Abstract
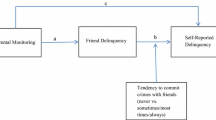
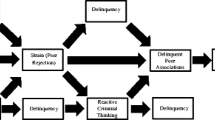
A link between delinquent peer affiliations and childhood delinquency has been consistently found in the literature. However, little to no research has examined how the characteristics of an individual may impact this association. Impulsivity may be an important individual characteristic to consider, as impulsivity is associated with childhood delinquency. Accordingly, the current study examined the potential moderating effect of impulsivity on the association between peer delinquency and child delinquency in a community sample of 89 children ranging from 9 to 12 years of age (mean = 10.4 ± 1.1 yrs). Findings suggest that at low levels of impulsivity peer delinquency and child delinquency were positively associated; however at high levels of impulsivity peer delinquency and child delinquency were not statistically related. These findings may suggest that children who exhibit low levels of impulsivity are particularly vulnerable to delinquent peer influences. Implications for findings are discussed.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aiken, L. S. & West, S. G. (1991). Multiple regression: Testing and interpreting interactions. Thousand Oaks: Sage.
Bagwell, C. L. Molina, B. S. G. Pelham, W. E. & Hoza, B. (2001). Attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder and problems in peer relations: predictions from childhood to adolescence. Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 40, 1285–1292.
Bauman, K. E. & Ennett, S. T. (1996). On the importance of peer influence for adolescent drug use: commonly neglected considerations. Addiction, 91, 185–198.
Biederman, J. Faraone, S. V. Milberger, S. Jetton, J. G. Chen, L. Mick, E. et al. (1996). Is childhood oppositional defiant disorder a precursor to adolescent conduct disorder? Findings from a four-year follow-up study of children with ADHD. Journal of the American Academy of Child & Adolescent Psychiatry, 35, 1193–1204.
Carroll, A. Hemingway, F. Bower, J. Ashman, A. Houghton, S. & Durkin, K. (2006). Impulsivity in juvenile delinquency: differences among early-onset, late-onset, and non-offenders. Journal of Youth and Adolescence, 35, 519–529.
Cashel, M. L. (2003). Validity of self-reports of delinquency and socio-emotional functioning among youth on probation. Journal of Offender Rehabilitation, 37, 11–23.
Caspi, A. Begg, D. Dickson, N. Harrington, H. Langley, J. Moffitt, T. E. et al. (1997). Personality differences predict health-risk behaviors in young adulthood: evidence from a longitudinal study. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 73, 1052–1063.
Cohen, J. Cohen, P. West, S. G. & Aiken, L. S. (2003). Applied multiple regression/correlation analyses for the behavioral sciences (3rd ed.). Mahwah: Erlbaum.
Coie, J. D. & Dodge, K. A. (1998). Aggression and antisocial behavior. In N. Eisenberg & W. Damon (Eds.), Handbook of child psychology: Social, emotional, and personality development, Vol. 3 (5th ed. pp. 779–862). New York: Wiley.
Coie, J. D. Terry, R. Zabriski, A. & Lochman, J. (1995). Early adolescent social influences on delinquent behaviour. In J. McCord (Ed.), Coercion and punishment in long term perspectives (pp. 229–244). Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Colder, C. R. & O’Connor, R. M. (2004). Gray’s reinforcement sensitivity model and child psychopathology: laboratory and questionnaire assessment of the BAS and BIS. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 32, 435–451.
Colder, C. R. & Stice, E. (1998). A longitudinal study of the interactive effects of impulsivity and anger on adolescent problem behavior. Journal of Youth and Adolescence, 27, 255–274.
Curran, P. J. Stice, E. & Chassin, L. (1997). The relation between adolescent alcohol use and peer alcohol use: a longitudinal random coefficients model. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 65, 130–140.
Darrick, J. Farrington, D. P. Hawkins, D. J. Catalano, R. F. Hill, K. G. & Kostermena, R. (2003). Predictive, concurrent, prospective and retrospective validity of self-reported delinquency. Criminal Behavior and Mental Health, 13, 179–197.
De Kemp, R. A. Scholte, R. H. Overbeek, G. & Engels, R. C. (2006). Early adolescent delinquency: the role of parents and best friends. Criminal Justice and Behavior, 33, 488–510.
Deptula, D. P. & Cohen, R. (2004). Aggressive, rejected, and delinquent children and adolescents: a comparison of their friendships. Aggression and Violent Behavior, 9, 75–104.
Dickman, S. J. (1993). Impulsivity and information processing. In W. G. McCown, J. L. Johnson & M. B. Shure (Eds.), The impulsive client: Theory, research, and treatment (pp. 151–184). Washington, D.C.: American Psychological Association.
Dishion, T. & Loeber, R. (1985). Adolescent marijuana and alcohol use: the role of parents and peers revisited. American Journal of Drug and Alcohol Abuse, 11, 1–25.
