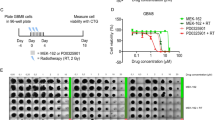
Abstract
Radiotherapy is a cancer treatment protocol which delivers high dose of ionizing radiation (IR) to tumor. Tumor resistance and side effects induced by IR still are the major challenges in radiotherapy. The purpose of this study was to evaluate the synergistic killing effect of fluoxetine (FL) with IR on glioma cancer cell (U-87 MG), as well as radioprotective effect of FL against cellular toxicity induced by IR on non-malignant human fibroblast cell (HFFF2). Firstly, the inhibitory effects of FL on cell proliferations were evaluated in U-87 MG and HFFF2 cells. The clonogenic and MTT assays were used to evaluate the radiosensitivity and radioprotective effects of FL on cancer and non-malignant cells. The frequencies of apoptotic cells were evaluated by flow cytometry on both cancer and normal cells. Results showed that FL exhibited anti-cancer effect on glioma cells, while cellular toxicity was low in HFFF2 cells treated with FL. FL decreased the viable colonies and enhanced apoptotic cells when U-87 cells were treated with FL prior irradiation. For comparison, FL exhibited radioprotective effect through increasing cellular proliferation rate and reducing apoptosis in HFFF2 cells against IR. The results showed that FL enhanced the IR-induced glioma cancer cell death and apoptosis, whereas it exhibited a radioprotective effect on normal fibroblast cells suggesting that FL administration may improve glioma radiotherapy.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Buch K, Peters T, Nawroth T, Sanger M, Schmidberger H, Langguth P (2012) Determination of cell survival after irradiation via clonogenic assay versus multiple MTT assay--a comparative study. Radiat Oncol 7:1. https://doi.org/10.1186/1748-717X-7-1
Caiaffo V, Oliveira BD, de Sa FB, Evencio Neto J (2016) Anti-inflammatory, antiapoptotic, and antioxidant activity of fluoxetine. Pharmacol Res Perspect 4(3):e00231. https://doi.org/10.1002/prp2.231
Cheki M, Shirazi A, Mahmoudzadeh A, Bazzaz JT, Hosseinimehr SJ (2016) The radioprotective effect of metformin against cytotoxicity and genotoxicity induced by ionizing radiation in cultured human blood lymphocytes. Mutat Res 809:24–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mrgentox.2016.09.001
Cho HJ, Ahn KC, Choi JY, Hwang SG, Kim WJ, Um HD et al (2015) Luteolin acts as a radiosensitizer in nonsmall cell lung cancer cells by enhancing apoptotic cell death through activation of a p38/ROS/caspase cascade. Int J Oncol 46(3):1149–1158. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijo.2015.2831
Choi JH, Jeong YJ, Yu AR, Yoon KS, Choe W, Ha J, Kim SS, Yeo EJ, Kang I (2017) Fluoxetine induces apoptosis through endoplasmic reticulum stress via mitogen-activated protein kinase activation and histone hyperacetylation in SK-N-BE(2)-M17 human neuroblastoma cells. Apoptosis 22(9):1079–1097. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-017-1390-2
Dagur RS, Hambarde S, Chandna S (2015) Bryostatin-1 causes radiosensitization of BMG-1 malignant glioma cells through differential activation of protein kinase-Cdelta not evident in the non-malignant AA8 fibroblasts. Mol Cell Biochem 401(1–2):49–59. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-014-2291-0
Fasih A, Elbaz HA, Huttemann M, Konski AA, Zielske SP (2014) Radiosensitization of pancreatic cancer cells by metformin through the AMPK pathway. Radiat Res 182(1):50–59. https://doi.org/10.1667/RR13568.1
Hosseinimehr SJ (2007) Trends in the development of radioprotective agents. Drug Discov Today 12(19–20):794–805. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.drudis.2007.07.017
Hosseinimehr SJ (2010) Flavonoids and genomic instability induced by ionizing radiation. Drug Discov Today 15(21):907–918
Hosseinimehr SJ, Zakaryaee V, Froughizadeh M (2006) Oral oxymetholone reduces mortality induced by gamma irradiation in mice through stimulation of hematopoietic cells. Mol Cell Biochem 287(1–2):193–199. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-005-9111-5
Hosseinimehr SJ, Nobakht R, Ghasemi A, Pourfallah TA (2015) Radioprotective effect of mefenamic acid against radiation-induced genotoxicity in human lymphocytes. Radiat Oncol J 33(3):256–260. https://doi.org/10.3857/roj.2015.33.3.256
Hosseinimehr SJ, Fathi M, Ghasemi A, Shiadeh SN, Pourfallah TA (2017) Celecoxib mitigates genotoxicity induced by ionizing radiation in human blood lymphocytes. Res Pharm Sci 12(1):82–87. https://doi.org/10.4103/1735-5362.199051
Hosseinimehr SJ, Safavi Z, Kangarani Farahani S, Noaparst Z, Ghasemi A, Asgarian-Omran H (2019) The synergistic effect of mefenamic acid with ionizing radiation in colon cancer. J Bioenerg Biomembr 51(3):249–257. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10863-019-09792-w
Kannen V, Garcia SB, Silva WA Jr, Gasser M, Monch R, Alho EJ et al (2015) Oncostatic effects of fluoxetine in experimental colon cancer models. Cell Signal 27(9):1781–1788. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cellsig.2015.05.008
