Abstract
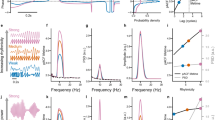
The scientific study of subjective experience is a current major research area in the neurosciences. Coordination patterns of brain activity are being studied to address the question of how brain function relates to behaviour, and particularly methods to estimate neuronal synchronization can unravel the spatio-temporal dynamics of the transient formation of neuronal assemblies. We report here a biophysical correlate of subjective experience. Subjects visualised figures with different levels of noise, while their brain activity was recorded using magnetoencephalography (MEG), and reported the moment in time (corresponding to a noise level) of figure recognition, which varied between individuals, as well as the moment when they saw the figure more clearly, which was mostly common among the participants (thus less subjective). This latter moment is considered to represent psychophysical stochastic resonance (PSR). Fluctuations in neuronal synchronization, quantified using a diffusion coefficient, were lower in occipital cortex when subjects recognised the figure, for a certain noise level, but did not correlate with the moment of PSR. A different pattern was observed in frontal cortex, where lower values of the diffusion coefficient in neuronal synchronization was maintained from the moment of recognition to the moment of PSR. No specific pattern was found analysing signals from temporal or parietal cortical areas. These observations provide support for distinct synchronization patterns in different cortical areas, and represent another demonstration that the subjective, first-person perspective is accessible to scientific methods.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adey, W.R.: Organization of brain tissue: is the brain a noisy processor? Intern. J. Neuroscience 3, 271–284 (1972)
Fatt, P., Katz, B.: Some observations on biological noise. Nature 166, 597–598 (1950)
Moss, F., Ward, L.M., Sannita, W.G.: Stochastic resonance and sensory information processing: a tutorial and review of application. Clin. Neurophysiol. 115, 267–281 (2004)
Manjarrez, E., Rojas-Piloni, J.G., Mendez, I., Martinez, L., Velez, D., Vazquez, D., Flores, A.: Internal stochastic resonance in the coherence between spinal and cortical neuronal ensembles in the cat. Neurosci. Lett. 326, 93–96 (2002)
Ward, L.M.: Psychophysics of stochastic resonance. Fluctuation and Noise Lett. 4, L11–L21 (2004)
Kitajo, K., Nozaki, D., Ward, L.M., Yamamoto, Y.: Behavioral stochastic resonance within the human brain. Phys. Rev. Lett. 90, 218103 (2003)
Simonotto, E., Riani, M., Seife, C., Roberts, M., Twitty, J., Moss, F.: Visual perception of stochastic resonance. Phys. Rev. Lett. 78, 1186–1189 (1997)
Ditzinger, T., Stadler, M., Strüber, D., Kelso, J.A.S.: Noise improves three-dimensional perception: stochastic resonance and other impacts of noise to perception of autostereograms. Phys. Rev. E 62, 2566–2575 (2000)
Piana, M., Canfora, M., Riani, M.: Role of noise in image processing by the human perceptive system. Phys. Rev. E 62, 1104–1109 (2000)
Richardson, K.A., Imhoff, T.T., Grigg, P., Collins, J.J.: Using electrical noise to enhance the ability of humans to detect subthreshold mechanical cutaneous stimuli. Chaos 8, 599–603 (1998)
Zeng, F.G., Fu, Q.J., Morse, R.: Human hearing enhanced by noise. Brain. Res. 869, 251–255 (2000)
Gluckman, B.J., Netoff, T.I., Neel, E.J., Ditto, W.L., Spano, M.L., Schiff, S.J.: Stochastic resonance in a neuronal network from mammalian brain. Phys. Rev. Lett. 77, 4098–5002 (1996)
Stacey, W.C., Durand, D.M.: Stochastic resonance improves signal detection in hippocampal CA1 neurons. J. Neurophysiol. 83, 1394–1402 (2000)
Varela, F.J., Lachaux, J.-P., Rodriguez, E., Martinerie, J.: The brainweb: phase synchronization and large scale integration. Nature Rev. Neurosci. 2, 229–239 (2001)
Friston, K.J.: Brain function, nonlinear coupling, and neuronal transients. Neuroscientist 7, 406–418 (2001)
Kelso, J.A.S.: Dynamic patterns: the self-organization of brain and behaviour. MIT Press, Massachusetts (1995)
Breakspear, M., Williams, L.M., Stam, C.J.: A novel method for the topographic analysis of neural activity reveals formation and dissolution of “dynamic cell assemblies”. J. Comp. Neurosci. 16, 49–68 (2004)