Dishion, T. J. Spracklen, K. M. Andrews, D. W. & Patterson, G. R. (1996). Deviancy training in male adolescents friendships. Behavior Therapy, 27, 373–390.
Dishion, T. J. Capaldi, D. M. & Yoerger, K. (1999). Middle childhood antecedents to progressions in male adolescent substance use: an ecological analysis of risk and protection. Journal of Adolescent Research, 14, 175–205.
Elliott, D. S. (1994). Longitudinal research in criminology: Promise and practice. In E. G. M. Weitekamp & H. J. Kerner (Eds.), Cross-national longitudinal research on human development and criminal behavior (pp. 189–201). Dordrecht: Kluwer Academic.
Elliott, D. S. Huizinga, D. & Ageton, S. S. (1985). Explaining delinquency and drug use. Newbury Park: Sage.
Eysenck, S. B. & Eysenck, H. J. (1977). The place of impulsiveness in a dimensional system of personality description. British Journal of Social and Clinical Psychology, 16, 57–68.
Farrington, D. P. & Loeber, R. (1999). Transatlantic replicability of risk factors in the development of delinquency. In P. Cohen, C. Slomkowski & L. N. Robins (Eds.), Historical and geographical influences on psychopathology (pp. 299–329). Mahwah: Erlbaum.
Fergusson, D. M. Woodward, L. J. & Horwood, L. (1999). Childhood peer relationship problems and young people’s involvement with deviant peers in adolescence. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 27, 357–369.
Fergusson, D. M. Swain-Campbell, N. R. & Horwood, L. (2002). Deviant peer affiliations, crime and substance use: a fixed effects regression analysis. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 30, 419–430.
Fite, P. J. & Colder, C. R. (2007). Proactive and reactive aggression and peer delinquency: implications for prevention and intervention. The Journal of Early Adolescence, 27, 223–240.
Fite, P. J. Colder, C. R. & O’Connor, R. M. (2006). Childhood behavior problems and peer selection and socialization: risk for adolescent alcohol use. Addictive Behaviors, 31, 1454–1459.
Fite, P. J., Wynn, P., & Pardini, D. A. (in press). Explaining discrepancies in arrest rates between black and white male juveniles. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology.
Gaertner, A. E., Fite, P. J., & Colder, C. R. (2009). Parenting and friendship quality as predictors of internalizing and externalizing symptoms in early adolescence. Journal of Child and Family Studies.
Hanlon, T. E. Bateman, R. W. Simon, B. D. O’Grady, K. E. & Carswell, S. B. (2002). An early community-based intervention for the prevention of substance abuse and other delinquent behavior. Journal of Youth and Adolescence, 31, 459–471.
Hawkins, J. Catalano, R. F. & Miller, J. Y. (1992). Risk and protective factors for alcohol and other drug problems in adolescence and early adulthood: Implications for substance abuse prevention. Psychological Bulletin, 112, 64–105.
Haynie, D. L. (2001). Delinquent peers revisited: does network structure matter? American Journal of Sociology, 106, 1013–1057.
Ingoldsby, E. M. Shaw, D. S. Winslow, E. Schonberg, M. Gilliom, M. & Criss, M. M. (2006). Neighborhood disadvantage, parent-child conflict, neighborhood peer relationships, and early antisocial behavior problem trajectories. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 34, 303–319.
Kandel, D. (1973). Adolescent marihuana use: role of parents and peers. Science, 181, 1067–1070.
Laird, R. D. Pettit, G. S. Dodge, K. A. & Bates, J. E. (1999). Best friendships, group relationships, and antisocial behavior in early adolescence. Journal of Early Adolescence, 19, 413–437.
Lochman, J. E. & Wells, K. C. (2002). The coping power program at the middle-school transition: universal and indicated prevention effects. Psychology of Addictive Behaviors, 16, S40–S54.
Loeber, R. (1990). Development and risk factors of juvenile antisocial behavior and delinquency. Clinical Psychology Review, 10, 1–41.
Logue, A. (1988). Research on self-control: an integrating framework. Behavioral and Brain Sciences, 11, 665–709.
Lynam, D. R. Caspi, A. Moffit, T. E. Wikstrom, P.-O. Loeber, R. & Novak, S. (2000). The interaction between impulsivity and neighborhood context on offending: the effects of impulsivity are stronger in poorer neighborhoods. Journal of Abnormal Psychology, 109, 563–574.
Marshal, M. P. Molina, B. S. & Pelham, W. E. Jr. (2003). Childhood ADHD and adolescent substance use: an examination of deviant peer group affiliation as a risk factor. Psychology of Addictive Behaviors, 17, 293–302.
Meier, M. H. Slutske, W. S. Arndt, S. & Cadoret, R. J. (2008). Impulsive and callous traits are more strongly associated with delinquent behavior in higher risk neighborhoods among boys and girls. Journal of Abnormal Psychology, 117, 377–385.