Kawada K, Yonei T, Ueoka H, Kiura K, Tabata M, Takigawa N et al (2002) Comparison of chemosensitivity tests: clonogenic assay versus MTT assay. Acta Med Okayama 56(3):129–134. https://doi.org/10.18926/AMO/31714
Kumar SS, Sengupta S, Lee K, Hura N, Fuller C, DeWire M et al (2017) BMI-1 is a potential therapeutic target in diffuse intrinsic pontine glioma. Oncotarget 8(38):62962–62975. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.18002
Liu KH, Yang ST, Lin YK, Lin JW, Lee YH, Wang JY et al (2015) Fluoxetine, an antidepressant, suppresses glioblastoma by evoking AMPAR-mediated calcium-dependent apoptosis. Oncotarget 6(7):5088–5101. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.3243
Liu Y, Shen Y, Sun T, Yang W (2017) Mechanisms regulating radiosensitivity of glioma stem cells. Neoplasma 64(5):655–665. https://doi.org/10.4149/neo_2017_502
Ma J, Yang YR, Chen W, Chen MH, Wang H, Wang XD, Sun LL, Wang FZ, Wang DC (2016) Fluoxetine synergizes with temozolomide to induce the CHOP-dependent endoplasmic reticulum stress-related apoptosis pathway in glioma cells. Oncol Rep 36(2):676–684. https://doi.org/10.3892/or.2016.4860
Materska M, Konopacka M, Rogolinski J, Slosarek K (2015) Antioxidant activity and protective effects against oxidative damage of human cells induced by X-radiation of phenolic glycosides isolated from pepper fruits Capsicum annuum L. Food Chem 168:546–553. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2014.07.023
Raaphorst GP, Feeley MM, Da Silva VF, Danjoux CE, Gerig LH (1989) A comparison of heat and radiation sensitivity of three human glioma cell lines. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 17(3):615–622. https://doi.org/10.1016/0360-3016(89)90114-4
Rizzo AE, Yu JS (2015) Radiation therapy for glioma stem cells. Adv Exp Med Biol 853:85–110. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-16537-0_6
Salehifar E, Hosseinimehr SJ (2016) The use of cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitors for improvement of efficacy of radiotherapy in cancers. Drug Discov Today 21(4):654–662. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.drudis.2016.02.019
Shan H, Bian Y, Shu Z, Zhang L, Zhu J, Ding J, Lu M, Xiao M, Hu G (2016) Fluoxetine protects against IL-1beta-induced neuronal apoptosis via downregulation of p53. Neuropharmacology 107:68–78. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropharm.2016.03.019
Slamon ND, Pentreath VW (2000) Antioxidant defense against antidepressants in C6 and 1321N1 cells. Chem Biol Interact 127(3):181–199
Sun D, Zhu L, Zhao Y, Jiang Y, Chen L, Yu Y, Ouyang L (2018) Fluoxetine induces autophagic cell death via eEF2K-AMPK-mTOR-ULK complex axis in triple negative breast cancer. Cell Prolif 51(2):e12402. https://doi.org/10.1111/cpr.12402
Tsuboi K, Moritake T, Tsuchida Y, Tokuuye K, Matsumura A, Ando K (2007) Cell cycle checkpoint and apoptosis induction in glioblastoma cells and fibroblasts irradiated with carbon beam. J Radiat Res 48(4):317–325. https://doi.org/10.1269/jrr.06081
Wu JY, Lin SS, Hsu FT, Chung JG (2018) Fluoxetine inhibits DNA repair and NF-kB-modulated metastatic potential in non-small cell lung Cancer. Anticancer Res 38(9):5201–5210. https://doi.org/10.21873/anticanres.12843
Yaman OM, Erman H, Guner I, Tok OE, Pala M, Esrefoglu M, Gelisgen R, Uzun H, Aksu U, Yelmen N, Sahin G (2018) Remote myocardial injury: the protective role of fluoxetine. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 96(4):319–327. https://doi.org/10.1139/cjpp-2017-0383
Yang Y, Zhou H, Zhang G, Xue X (2019) Targeting the canonical Wnt/beta-catenin pathway in cancer radioresistance: updates on the molecular mechanisms. J Cancer Res Ther 15(2):272–277. https://doi.org/10.4103/jcrt.JCRT_421_18
Yazdannejat H, Hosseinimehr SJ, Ghasemi A, Pourfallah TA, Rafiei A (2016) Losartan sensitizes selectively prostate cancer cell to ionizing radiation. Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand) 62(1):30–33
Zhou T, Duan J, Wang Y, Chen X, Zhou G, Wang R, Fu L, Xu F (2012) Fluoxetine synergys with anticancer drugs to overcome multidrug resistance in breast cancer cells. Tumour Biol 33(5):1299–1306. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-012-0377-4
Acknowledgments
Mazandaran University of Medical Sciences (Iran) supported this study (Grant ID = 2774).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article was not containing any study with human participants or animals.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hosseinimehr, S.J., Najafi, S.H., Shafiee, F. et al. Fluoxetine as an antidepressant medicine improves the effects of ionizing radiation for the treatment of glioma. J Bioenerg Biomembr 52, 165–174 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10863-020-09833-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10863-020-09833-9