Greenfield, S.A., Collins, T.F.T.: In the boundaries of consciousness. Elsevier, Amsterdam (2005)
Neiman, A., Silchenko, A., Anishchenko, V., Schimansky-Geier, L.: Stochastic resonance: noise-induced phase coherence. Phys. Rev. E 58, 7118–7125 (1998)
Anishchenko, V.S., Vadivasova, T.E.: Synchronization of self-oscillations and noise-induced oscillations. J. Commun. Technol. Electron. 47, 117–148 (2002)
Mori, T., Kai, S.: Noise-induced entrainment and stochastic resonance in human brain waves. Phys. Rev. Lett. 88, 218101 (2002)
Sorrentino, A., Parkkonen, L., Piana, M., Massone, A.M., Narici, L., Carozzo, S., Riani, M., Sannita, W.G.: Modulation of brain and behavioural responses to cognitive visual stimuli with varying signal-to-noise ratios. Clin. Neurophysiol. 117, 1098–1105 (2006)
Garcia Dominguez, L., Wennberg, R.A., Gaetz, W., Cheyne, D., Snead, O.C., Perez Velazquez, J.L.: Enhanced synchrony in epileptiform activity? Local versus distant phase synchronization in generalized seizures. J. Neurosci. 31, 8077–8084 (2005)
Pikovsky, A., Rosemblum, M.G., Kurths, J.: Synchronization: a universal concept in nonlinear sciences. Cambrige University Press, Cambridge (2001)
Simonotto, E., Spano, F., Riani, M., Ferrari, A., Levrero, F., Pilot, A., Renzetti, P., Parodi, R.C., Sardanelli, F., Vitali, P., Twitty, J., Chiou-Tan, F., Moss, F.: fMRI studies of visual cortical activity during noise stimulation. Neurocomputing 26–27, 511–516 (1999)
Anishchenko, V.S., Astakhov, V.V., Neiman, A.B., Vadivasova, T.E., Schimansky-Geier, L.: Nonlinear dynamics of chaotic and stochastic systems. Springer, Berlin (2002)
Guevara Erra, R., Pérez Velazquez, J.L., Nenadovic, V., Wennberg, R., Senjanovic, G., García Dominguez, L.: Phase synchronization measurements using electroencephalographic recordings: what can we really say about neuronal synchrony? Neuroinformatics 3, 301–313 (2005)
Levelt, W.J.: Binocular brightness averaging and contour information. Br. J. Psychol. 56, 1–13 (1965)
Babiloni, C., Bares, M., Vecchio, F., Brazdil, M., Jurak, P., Moretti, D.V., Usbaldi, A., Rossini, P.M., Rektor, I.: Synchronization of gamma oscillations increases functional connectivity of human hippocampus and inferior-middle temporal cortex during repetitive visuomotor events. Eur. J. Neurosci. 19, 3088–3098 (2004)
Srinivasan, R., Russell, D.P., Edelman, G.M., Tononi, G.: Increased synchronization of neuromagnetic responses during conscious perception. J. Neurosci. 19, 5435–5448 (1999)
Mima, T., Oluwatimilehin, T., Hiraoka, T., Hallett, M.: Transient interhemispheric neuronal synchrony correlates with object recognition. J. Neurosci. 21, 3942–3948 (2001)
Desmedt, J., Tomberg, C.: Transient phase-locking of 40 Hz electrical oscillations in prefrontal and parietal human cortex reflects the process of conscious somatic perception. Neurosci. Lett. 168, 126–129 (1994)
Lamme, V.A.F.: Why visual attention and awareness are different. Trends Cogn. Sci. 7, 12–18 (2003)
Tononi, G., Edelman, G.M., Sporns, O.: Complexity and coherency: integrating information in the brain. Trends Cogn. Sci. 2, 474–484 (1998)
Kitajo, K., Yamanaka, Nozaki, D., Ward, L.M., Yamamoto, Y.: Behavioral stochastic resonance is associated with large-scale synchronization of human brain activity. In: Abbott, Bezrukov, Sanchez (eds.) Fluctuations and noise in biological, biophysical, and biomedical systems II. Proc. of SPIE Vol 5467 (2004)
Fuster, J.M.: The prefrontal cortex: anatomy, physiology and neuropsychology of the frontal lobe. Lippincott-Raven, Philadelphia (1997)
Fuster, J.M.: Cortex and mind. Oxford University Press, Oxford (2003)
Lumer E.D., Rees, G.: Covariation of activity in visual and prefrontal cortex associated with subjective visual perception. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 96, 1669–1673 (1999)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Velazquez, J.L.P., Dominguez, L.G. & Erra, R.G. Fluctuations in Neuronal Synchronization in Brain Activity Correlate with the Subjective Experience of Visual Recognition. J Biol Phys 33, 49–59 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10867-007-9041-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10867-007-9041-4