Abstract
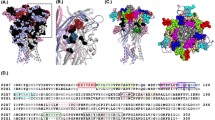
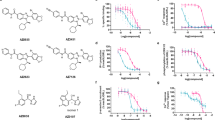
The P2X7 receptor (P2X7R) is an ion channel which is activated by interactions with the extracellular ATP molecules. The molecular complex P2X7R/ATP induces conformational changes in the protein subunits, opening a pore in the ion channel macromolecular structure. Currently, the P2X7R has been studied as a potential therapeutic target of anti-inflammatory drugs. Based on this, a series of eight boronic acids (NO) analogs were evaluated on the biologic effect of this pharmacophoric group on the human and murine P2X7R. The boronic acids derivatives NO-01 and NO-12 inhibited in vitro human and murine P2X7R function. These analogs compounds showed effect better than compound BBG and similar to inhibitor A740003 for inhibiting dye uptake, in vitro IL-1β release and ATP-induced paw edema in vivo. In both, in vitro and in vivo assays the compound NO-01 showed to be the hit compound in the present series of the arylboronic acids analogs. The molecular docking suggests that the NO derivatives bind into the upper body domain of the P2X7 pore and that the main intermolecular interaction with the two most active NO derivatives occur with the residues Phe 95, 103 and 293 by hydrophobic interactions and with Leu97, Gln98 and Ser101 by hydrogen bonds.. These results indicate that the boronic acid derivative NO-01 shows the lead compound characteristics to be used as a scaffold structure to the development of new P2X7R inhibitors with anti-inflammatory action.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmed V, Liu Y, Silvestro C, Taylor SD (2006) Boronic acids as inhibitors of steroid sulfatase. Bioorg Med Chem 14:8564–8573. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmc.2006.08.033
Allsopp RC, Dayl S, Schmid R, Evans RJ (2017) Unique residues in the ATP gated human P2X7 receptor define a novel allosteric binding pocket for the selective antagonist AZ10606120. Sci Rep 7:725
Asano T, Nakamura H, Uehara Y, Yamamoto Y (2004) Design, synthesis, and biological evaluation of aminoboronic acids as growth-factor receptor inhibitors of EGFR and VEGFR-1 tyrosine kinases. Chembiochem Eur J Chem Biol 5:483–490. https://doi.org/10.1002/cbic.200300748
Baas T (2012) Paradoxical P2X7. Sci-Bus Exch 5:512–512. https://doi.org/10.1038/scibx.2012.512
Baker SJ, Ding CZ, Akama T, Zhang Y-K, Hernandez V, Xia Y (2009) Therapeutic potential of boron-containing compounds. Future Med Chem 1:1275–1288. https://doi.org/10.4155/fmc.09.71
Ban HS, Nakamura H (2015) Boron-based drug design. Chem Rec N Y N 15:616–635. https://doi.org/10.1002/tcr.201402100
Ban HS, Usui T, Nabeyama W, Morita H, Fukuzawa K, Nakamura H (2009) Discovery of boron-conjugated 4-anilinoquinazoline as a prolonged inhibitor of EGFR tyrosine kinase. Org Biomol Chem 7:4415–4427. https://doi.org/10.1039/b909504g
Bartlett R, Stokes L, Sluyter R (2014) The P2X7 receptor channel: recent developments and the use of P2X7 antagonists in models of disease. Pharmacol Rev 66:638–675. https://doi.org/10.1124/pr.113.008003
Baudelet D, Lipka E, Millet R, Ghinet A (2015) Involvement of the P2X7 purinergic receptor in inflammation: an update of antagonists series since 2009 and their promising therapeutic potential. Curr Med Chem 22:713–729
Bhattacharya B, Maity DK, Pachfule P, Colacio E, Ghoshal D (2014) Syntheses, X-ray structures, catalytic activity and magnetic properties of two new coordination polymers of Co(II) and Ni(II) based on benzenedicarboxylate and linear N,N′-donor Schiff base linkers. Inorg Chem Front 1:414–425. https://doi.org/10.1039/c4qi00032c
Bradke TM, Hall C, Carper SW, Plopper GE (2008) Phenylboronic acid selectively inhibits human prostate and breast cancer cell migration and decreases viability. Cell Adhes Migr 2:153–160