Miller, J. D. & Lynam, D. (2001). Structural models of personality and their relation to antisocial behavior: a meta-analytic review. Criminology, 39, 765–798.
Moffitt, T. E. (1990). The neuropsychology of delinquency: A critical review of theory and research. In N. Morris & M. Tonry (Eds.), Crime and justice (Vol. 12, pp. 99–169). Chicago: University of Chicago Press.
Moffitt, T. E. (1993). Adolescence-limited and life-course-persistent antisocial behavior: a developmental taxonomy. Psychological Review, 100, 674–701.
Moore, R. S. & Ames, G. M. (2002). Survey confidentiality vs. anonymity: young men’s self-reported substance use. Journal of Alcohol and Drug Education, 47, 32.
Morgan, A. B. & Lilienfeld, S. O. (2000). A meta-analytic review of the relation between antisocial behavior and neuropsychological measures of executive function. Clinical Psychology Review, 20, 113–156.
Mrug, S. Hoza, B. & Bukowski, W. M. (2004). Choosing or being chosen by aggressive-disruptive peers: do they contribute to children’s externalizing and internalizing problems? Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 32, 53–65.
Muthen, L. K. & Muthen, B. O. (2009). Mplus user’s guide. Los Angeles: Muthen & Muthen.
Newman, J. P. & Wallace, J. F. (1993). Diverse pathways to deficient self-regulation: implications for disinhibitory psychopathology in children. Clinical Psychology Review, 13, 699–720.
Olson, S. L. (1992). Development of conduct problems and peer rejection in preschool children: a social systems analysis. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 20, 327–350.
Patterson, G. R. & Dishion, T. J. (1985). Contribution of families and peers to delinquency. Criminology, 23, 63–77.
Patterson, C. & Newman, J. P. (1993). Reflectivity and learning from aversive events: toward a psychological mechanism for the syndromes of disinhibition. Psychological Review, 100, 716–736.
Patton, J. Stanford, M. & Barratt, E. (1995). Factor structure of the Barratt impulsiveness scale. Journal of Clinical Psychology, 51, 768–774.
Pollard, J. A. Hawkins, J. D. & Arthur, M. W. (1999). Risk and protection: are both necessary to understand diverse behavioral outcomes in adolescence? Social Work Research, 23(8), 145–158.
Poulin, F. Dishion, T. J. & Haas, E. (1999). The peer influence paradox: friendship quality and deviancy training within male adolescent friendships. Merrill-Palmer Quarterly, 45, 42–61.
Semple, S. J. Zians, J. Grant, I. & Patterson, T. L. (2005). Impulsivity and methamphetamine use. Journal of Substance Abuse Treatment, 29, 85–93.
Snyder, H. (2001). Epidemiology of official offending. In R. Loeber & D. P. Farrington (Eds.), Child delinquents: Development, intervention, and service needs (pp. 25–46). Thousand Oaks: Sage.
Snyder, H. (2008). Juvenile Arrests 2006. Office of Juvenile Justice and Delinquency Prevention.
Snyder, J. Prichard, J. Schrepferman, L. Patrick, M. & Stoolmiller, M. (2004). Child impulsiveness-inattention, early peer experiences, and the development of early onset conduct problems. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 32, 579–594.
Stattin, H. & Kerr, M. (2000). Parental monitoring: a reinterpretation. Child Development, 71, 1072–1085.
Torrubia, R. & Tobena, A. (1984). A scale for the assessment of susceptibility to punishment as a measure of anxiety: preliminary results. Personality and Individual Differences, 5, 371–375.
Tremblay, R. E. Pihl, R. O. Vitaro, F. & Dobkin, P. L. (1994). Predicting early onset of male antisocial behavior from preschool behavior. Archives of General Psychiatry, 51, 732–739.
Vitaro, F. Brendgen, M. & Tremblay, R. E. (2000). Influence of deviant friends on delinquency: searching for moderator variables. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 28, 313–325.
White, J. L. Moffitt, T. E. Caspi, A. Bartusch, D. J. Needles, D. J. & Stouthamer-Loeber, M. (1994). Measuring impulsivity and examining its relationship to delinquency. Journal of Abnormal Psychology, 103, 192–205.
Whiteside, S. & Lynam, D. R. (2001). The five factor model and impulsivity: using a structural model of personality to understand impulsivity. Personality and Individual Differences, 30, 669–689.
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank members of the Child Behavior Lab for their assistance with data collection. Additionally, we would like to thank the families who participated in the study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vitulano, M.L., Fite, P.J. & Rathert, J.L. Delinquent Peer Influence on Childhood Delinquency: The Moderating Effect of Impulsivity. J Psychopathol Behav Assess 32, 315–322 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10862-009-9160-2
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10862-009-9160-2