pattern generators: a comparative mechanistic analysis. J. Comput. Neurosci. 27, 3–36 (2009)
Rubin, J., Terman, D.: Geometric singular perturbation analysis of neuronal dynamics. In: B. Fiedler (ed.) Handbook of Dynamical Systems, vol. 2. Elsevier, Amsterdam (2002)
Channell, P., Cymbalyuk, G., Shilnikov, A.: Origin of bursting through homoclinic spike adding in a neuron model. Phys. Rev. Lett. 98(13), 134,101 (2007)
Acknowledgements
The author would like to thank R. Lin and the anonymous reviewers for their helpful input.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by NSF CISE/CCF-0829742.
An erratum to this article can be found online at http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s10867-012-9285-5.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Clewley, R. Inferring and quantifying the role of an intrinsic current in a mechanism for a half-center bursting oscillation. J Biol Phys 37, 285–306 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10867-011-9220-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10867-011-9220-1