Buac D, Shen M, Schmitt S, Kona FR, Deshmukh R, Zhang Z, Neslund-Dudas C, Mitra B, Dou QP (2013) From bortezomib to other inhibitors of the proteasome and beyond. Curr Pharm Des 19:4025–4038
Burnstock G, Knight GE (2018) The potential of P2X7 receptors as a therapeutic target, including inflammation and tumour progression. Purinergic Signal 14:1–18. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11302-017-9593-0
Cabello JA, Campelo JM, Garcia A, Luna D, Marinas JM (1984) Knoevenagel condensation in the heterogeneous phase using aluminum phosphate-aluminum oxide as a new catalyst. J Org Chem 49:5195–5197. https://doi.org/10.1021/jo00200a036
Cambre JN, Sumerlin BS (2011) Biomedical applications of boronic acid polymers. Polymer 52:4631–4643. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymer.2011.07.057
Caseleya EA, Muencha SP, Fishwickb CW, Jiang L (2016) Structure-based identification and characterisation of structurally novel human P2X7 receptor antagonists. Biochem Pharmacol 116(15):130–139
Chen Z, He L, Li L, Chen L (2018) The P2X7 purinergic receptor: an emerging therapeutic target in cardiovascular diseases. Clin Chim Acta Int J Clin Chem 479:196–207. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cca.2018.01.032
Cheng F, Li W, Zhou Y, Shen J, Wu Z, Liu G, Lee PW, Tang Y (2012) admetSAR: a comprehensive source and free tool for assessment of chemical ADMET properties. J Chem Inf Model 52:3099–3105. https://doi.org/10.1021/ci300367a
Das BC, Thapa P, Karki R, Schinke C, Das S, Kambhampati S, Banerjee SK, Van Veldhuizen P, Verma A, Weiss LM, Evans T (2013) Boron chemicals in diagnosis and therapeutics. Future Med Chem 5:653–676. https://doi.org/10.4155/fmc.13.38
de Resende Filho JBM, Pires GP, de Oliveira Ferreira JMG, Teotonio EES, Vale JA (2017) Knoevenagel condensation of aldehydes and ketones with Malononitrile catalyzed by amine compounds-tethered Fe3O4@SiO2 nanoparticles. Catal Lett 147:167–180. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10562-016-1916-1
Deb, M.L., Bhuyan, P.J., 2005. Uncatalysed Knoevenagel condensation in aqueous medium at room temperature - PDF free download [WWW document]. Tetrahedron Lett. URL https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S004040390501631X (accessed 9.20.18)
Diaz DB, Yudin AK (2017) The versatility of boron in biological target engagement. Nat Chem 9:731–742. https://doi.org/10.1038/nchem.2814
Dimitrova P, Ivanovska N (2013) Tyrphostins as a promising therapeutic tool in inflammation-related conditions. OA Inflamm 1. https://doi.org/10.13172/2052-787X-1-1-608
Donnelly-Roberts DL, Namovic MT, Surber B, Vaidyanathan SX, Perez-Medrano A, Wang Y, Carroll WA, Jarvis MF (2009) [3H]A-804598 ([3H]2-cyano-1-[(1S)-1-phenylethyl]-3-quinolin-5-ylguanidine) is a novel, potent, and selective antagonist radioligand for P2X7 receptors. Neuropharm. 56:223–229
Dou QP, Zonder JA (2014) Overview of proteasome inhibitor-based anti-cancer therapies: perspective on bortezomib and second generation proteasome inhibitors versus future generation inhibitors of ubiquitin-proteasome system. Curr. Cancer Drug Targets 14:517–536
Faria RX, Freitas HR, Reis RAM (2017) P2X7 receptor large pore signaling in avian Müller glial cells. J Bioenerg Biomembr 49:215–229. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10863-017-9717-9
Faria RX, Oliveira FH, Salles JP, Oliveira AS, von Ranke NL, Bello ML, Rodrigues CR, Castro HC, Louvis AR, Martins DL, Ferreira VF (2018) 1,4-naphthoquinones potently inhibiting P2X7 receptor activity. Eur J Med Chem 143:1361–1372. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmech.2017.10.033
Fleming FF, Yao L, Ravikumar PC, Funk L, Shook BC (2010) Nitrile-containing pharmaceuticals: efficacious roles of the nitrile pharmacophore. J Med Chem 53:7902–7917. https://doi.org/10.1021/jm100762r
