Abstract
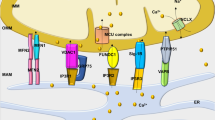
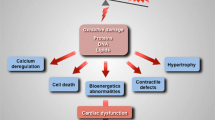
Ca2+ has been well accepted as a signal that coordinates changes in cytosolic workload with mitochondrial energy metabolism in cardiomyocytes. During increased work, Ca2+ is accumulated in mitochondria and stimulates ATP production to match energy supply and demand. The kinetics of mitochondrial Ca2+ ([Ca2+]m) uptake remains unclear, and we review the debate on this subject in this article. [Ca2+]m has multiple targets in oxidative phosphorylation including the F1/FO ATPase, the adenine nucleotide translocase, and Ca2+-sensitive dehydrogenases (CaDH) of the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle. The well established effect of [Ca2+]m is to activate CaDHs of the TCA cycle to increase NADH production. Maintaining NADH level is not only critical to keep a high oxidative phosphorylation rate during increased cardiac work, but is also necessary for the reducing system of the cell to maintain its reactive oxygen species (ROS) —scavenging capacity. Further, we review recent data demonstrating the deleterious effects of elevated Na+ in cardiac pathology by blunting [Ca2+]m accumulation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Babsky A, Doliba N, Doliba N, Savchenko A, Wehrli S, Osbakken M (2001) Exp Biol Med (Maywood) 226:543–551
Balaban RS (2002) J Mol Cell Cardiol 34:1259–1271
Balaban RS, Kantor HL, Katz LA, Briggs RW (1986) Science 232:1121–1123
Bell CJ, Bright NA, Rutter GA, Griffiths EJ (2006) J Biol Chem 281:28058–28067
Bender E, Kadenbach B (2000) FEBS Lett 466:130–134
Bers DM, Barry WH, Despa S (2003) Cardiovasc Res 57:897–912
Brandes R, Bers DM (2002) Biophys J 83:587–604
Chance B, Williams GR (1955) Nature 176:250–254
Cox DA, Matlib MA (1993) J Biol Chem 268:938–947
Crompton M, Heid I (1978) Eur J Biochem 91:599–608
Denton RM, McCormack JG (1990) Annu Rev Physiol 52:451–466
Droge W (2002) Physiol Rev 82:47–95
Giordano FJ (2005) J Clin Invest 115:500–508
Griffiths EJ, Wei SK, Haigney MC, Ocampo CJ, Stern MD, Silverman HS (1997) Cell Calcium 21:321–329
Gunter TE, Gunter KK, Sheu SS, Gavin CE (1994) Am J Physiol 267:C313–339
Gunter TE, Pfeiffer DR (1990) Am J Physiol 258:C755–786
Gunter TE, Yule DI, Gunter KK, Eliseev RA, Salter JD (2004) FEBS Lett 567:96–102
Hansford RG (1991) J Bioenerg Biomembr 23:823–854
Hansford RG, Castro F (1985) Biochem J 227:129–136
Harris DA, Das AM ((1991) Biochem J 280(Pt 3):561–573
Jo H, Noma A, Matsuoka S (2006) J Mol Cell Cardiol 40:394–404
Katz LA, Swain JA, Portman MA, Balaban RS (1989) Am J Physiol 256:H265–274
Kirichok Y, Krapivinsky G, Clapham DE (2004) Nature 427:360–364
Knopp A, Kohlhaas M, Maack C (2009) Biophys J 93:514a
Korzeniewski B (1998) Biochem J 330(Pt 3):1189–1195
Liu T, Brown DA, O’Rourke B (2009) CGP-37157 Abrogates The Adverse Effect Of Ouabain On Mitochondrial Energetics, in Biophys J p 243a.
Liu T, O’Rourke B (2008) Circ Res 103:279–288
Maack C, Cortassa S, Aon MA, Ganesan AN, Liu T, O’Rourke B (2006) Circ Res 99:172–182
Maack C, O’Rourke B (2007) Basic Res Cardiol 102:369–392
Mackenzie L, Roderick HL, Berridge MJ, Conway SJ, Bootman MD (2004) J Cell Sci 117:6327–6337
McCormack JG, Halestrap AP, Denton RM (1990) Physiol Rev 70:391–425
Mootha VK, Arai AE, Balaban RS (1997) Am J Physiol 272:H769–775
Moreno-Sanchez R (1985) J Biol Chem 260:12554–12560
Neely JR, Denton RM, England PJ, Randle PJ (1972) Biochem J 128:147–159
Nicholls D (2002) Sci Aging Knowledge Environ 2002:pe12.
O’Rourke B, Blatter LA (2009) J Mol Cell Cardiol Online in press.
O’Rourke B, Maack C (2007) Drug Discov Today Dis Models 4:207–217
Pfeiffer DR, Gunter TE, Eliseev R, Broekemeier KM, Gunter KK (2001) IUBMB Life 52:205–212
Pieske B, Houser SR (2003) Cardiovasc Res 57:874–886
Pogwizd SM, Sipido KR, Verdonck F, Bers DM (2003) Cardiovasc Res 57:887–896
Puskin JS, Gunter TE, Gunter KK, Russell PR (1976) Biochemistry 15:3834–3842
Robert V, Gurlini P, Tosello V, Nagai T, Miyawaki A, Di Lisa F, Pozzan T (2001) Embo J 20:4998–5007
Robitaille PM, Merkle H, Sako E, Lang G, Clack RM, Bianco R, From AH, Foker J, Ugurbil K (1990) Magn Reson Med 15:8–24
Rosier RN, Tucker DA, Meerdink S, Jain I, Gunter TE (1981) Arch Biochem Biophys 210:549–564
Saks V, Dzeja P, Schlattner U, Vendelin M, Terzic A, Wallimann T (2006) J Physiol 571:253–273
Saotome M, Katoh H, Satoh H, Nagasaka S, Yoshihara S, Terada H, Hayashi H (2005) Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 288:H1820–1828
Saris NE, Carafoli E (2005) Biochemistry (Mosc) 70:187–194
Schaefer S, Schwartz GG, Steinman SK, Meyerhoff DJ, Massie BM, Weiner MW (1992) Magn Reson Med 25:260–272
Sedova M, Dedkova EN, Blatter LA (2006) Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 291:C840–850
Seguchi H, Ritter M, Shizukuishi M, Ishida H, Chokoh G, Nakazawa H, Spitzer KW, Barry WH (2005) Cell Calcium 38:1–9
Territo PR, Mootha VK, French SA, Balaban RS (2000) Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 278:C423–435
Valko M, Leibfritz D, Moncol J, Cronin MT, Mazur M, Telser J (2007) Int J Biochem Cell Biol 39:44–84
Verdonck F, Volders PG, Vos MA, Sipido KR (2003) J Mol Cell Cardiol 35:5–25
Vogel R, Wiesinger H, Hamprecht B, Dringen R (1999) Neurosci Lett 275:97–100
Weiss RG, Bottomley PA, Hardy CJ, Gerstenblith G (1990) N Engl J Med 323:1593–1600
White RL, Wittenberg BA (1995) Biophys J 69:2790–2799
Yamada EW, Huzel NJ (1988) J Biol Chem 263:11498–11503
Zhou Z, Matlib MA, Bers DM (1998) J Physiol 507(Pt 2):379–403
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, T., O’Rourke, B. Regulation of mitochondrial Ca2+ and its effects on energetics and redox balance in normal and failing heart. J Bioenerg Biomembr 41, 127–132 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10863-009-9216-8
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10863-009-9216-8