Gonzaga DTG, Gomes LB, Costa TEMC, von Ranke NL, Pacheco PAF, Simões APS, Arruda JC, Dantas LP, de Freiras HR, Reis RA, Penido C, Bello ML, Castro HC, Rodrigues CRR, Ferreira VF, Faria RX, Silva FC (2017) 1-Aryl-1H- and 2-aryl-2H-1,2,3-triazole derivatives blockade P2X7 receptor in vitro and inflammatory response in vivo. Eur J Med Chem 139:698–717. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmech.2017.08.034
Gorodeski GI (2012) P2X7 receptors and epithelial cancers. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Membr Transp Signal 1:349–371. https://doi.org/10.1002/wmts.33
Groziak MP (2001) Boron therapeutics on the horizon. Am J Ther 8:321–328
Gyurkovska V, Stefanova T, Dimitrova P, Danova S, Tropcheva R, Ivanovska N (2014) Tyrosine kinase inhibitor tyrphostin AG490 retards chronic joint inflammation in mice. Inflammation 37:995–1005. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-014-9820-6
Halgren TA (1996) Merck molecular force field. I. Basis, form, scope, parameterization, and performance of MMFF94. J Comput Chem 17:490–519. https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1096-987X(199604)17:5/6<490::AID-JCC1>3.0.CO;2-P
Hiller N d J, Silva NAAE, Faria RX, Souza ALA, Resende JALC, Borges Farias A, Correia Romeiro N, de Luna Martins D (2018) Synthesis and evaluation of the anticancer and Trypanocidal activities of Boronic Tyrphostins. ChemMedChem 13:1395–1404. https://doi.org/10.1002/cmdc.201800206
Humphreys, B.D., Virginio, C., Surprenant, A., Rice, J., Dubyak, G.R., 1998. Isoquinolines as antagonists of the P2X7 nucleotide receptor: high selectivity for the human versus rat receptor homologues. Mol Pharmacol. Jul;54(1):22-32
Jiang LH, MacKenzie AB, North RA, Surprenant A (2000) BBG selectively blocks ATP-gated rat P2X7 receptors. Mol Pharmacol 58:82–88
Karasawa A, Kawate T (2016) Structural basis for subtype-specific inhibition of the P2X7 receptor. eLife 5. https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.22153
Kim M, Jiang LH, Wilson HL, North RA, Surprenant A (2001) Proteomic and functional evidence for a P2X7 receptor signalling complex. EMBO J 20:6347–6358. https://doi.org/10.1093/emboj/20.22.6347
Koehler KA, Lienhard GE (1971) 2-phenylethaneboronic acid, a possible transition-state analog for chymotrypsin. Biochemistry 10:2477–2483
Kumar SK, Hager E, Pettit C, Gurulingappa H, Davidson NE, Khan SR (2003) Design, synthesis, and evaluation of novel boronic-chalcone derivatives as antitumor agents. J Med Chem 46:2813–2815. https://doi.org/10.1021/jm030213+
Kwak SH, Shin S, Lee JH, Shim JK, Kim M, Lee SD, Lee A, Bae J, Park JH, Abdelrahman A, Müller CE, Cho SK, Kang SG, Bae MA, Yang JY, Ko H, Goddard WA, Kim YC (2018) Synthesis and structure-activity relationships of quinolinone and quinoline-based P2X7 receptor antagonists and their anti-sphere formation activities in glioblastoma cells. Eur J Med Chem 151:462–481
Lagunin A, Filimonov D, Zakharov A, Xie W, Huang Y, Zhu F, Shen T, Yao J, Poroikov V (2009) Computer-aided prediction of rodent carcinogenicity by PASS and CISOC-PSCT. QSAR Comb Sci 28:806–810. https://doi.org/10.1002/qsar.200860192
LeBeau AM, Singh P, Isaacs JT, Denmeade SR (2008) Potent and selective peptidyl Boronic acid inhibitors of the serine protease prostate-specific antigen. Chem Biol 15:665–674. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chembiol.2008.05.020
Li G, Xiao J, Zhang W (2011) Knoevenagel condensation catalyzed by a tertiary-amine functionalized polyacrylonitrile fiber. Green Chem 13:1828–1836. https://doi.org/10.1039/C0GC00877J
Marchese Robinson RL, Glen RC, Mitchell JBO (2011) Development and comparison of hERG blocker classifiers: assessment on different datasets yields markedly different results. Mol Inform 30:443–458. https://doi.org/10.1002/minf.201000159
Matthews DA, Alden RA, Birktoft JJ, Freer ST, Kraut J (1975) X-ray crystallographic study of boronic acid adducts with subtilisin BPN’ (novo). A model for the catalytic transition state J Biol Chem 250:7120–7126
Mehta N, Kaur M, Singh M, Chand S, Vyas B, Silakari P, Bahia MS, Silakari O (2014) Purinergic receptor P2X7: a novel target for anti-inflammatory therapy. Bioorg Med Chem 22:54–88. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmc.2013.10.054
Modzelewska A, Pettit C, Achanta G, Davidson NE, Huang P, Khan SR (2006) Anticancer activities of novel chalcone and bis-chalcone derivatives. Bioorg Med Chem 14:3491–3495. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmc.2006.01.003
Mukhopadhyay C, Datta A (2008) A simple, efficient and green procedure for the Knoevenagel condensation of aldehydes with N-Methylpiperazine at room temperature under solvent-free conditions. Synth Commun 38:2103–2112. https://doi.org/10.1080/00397910802029364
Nakamura H, Kuroda H, Saito H, Suzuki R, Yamori T, Maruyama K, Haga T (2006) Synthesis and biological evaluation of boronic acid containing cis-stilbenes as apoptotic tubulin polymerization inhibitors. ChemMedChem 1:729–740. https://doi.org/10.1002/cmdc.200600068
North RA (2002) Molecular physiology of P2X receptors. Physiol Rev 82:1013–1067. https://doi.org/10.1152/physrev.00015.2002
O'Brien-Brown, J., Jackson, A., Reekie, T.A., Barron, M.L., Werry, E.L., Schiavini, P., McDonnell, M., Munoz, L., Wilkinson, S., Noll, B., Wang, S., Kassiou, M., 2017. Discovery and pharmacological evaluation of a novel series of adamantyl cyanoguanidines as P2X7 receptor antagonists. Eur J med Chem. Apr 21;130:433-439
Pacheco PAF, Galvão RMS, Faria AFM, von Ranke, NL, Rangel MS, Ribeiro TM, Bello ML, Rodrigues CF, Ferreira VF, da Rocha DR, Faria RX (2018) 8-Hydroxy-2-(1H-1,2,3-triazol-1-yl)-1,4-naphtoquinone derivatives inhibited P2X7 Receptor-Induced dye uptake into murine Macrophages. Bioorg Med Chem 27:1449–1455
Pham The H, González-Álvarez I, Bermejo M, Mangas Sanjuan V, Centelles I, Garrigues TM, Cabrera-Pérez MÁ (2011) In silico prediction of Caco-2 cell permeability by a classification QSAR approach. Mol. Inform. 30:376–385. https://doi.org/10.1002/minf.201000118
Philipp M, Bender ML (1971) Inhibition of serine proteases by arylboronic acids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 68:478–480
Rech JC, Bhattacharya A, Letavic MA, Savall BM (2016) The evolution of P2X7 antagonists with a focus on CNS indications. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 26:3838–3845. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmcl.2016.06.048
Ren Y, Cai C (2007) Knoevenagel condensation of aromatic aldehydes with active methylene compounds using a catalytic amount of iodine and K 2 CO 3 at room temperature. Synth Commun 37:2209–2213. https://doi.org/10.1080/00397910701397375
Rocha GB, Freire RO, Simas AM, Stewart JJP (2006) RM1: a reparameterization of AM1 for H, C, N, O, P, S, F, cl, Br, and I. J Comput Chem 27:1101–1111. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcc.20425
Savio LEB, de Andrade Mello P, da Silva CG, Coutinho-Silva R (2018) The P2X7 receptor in inflammatory diseases: angel or demon? Front Pharmacol 9:52. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2018.00052
Shemon AN, Sluyter R, Fernando SL, Clarke AL, Dao-Ung L-P, Skarratt KK, Saunders BM, Tan KS, Gu BJ, Fuller SJ, Britton WJ, Petrou S, Wiley JS (2006) A Thr357 to Ser polymorphism in homozygous and compound heterozygous subjects causes absent or reduced P2X7 function and impairs ATP-induced mycobacterial killing by macrophages. J Biol Chem 281:2079–2086. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M507816200
Shen J, Cheng F, Xu Y, Li W, Tang Y (2010) Estimation of ADME properties with substructure pattern recognition. J Chem Inf Model 50:1034–1041. https://doi.org/10.1021/ci100104j
Shimizu K, Maruyama M, Yasui Y, Minegishi H, Ban HS, Nakamura H (2010) Boron-containing phenoxyacetanilide derivatives as hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)-1alpha inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 20:1453–1456. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmcl.2009.12.037
Skaper SD (2011) Ion channels on microglia: therapeutic targets for neuroprotection. CNS Neurol. Disord. Drug Targets 10:44–56
Suenaga H, Nakashima K, Mikami M, Yamamoto H, James TD, Sandanayake KRAS, Shinkai S (1996) Screening of arylboronic acids to search for a strong inhibitor for γ-glutamyl transpeptidase (γ-GTP). Recl Trav Chim Pays-Bas-J R Neth 115:44–48
Sugiyama T (2014) Role of P2X7 receptors in the development of diabetic retinopathy. World J Diabetes 5:141–145. https://doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v5.i2.141
Swain M (2012) Chemicalize.Orgchemicalize.Orgby ChemAxon ltd. J Chem Inf Model 52:613–615. https://doi.org/10.1021/ci300046g
Thomsen R, Christensen MH (2006) MolDock: a new technique for high-accuracy molecular docking. J Med Chem 49:3315–3321. https://doi.org/10.1021/jm051197e
Tsuda M, Tozaki-Saitoh H, Inoue K (2010) Pain and purinergic signaling. Brain Res Rev 63:222–232. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainresrev.2009.11.003
Volonté C, Apolloni S, Skaper SD, Burnstock G (2012) P2X7 receptors: channels, pores and more. CNS Neurol. Disord. Drug Targets 11:705–721
Wang S, Ren Z, Cao W, Tong W (2001) The Knoevenagel condensation of aromatic aldehydes with Malononitrile or ethyl Cyanoacetate in the presence of Ctmab in water. Synth Commun 31:673–677. https://doi.org/10.1081/SCC-100103255
Weston GS, Blázquez J, Baquero F, Shoichet BK (1998) Structure-based enhancement of boronic acid-based inhibitors of AmpC beta-lactamase. J Med Chem 41:4577–4586. https://doi.org/10.1021/jm980343w
Young CNJ, Górecki DC (2018) P2RX7 Purinoceptor as a therapeutic target-The second coming? Front Chem 6:248. https://doi.org/10.3389/fchem.2018.00248
Zervosen A, Sauvage E, Frère J-M, Charlier P, Luxen A (2012) Development of new drugs for an old target: the penicillin binding proteins. Mol Basel Switz 17:12478–12505. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules171112478
Acknowledgements
CAPES, CNPq, FAPERJ, UFRJ, UFF.
Funding
This work was supported by CNPq (National Council of Research of Brazil) (Fellowship Process Number 304716/2014–6).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Supplemental Figure 1
Representative macroscopic ionic currents obtained from peritoneal macrophages treated with ATP alone or in the presence of P2X7R antagonists. The arrow represents the moment of ATP addition. NO-01 and A740003 were added 5 minutes before ATP application. All recordings were measured in a holding potential of – 60 mV.
Supplemental Figure 2
Representative macroscopic ionic currents obtained from peritoneal macrophages treated with ATP alone or in the presence of P2X7R antagonists. The arrow represents the moment of ATP addition. NO-12 and A740003 were added 5 minutes before ATP application. All recordings were measured in a holding potential of – 60 mV.
ESM 3
(DOC 122 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Faria, R.X., de Jesus Hiller, N., Salles, J.P. et al. Arylboronic acids inhibit P2X7 receptor function and the acute inflammatory response. J Bioenerg Biomembr 51, 277–290 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10863-019-09802-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10863-019-09802-x